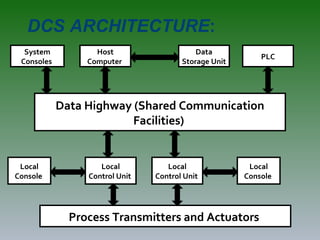
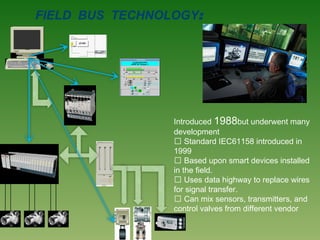
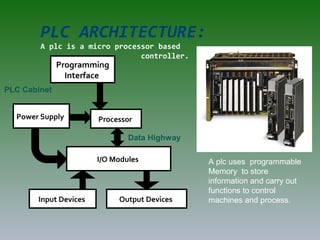
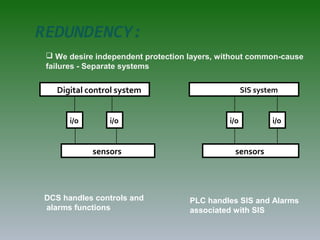
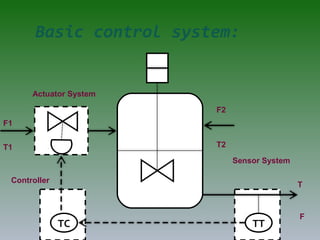
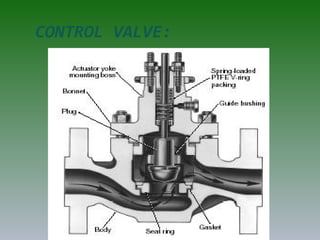
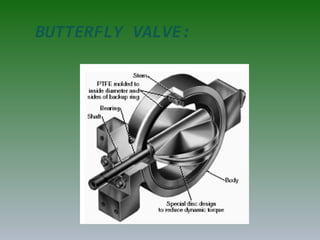
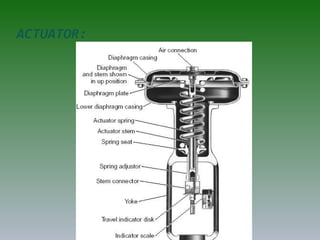
The document discusses plant operation systems and distributed control systems. It describes typical objectives of plant operation which include protecting people, the environment, and equipment while maintaining smooth operations, product rates and quality to optimize profit. It then discusses distributed control system architecture, field bus technology, PLC architecture, redundancy, inputs, outputs, and applications of control systems. Actuator systems including on/off and variable position systems are also summarized along with examples of control valves and positioning.