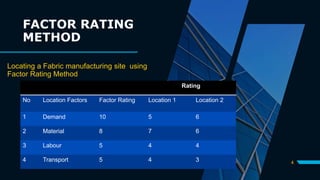
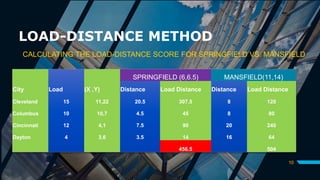
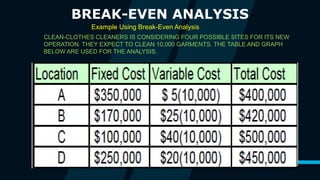
The document discusses various location selection models including the factor rating method, weighted factor rating method, load-distance method, center of gravity method, and break-even analysis. It provides examples of how to use the load-distance method and center of gravity method to determine an ideal location for a manufacturing plant and warehouse. The break-even analysis example determines the most suitable location for a cleaners based on expected demand.