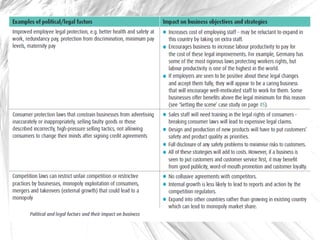
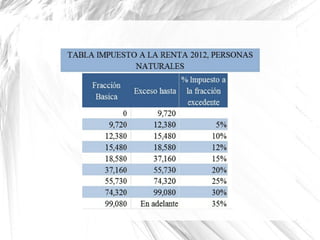
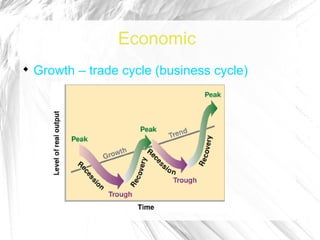
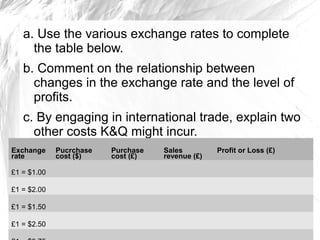
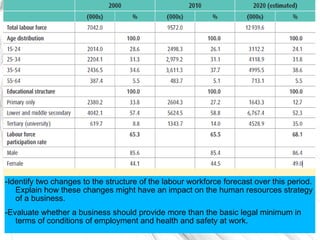
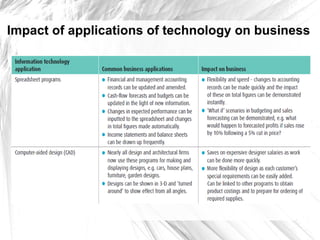
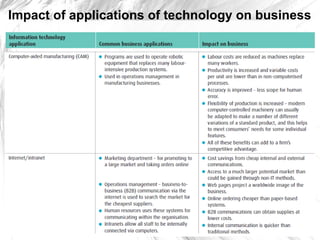
The document discusses how businesses are affected by factors in the external environment that are outside of their control, including political, economic, social, technological factors. It introduces the PEST analysis framework for examining the external environment and provides examples of how different external factors impact businesses and should be considered in their objectives and strategies. The document also gives specific examples analyzing how certain external and economic factors impact businesses.