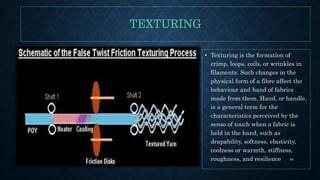
This document discusses the production of polyester fiber through various fiber production processes. It begins by defining polyester as a long-chain polymer composed of at least 85% ester units formed from the reaction of alcohols and acids. The key raw materials used are terephthalic acid, ethylene glycol, and dimethyl terephthalate. Polyester fiber can be produced through two main routes - the dimethyl terephthalate route and the terephthalic acid route. The document provides detailed information on the chemical reactions, catalysts, side reactions, degradation processes, and thermal stabilizers used in each production route.




















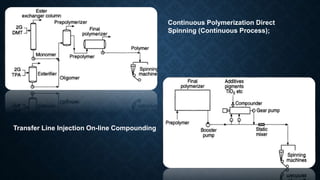
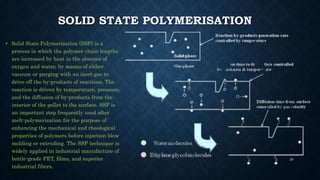
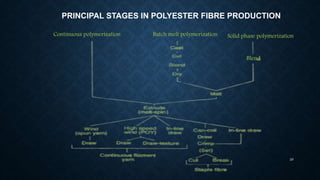


















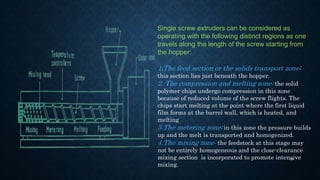
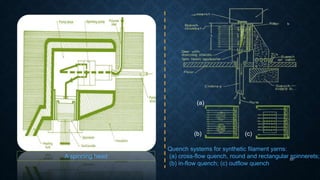
![DRAWING
The spinning processes described above produce some orientation of the long polymers that form spun
filaments. Orientation is completed by stretching, or drawing, the filament, a process that pulls the long
polymer chains into alignment along the longitudinal axis of the fibre and causes them to pack closely together
and develop cohesion
• During the drawing operation the polymer chains slide over one another as they are pulled into alignment
along the longitudinal axis of the fibers .
• As drawing continues, more and more of the molecules are brought to a state where they can pack alongside
one another into crystallites. In these regions the molecules are able to hold tightly together as a result of
intermolecular forces and resist further movement with respect to one another.
• The degree of alignment of fibre molecules affects the properties of a fibre in several ways. The more closely
the molecules pack together, the greater is the ultimate strength, or breaking strength, of the fibre.
• Fibres can be drawn either as an integral part of the spinning operation or in a separate step .
• Fibres such as nylon and polypropylene can be drawn without applying external heat (or at a temperature no
greater than about 70 °C [160 °F])-a process referred to as cold drawing.
49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polyesterfibre-200720170149/85/Polyester-fibre-49-320.jpg)