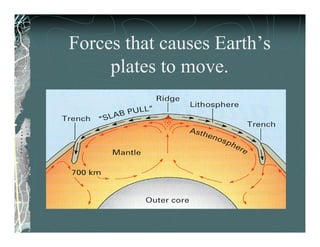
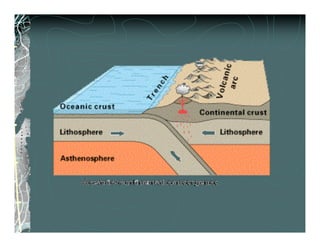
The document summarizes plate tectonic theory, which states that pieces of the Earth's lithosphere are in constant, slow motion driven by convection currents in the mantle. It describes how convection currents in the asthenosphere drag and move the overlying tectonic plates. It also explains the three types of plate boundaries - divergent boundaries where plates move apart, convergent boundaries where they move together, and transform boundaries where they slip past each other.