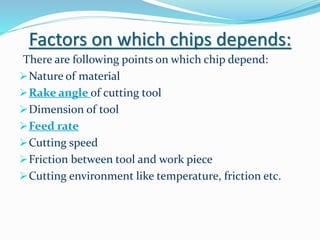
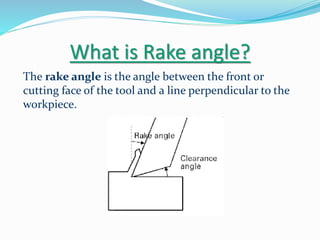
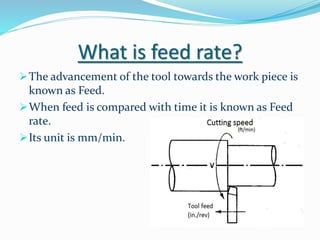
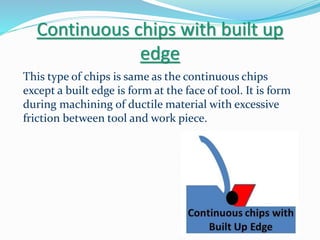
The document discusses chip formation during mechanical cutting processes and categorizes chips into three types: continuous, discontinuous, and continuous with built-up edges. Factors affecting chip characteristics include material nature, rake angle, tool dimensions, and cutting conditions. Continuous chips provide advantages like high surface finish and tool life, while discontinuous chips are better for brittle materials but lead to poorer finishes.