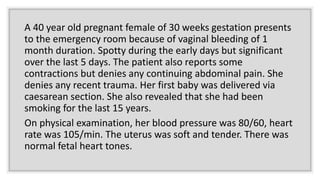
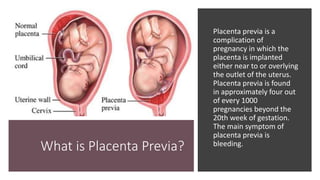
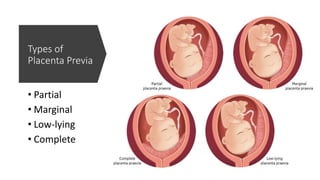
A 40-year-old pregnant woman at 30 weeks gestation presented with significant vaginal bleeding, potentially indicating placenta previa, a condition where the placenta is near or over the cervical opening. This diagnosis is common in late pregnancy, with bleeding being the primary symptom, often painless, and requiring ultrasound for confirmation. The document outlines symptoms, types, and diagnostic methods for placenta previa, emphasizing the importance of managing such cases to avoid complications.