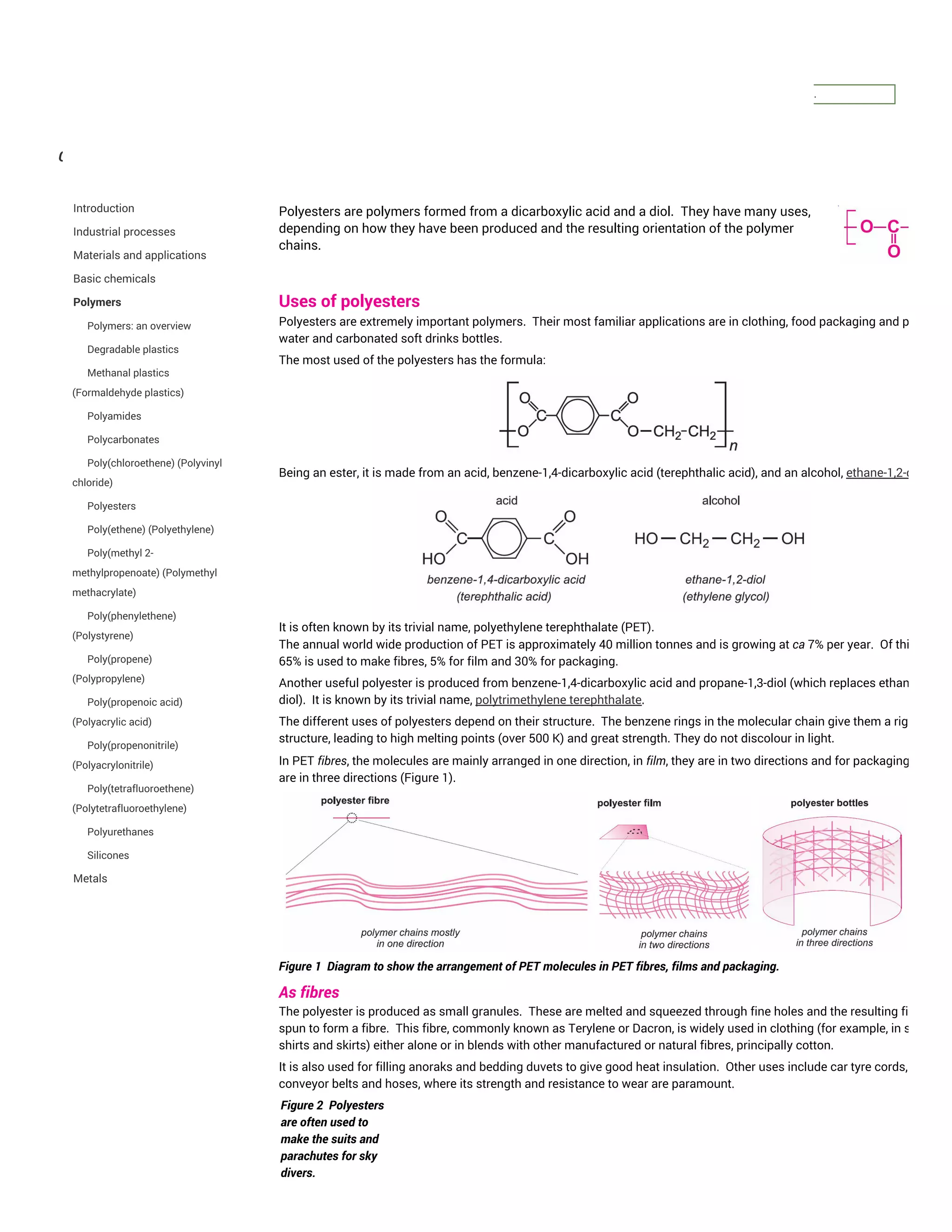
Polyesters are polymers formed from dicarboxylic acids and diols. The most commonly used polyester is polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is formed from terephthalic acid and ethane-1,2-diol. PET has many applications including clothing fibers, plastic bottles, and food packaging. It is a rigid polymer with a high melting point that provides strength and does not discolor in light. The structure and properties of PET allow it to be formed into fibers with molecules arranged in one direction, films with molecules in two directions, or packaging with molecules in three directions.