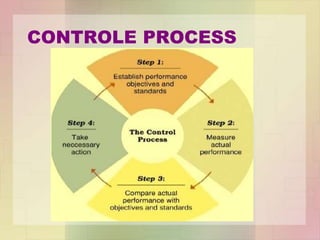
This document provides an overview of planning and control processes for an organization. It defines planning as preparing a blueprint that decides objectives, actions, timing, roles and locations in advance. Control is measuring performance against objectives and standards, comparing results, and taking corrective actions. The document outlines principles, essentials and methods of planning, as well as advantages, disadvantages and steps in the control process including establishing standards, measuring performance, comparing to standards, and correcting deviations.