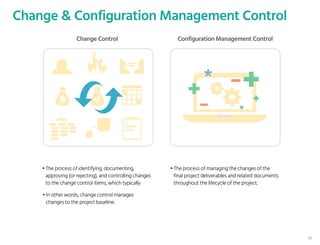
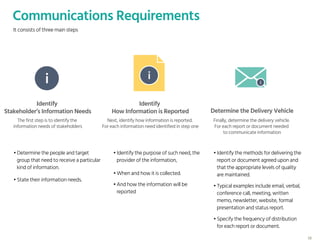
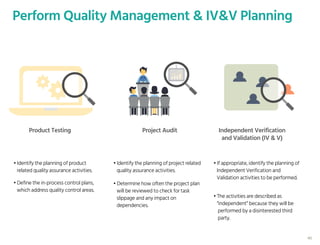
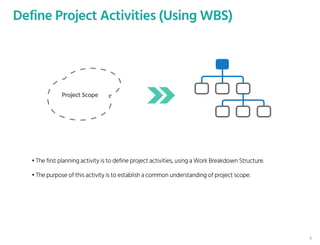
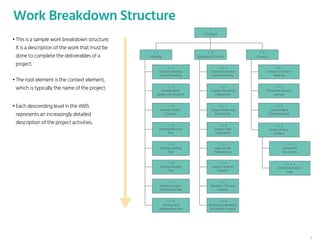
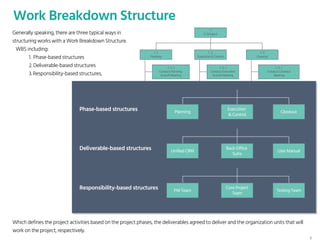
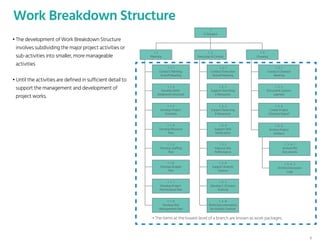
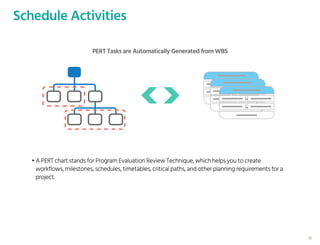
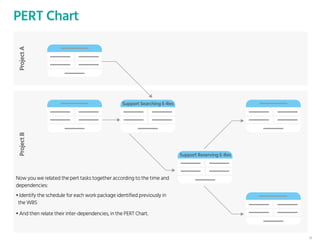
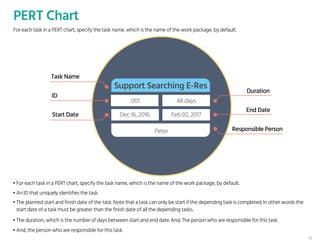
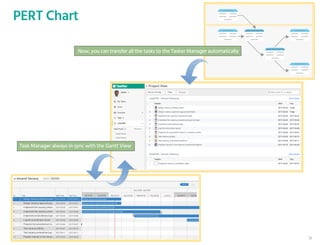
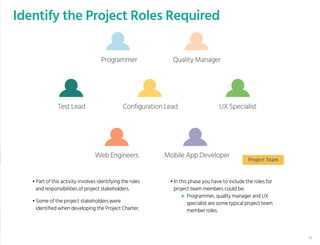
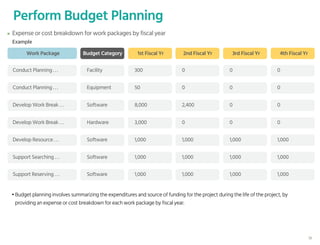
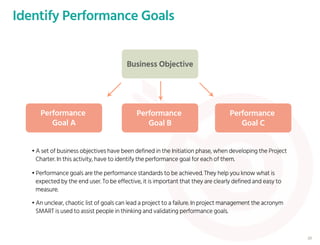
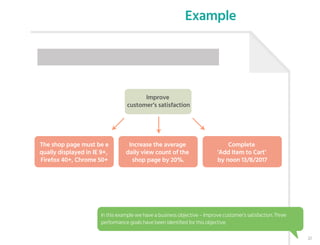
The document outlines the planning phase of an IT project management framework, detailing various activities necessary for successful project completion, such as resource planning, budget planning, and risk management. It emphasizes the importance of defining project activities through a work breakdown structure and conducting a planning kick-off meeting to set team expectations. Additionally, it highlights the need for clear performance goals to ensure alignment with business objectives and facilitate effective monitoring of project progress.













![Risk Register – Major Elements
• Identify project risks by following the risk management
approach described under the Risk Management Plan.
• Information of each identified risk is stored in Risk Register.
• The Risk Register is a log of all identified risks.
• It shows the probability and impact of the risks to the
project, mitigation strategy, and when the risk is estimated
to occur.
• This Risk Register is created in the Planning phase of the
project, and be updated in the Execution and Control phase
with the risks identified during the execution of project
activities.
Elements of Risk Register
Affected Work Packages
Probability [1 of 10]
Impact [1 of 10]
Risk Score [Probability x Impact]
Risk Management Approach / Migration Actions
Early Warning Signs / Trigger
Risk Owner
Date of Last Update
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/it-planning-final-170619033304/85/PMBOK-Planning-Process-Group-33-320.jpg)