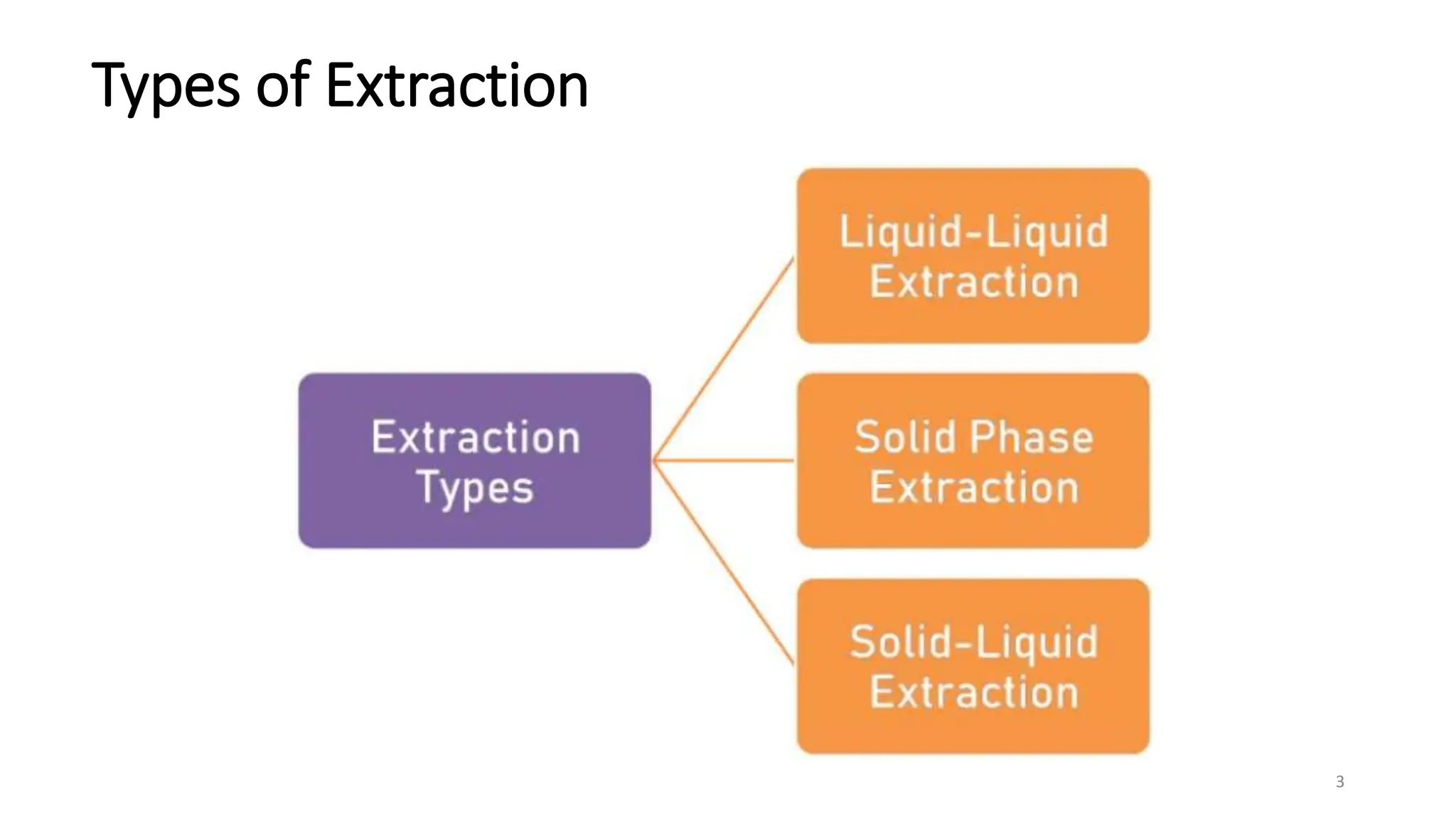
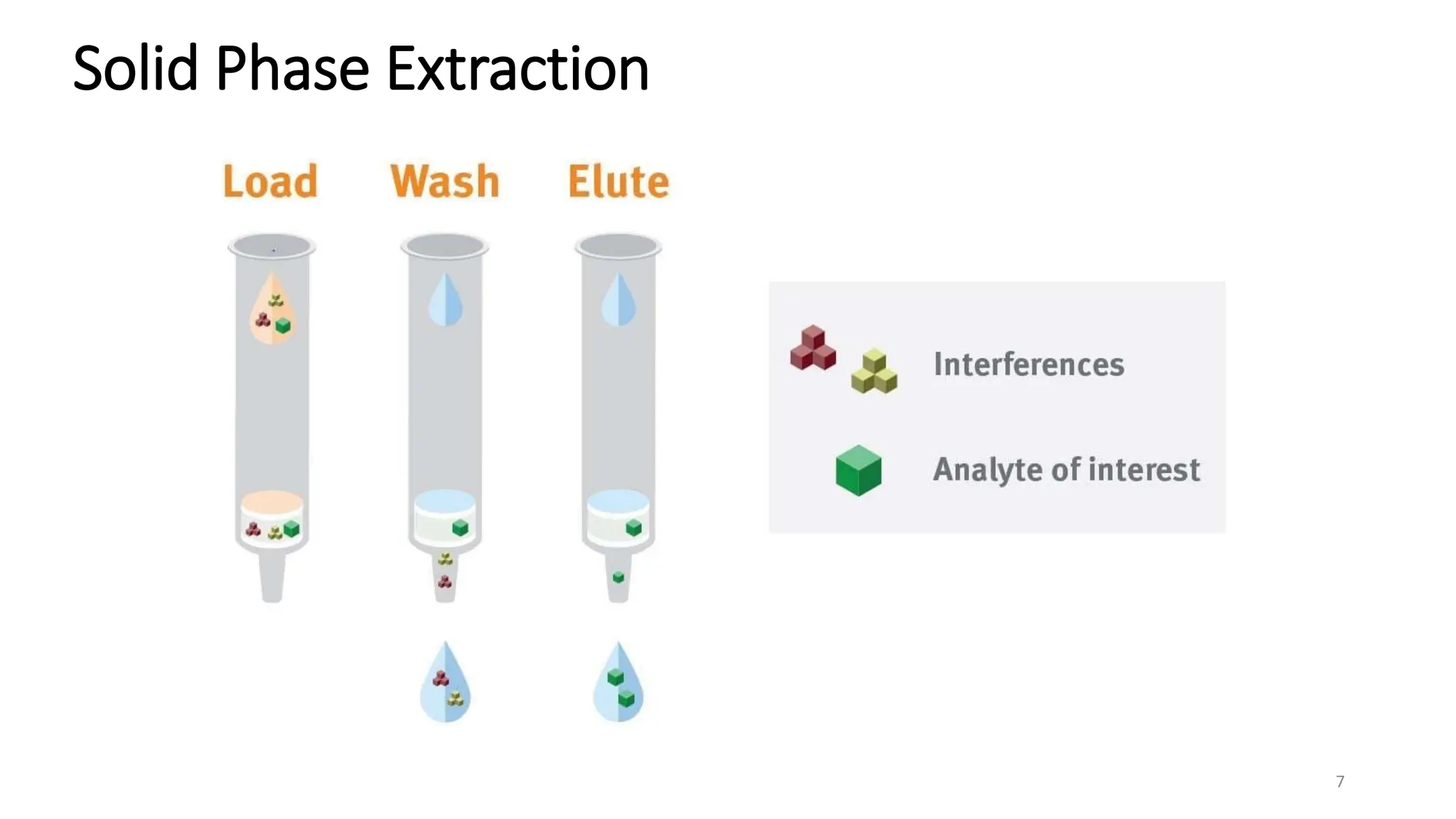
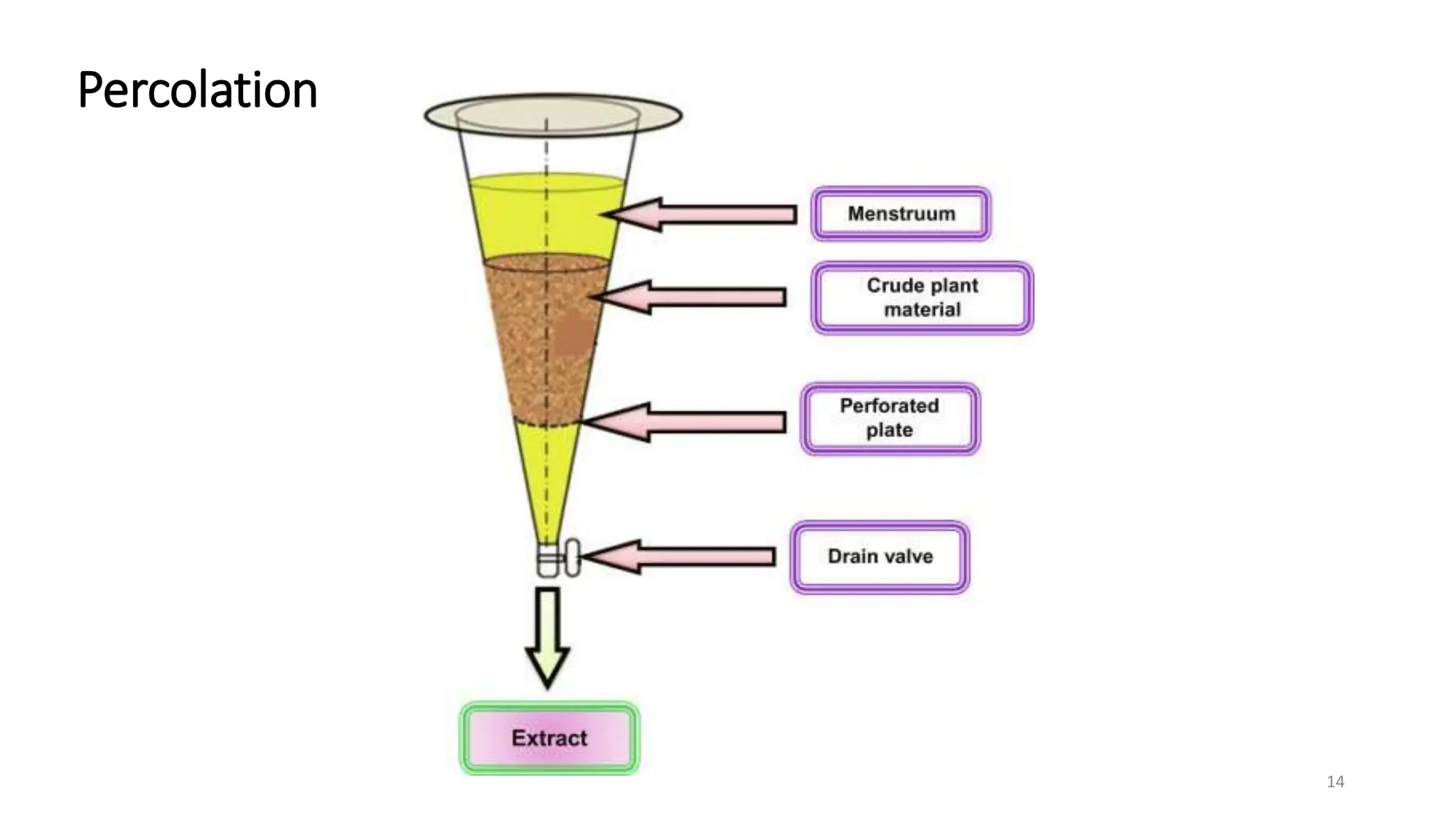
Extraction is a method used to separate medicinally active components from plant or animal tissues using selective solvents. There are several types of extraction including liquid-liquid extraction, solid phase extraction, solid-liquid extraction, and supercritical fluid extraction. Specific extraction techniques include maceration, percolation, digestion, decoction, infusion, Soxhlet extraction, microwave assisted extraction, sonication extraction, and accelerated solvent extraction. Extraction has various applications including separating antibiotics, recovering proteins, and isolating therapeutically active plant constituents.