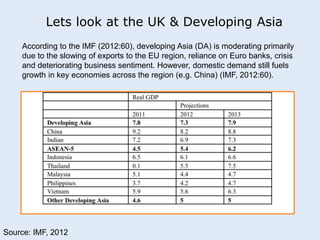
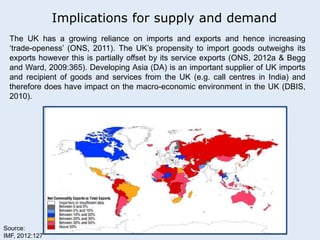
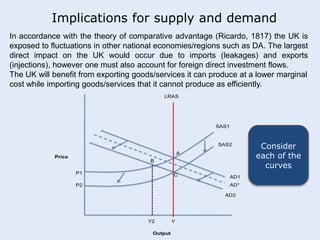
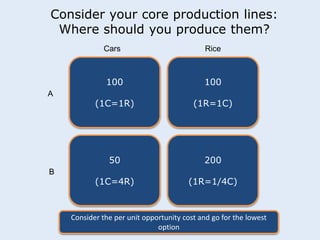
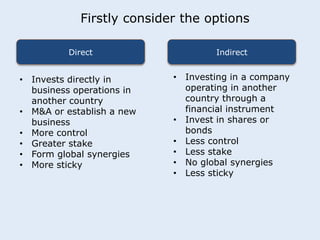
This seminar discusses applying economic concepts to business. Participants will analyze supply and demand factors and how a slowing Asian economy could impact their business. They will also evaluate key economic indicators such as GDP, inflation, and employment. The concept of comparative advantage will be explored and how it can benefit businesses. Finally, participants will consider whether direct or indirect foreign direct investment would be best if investing abroad, based on their business needs and resources.