Embed presentation
Downloaded 52 times










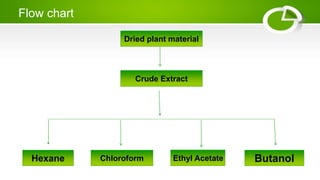

This document discusses various plant extraction and fractionation methods. Extraction involves separating the medicinally active parts of plants from inactive components using selective solvents. Common extraction methods include maceration, infusion, digestion, and decoction. Maceration soaks plants in solvents, infusion uses hot or cold water, digestion uses gentle heat, and decoction boils plants in water. Fractionation further separates crude extracts into portions by solvent polarity in a fractional process.










