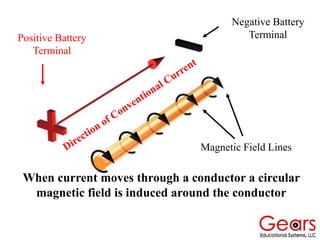
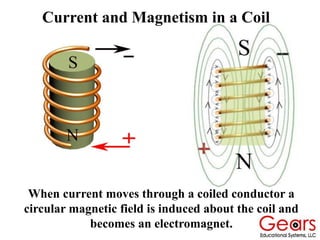
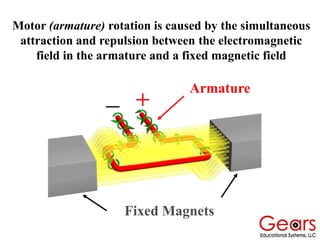
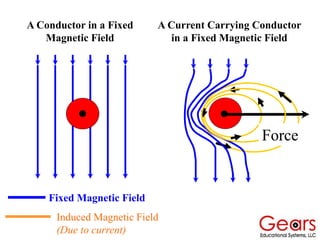
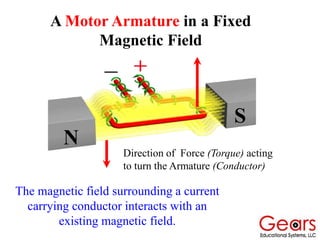
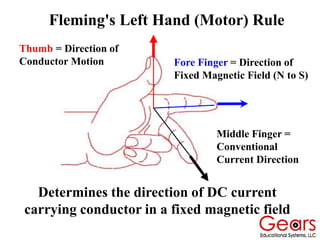
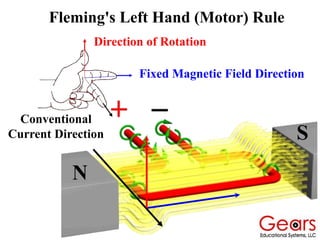
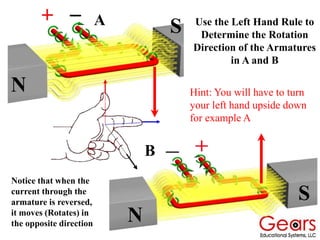
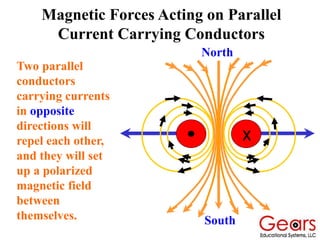
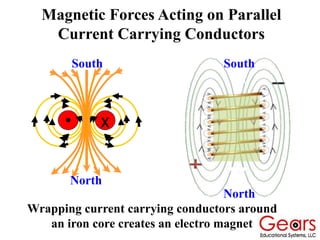
DC motors convert electrical energy into mechanical motion using either AC or DC power sources, producing rotational or translational movement of the output shaft based on specified load limits. Their selection depends on application characteristics such as speed, weight, size, cost, and control accuracy, with performance described through parameters like rated speed, torque, and horsepower. The principle of operation involves electrical currents generating magnetic fields that induce torque, causing rotation as the armature interacts with fixed magnetic fields.