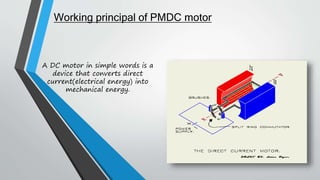
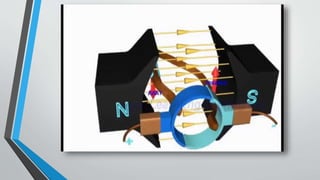
This document discusses the construction and working principle of a permanent magnet DC (PMDC) motor. It begins with an introduction stating that a DC motor converts direct current into mechanical energy. It then describes the key components of a PMDC motor: the stator, which contains permanent magnets; the rotor or armature, made of wound coils; and how each conductor on the armature experiences a force when inside the magnetic field based on Fleming's left hand rule, causing the armature to rotate. Advantages are listed as reduced size, cost and increased efficiency over traditional DC motors requiring field excitation coils. Applications include toys, drills and automatic doors.