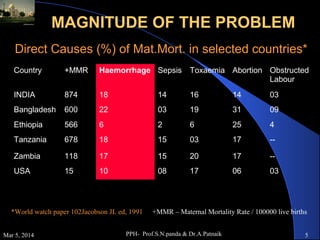
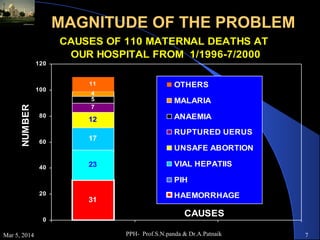
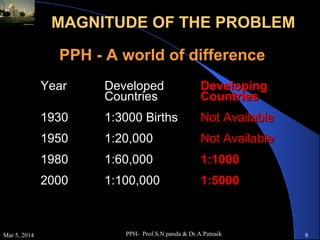
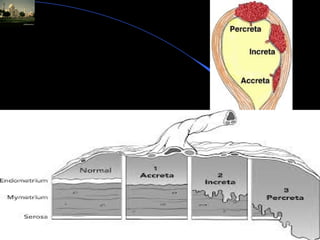
Postpartum haemorrhage (PPH) is the leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide, accounting for 25-50% of deaths. PPH is defined as blood loss of 500ml or more within 24 hours of delivery. Uterine atony is the most common cause, occurring in 80% of cases. Other causes include retained placenta, genital tract trauma, and coagulation disorders. Prevention strategies include active management of the third stage of labour and treatment involves restoring blood volume, ensuring uterine contraction, and potential surgical interventions if bleeding cannot be controlled. Without timely treatment, PPH can lead to complications like shock and death within a short period.