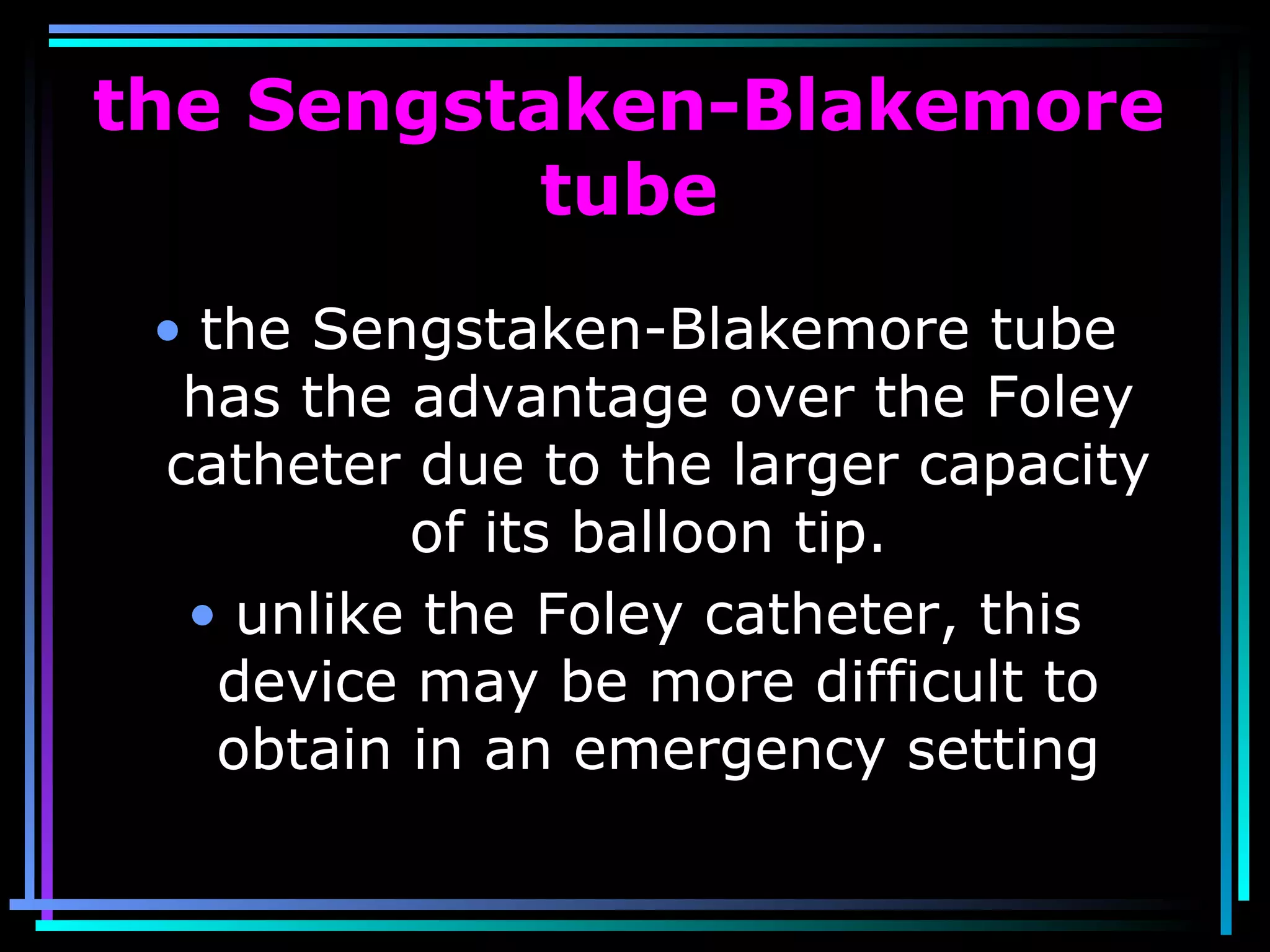
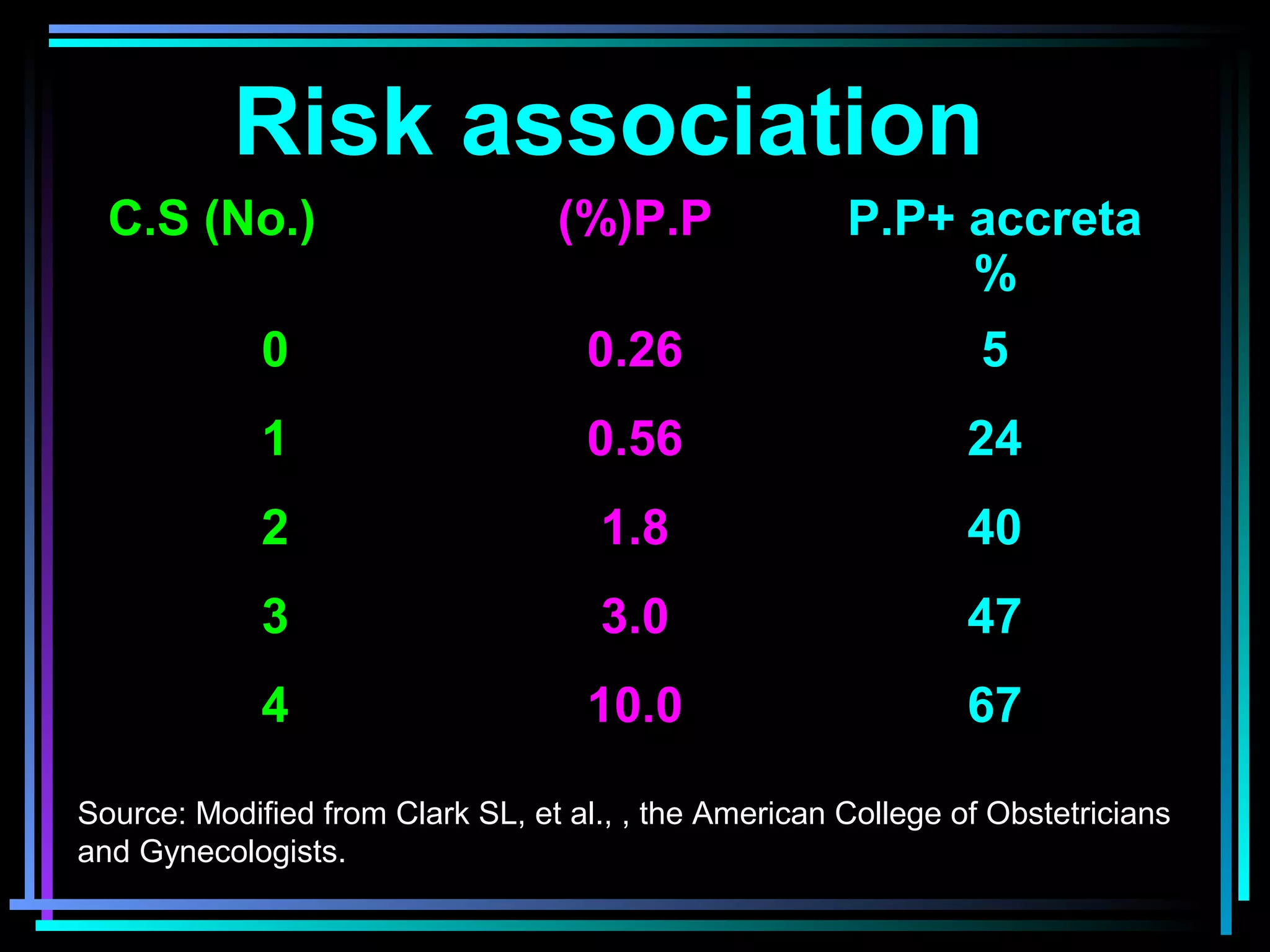
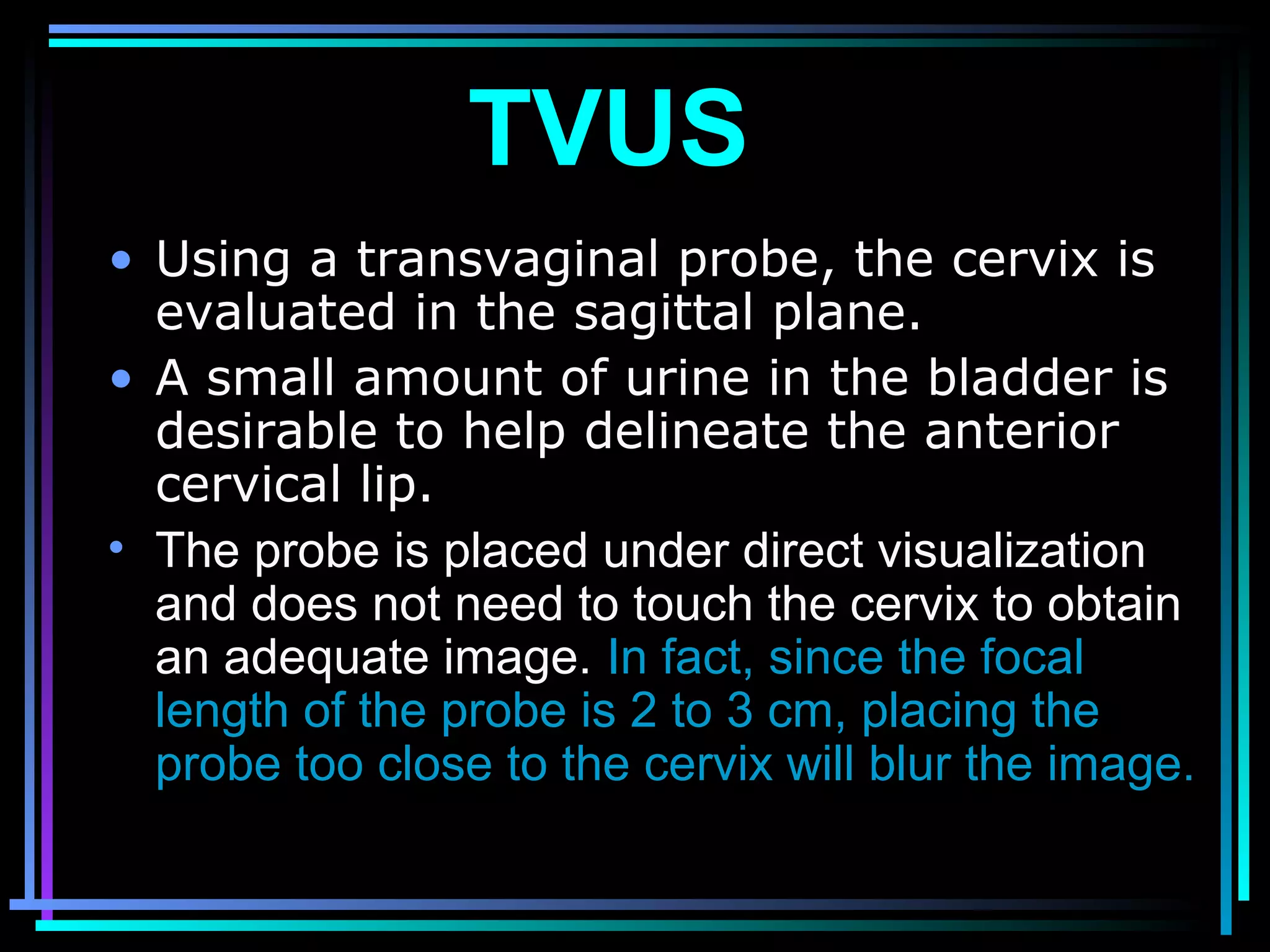
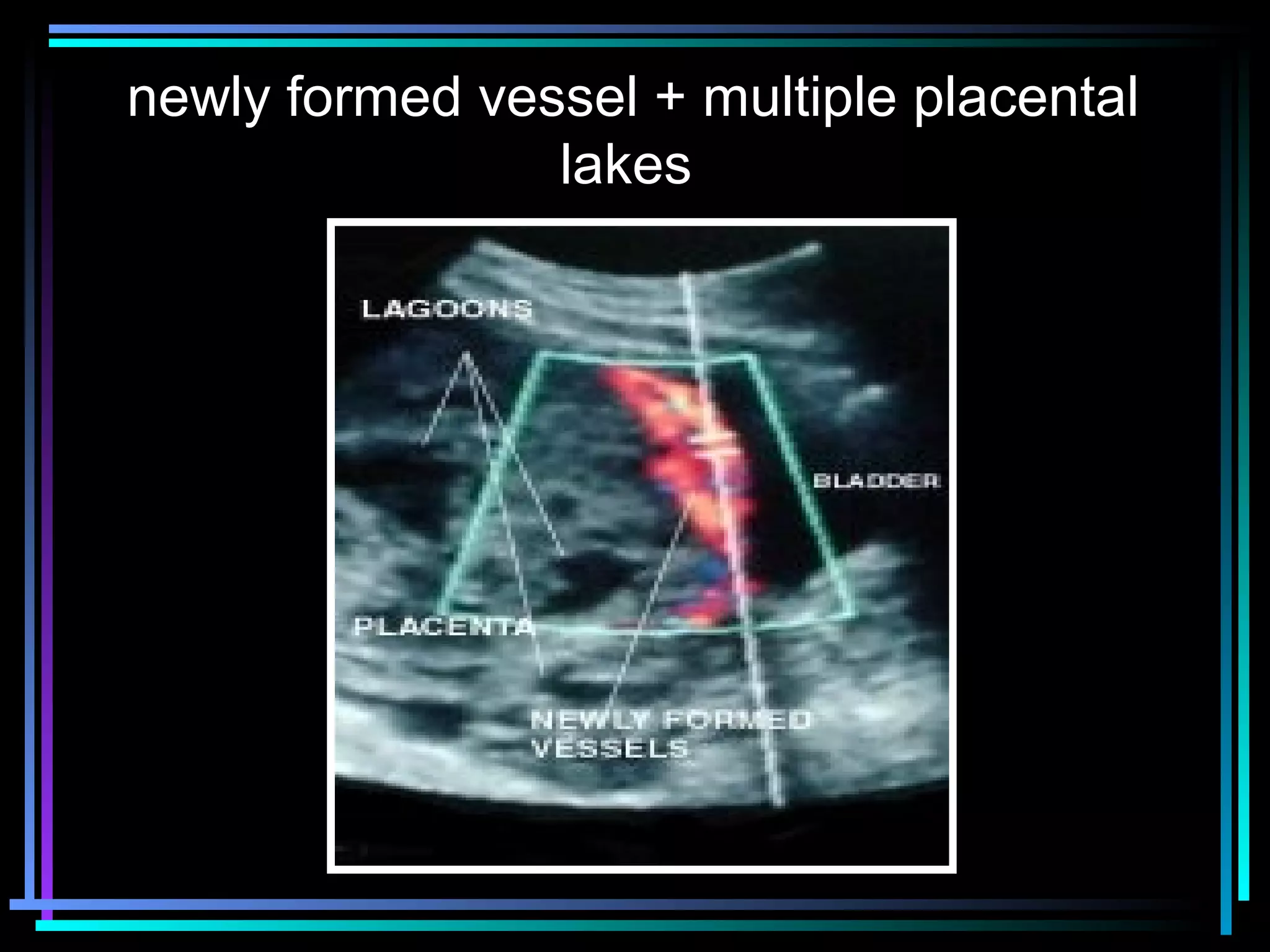
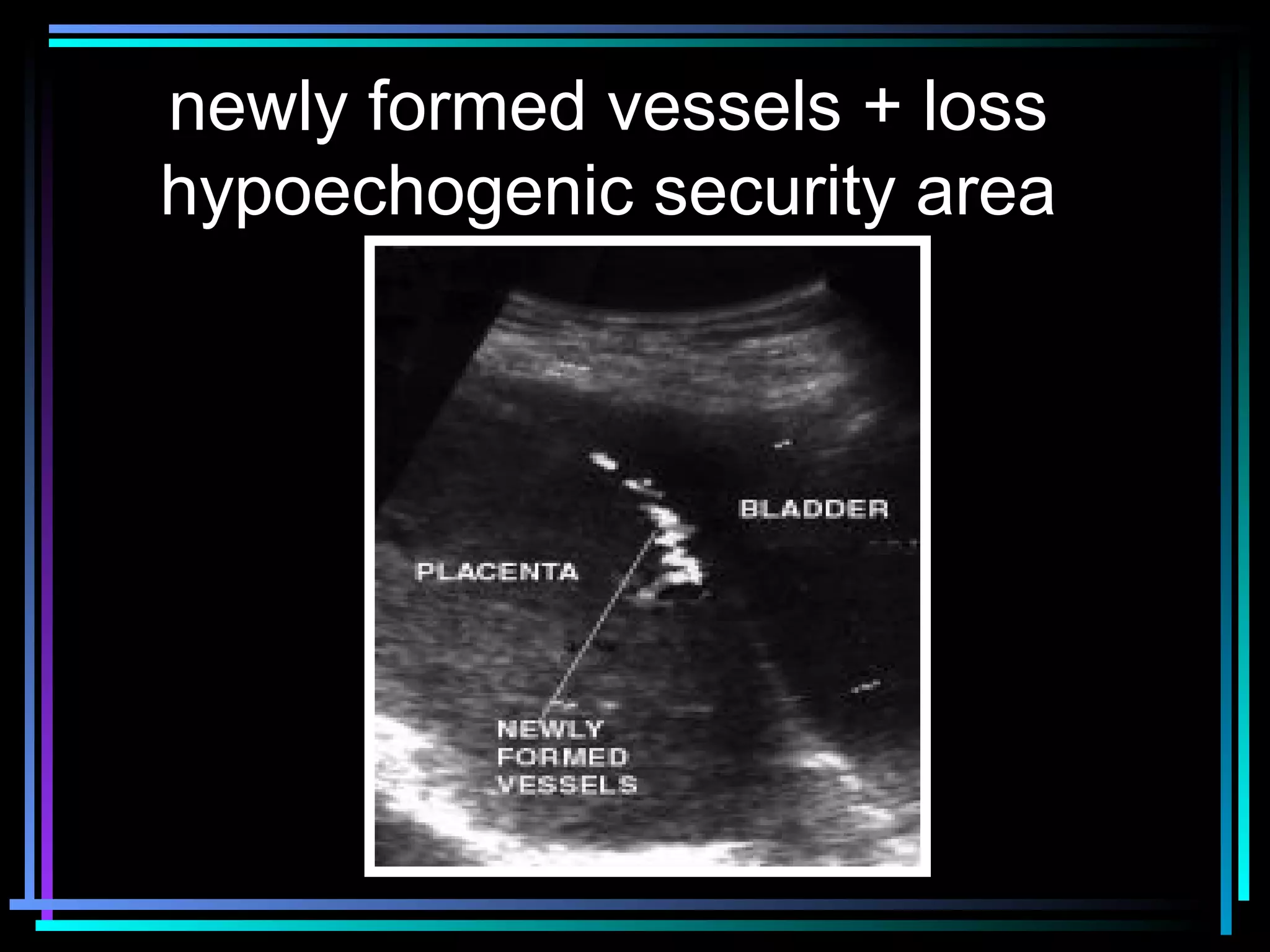
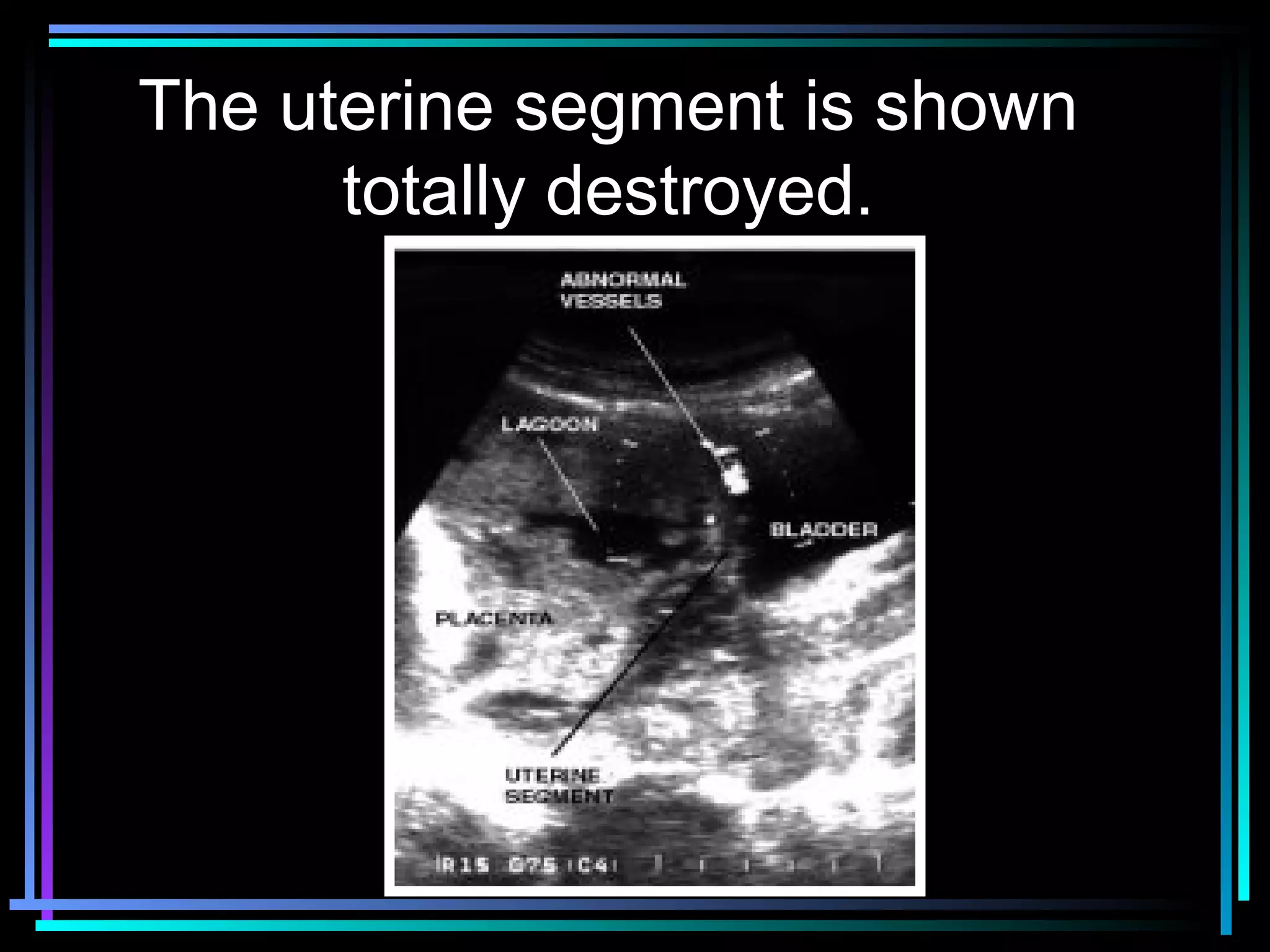
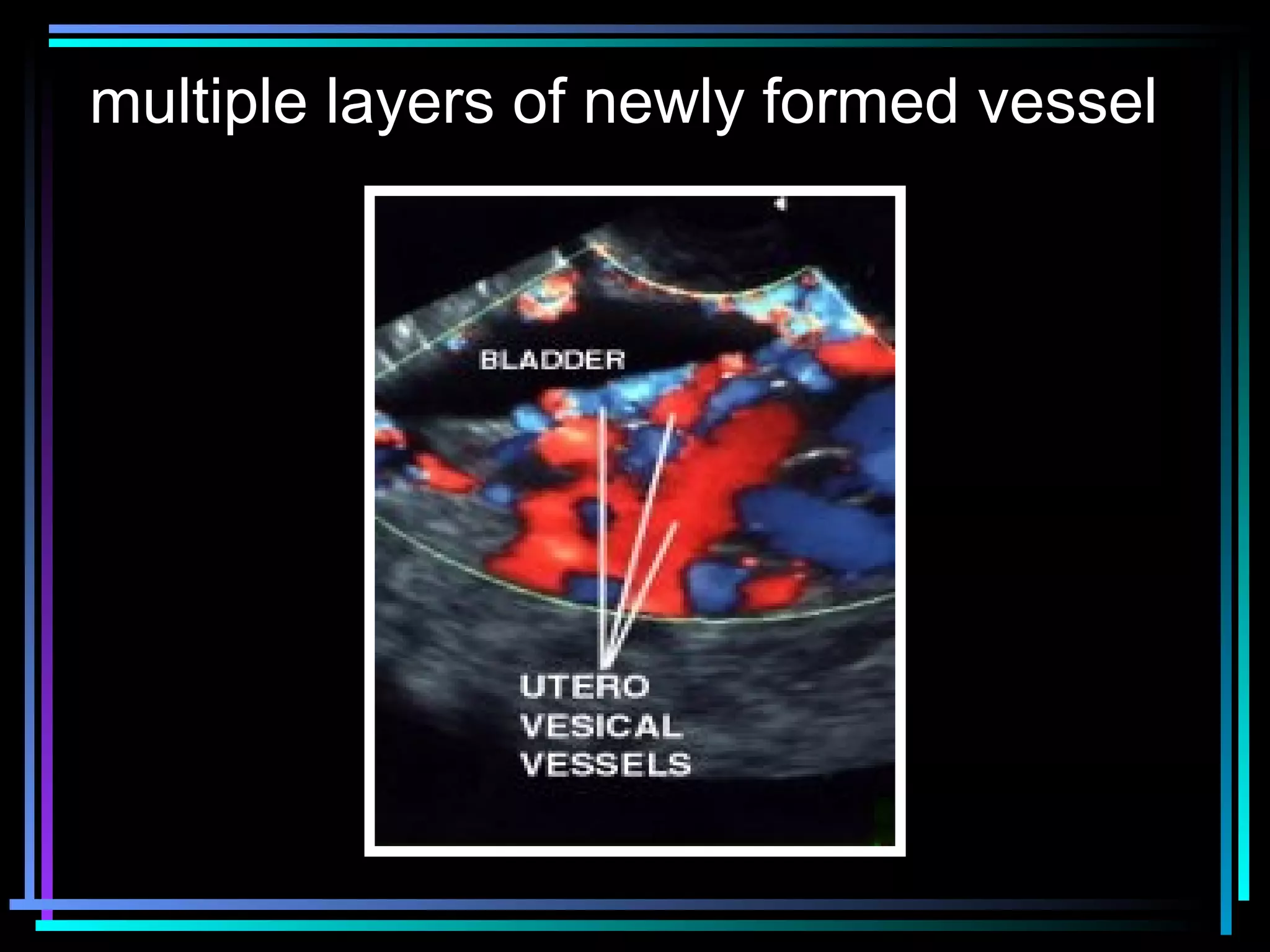
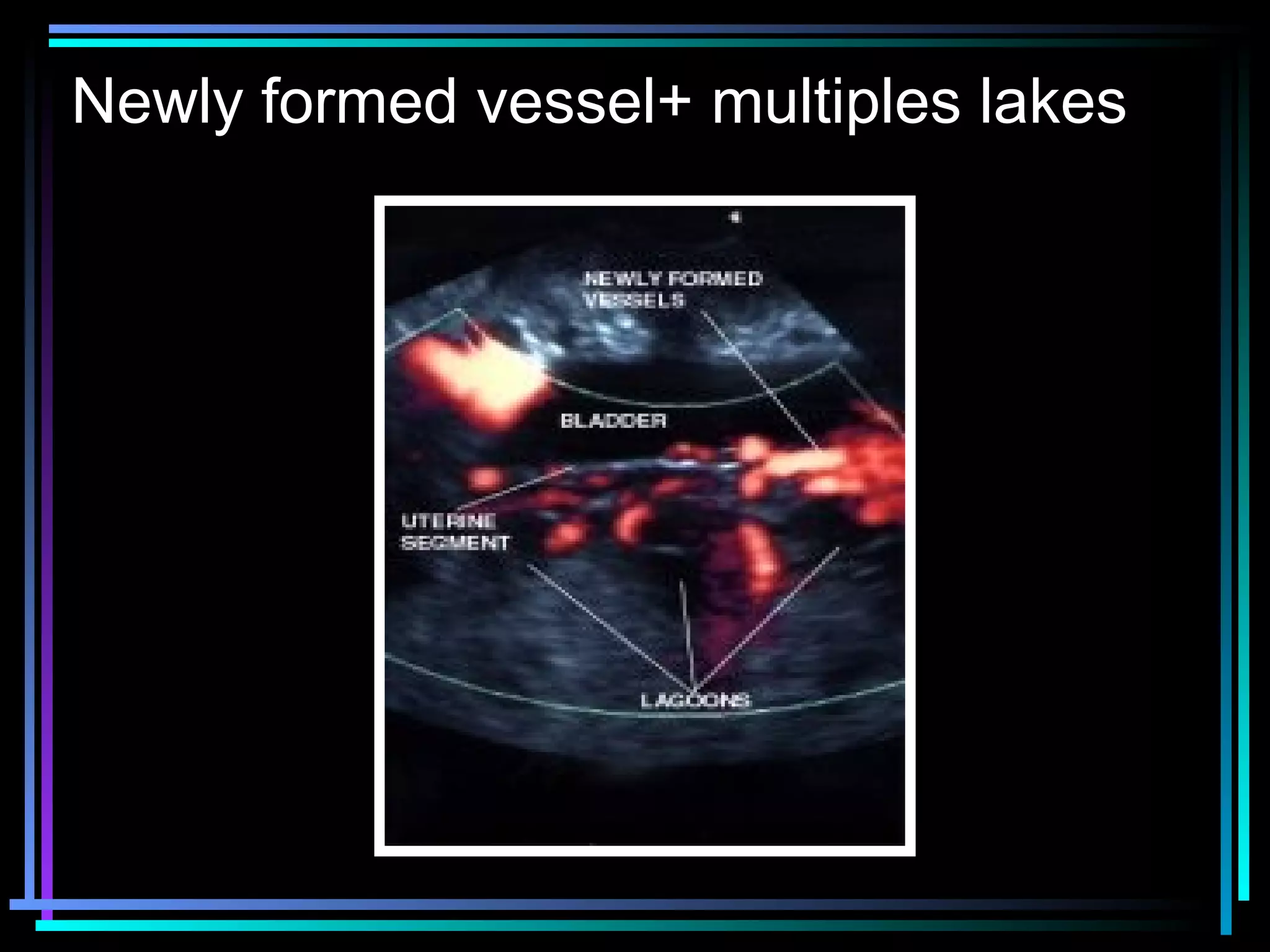
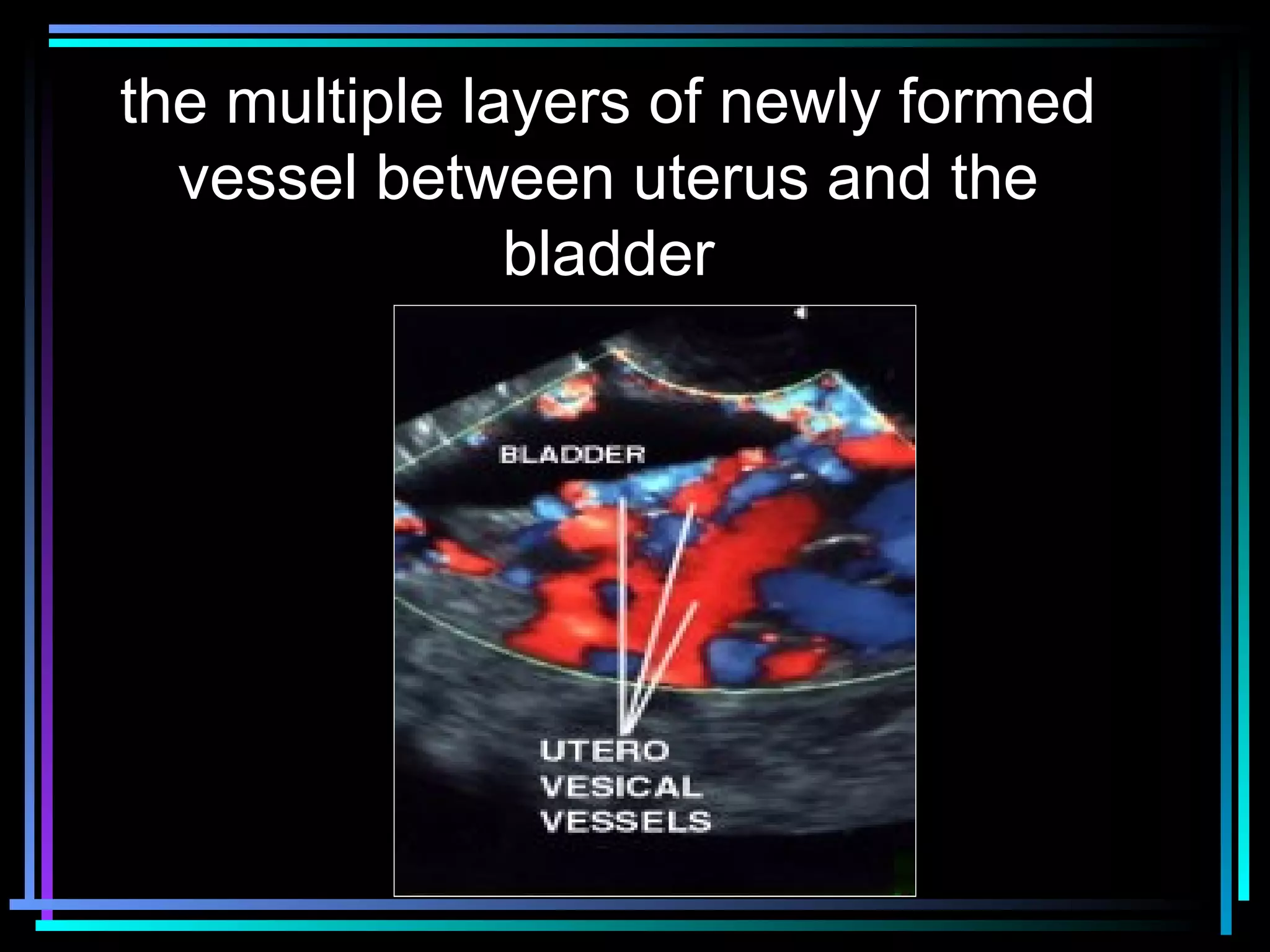
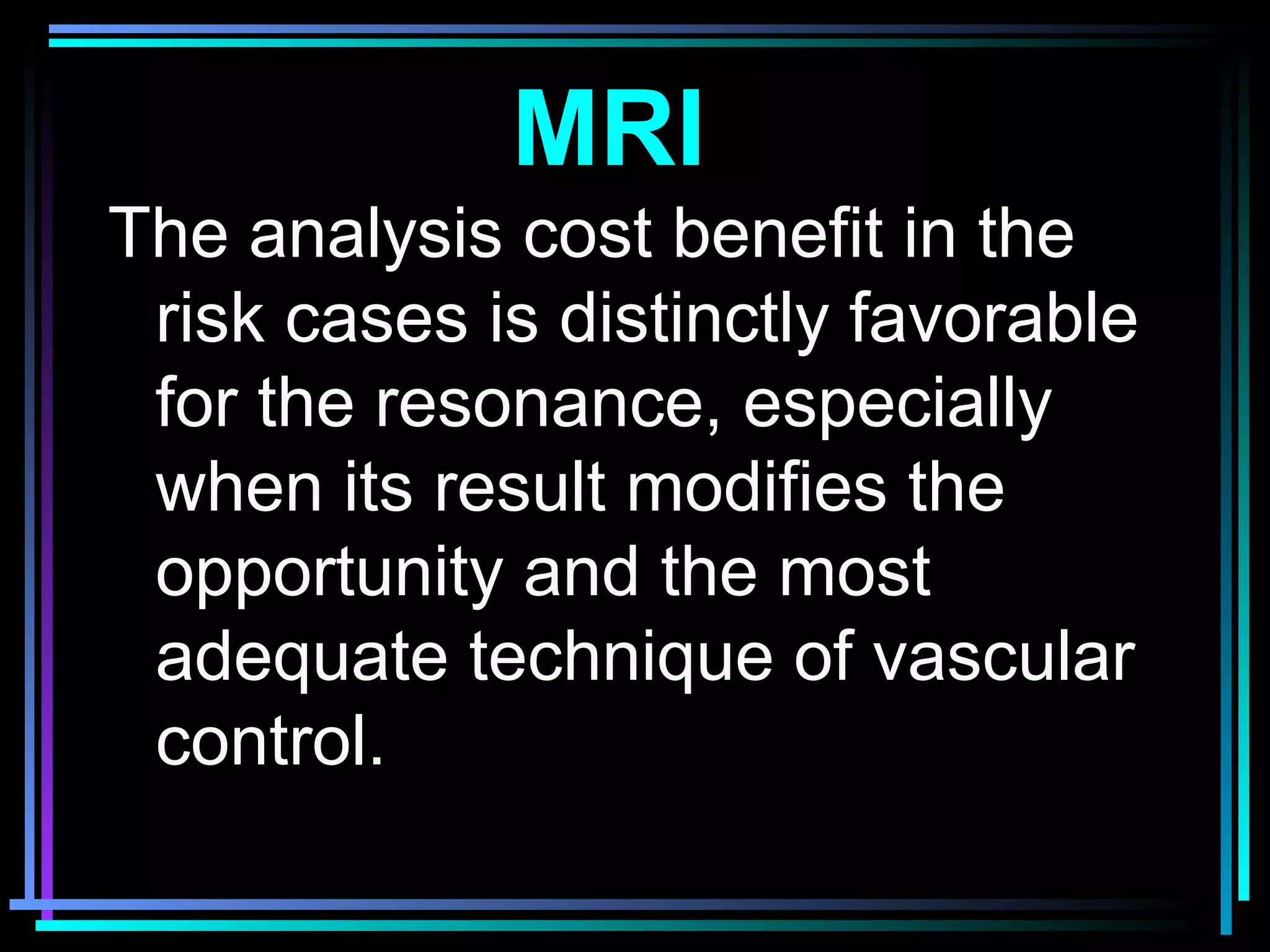
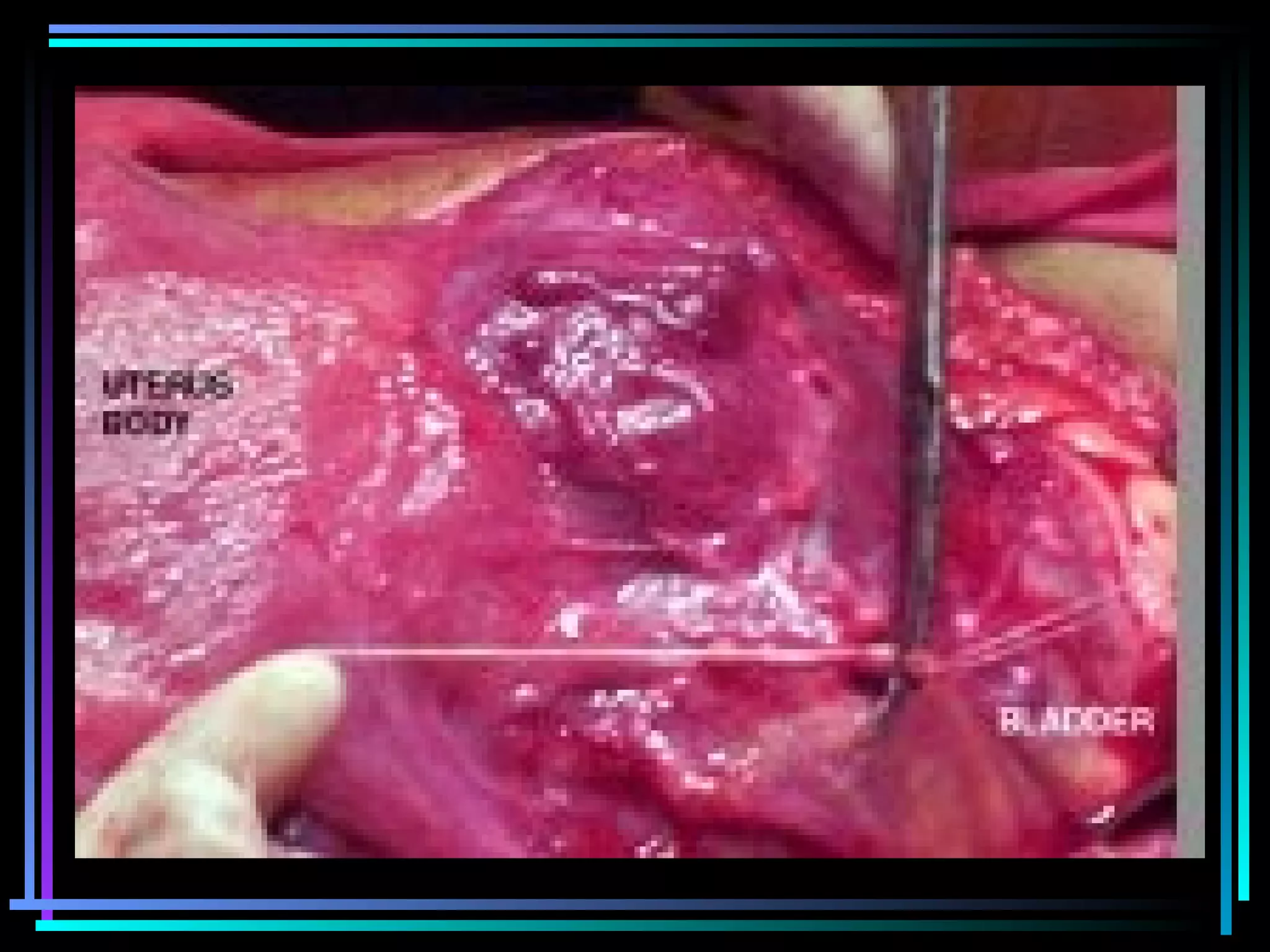
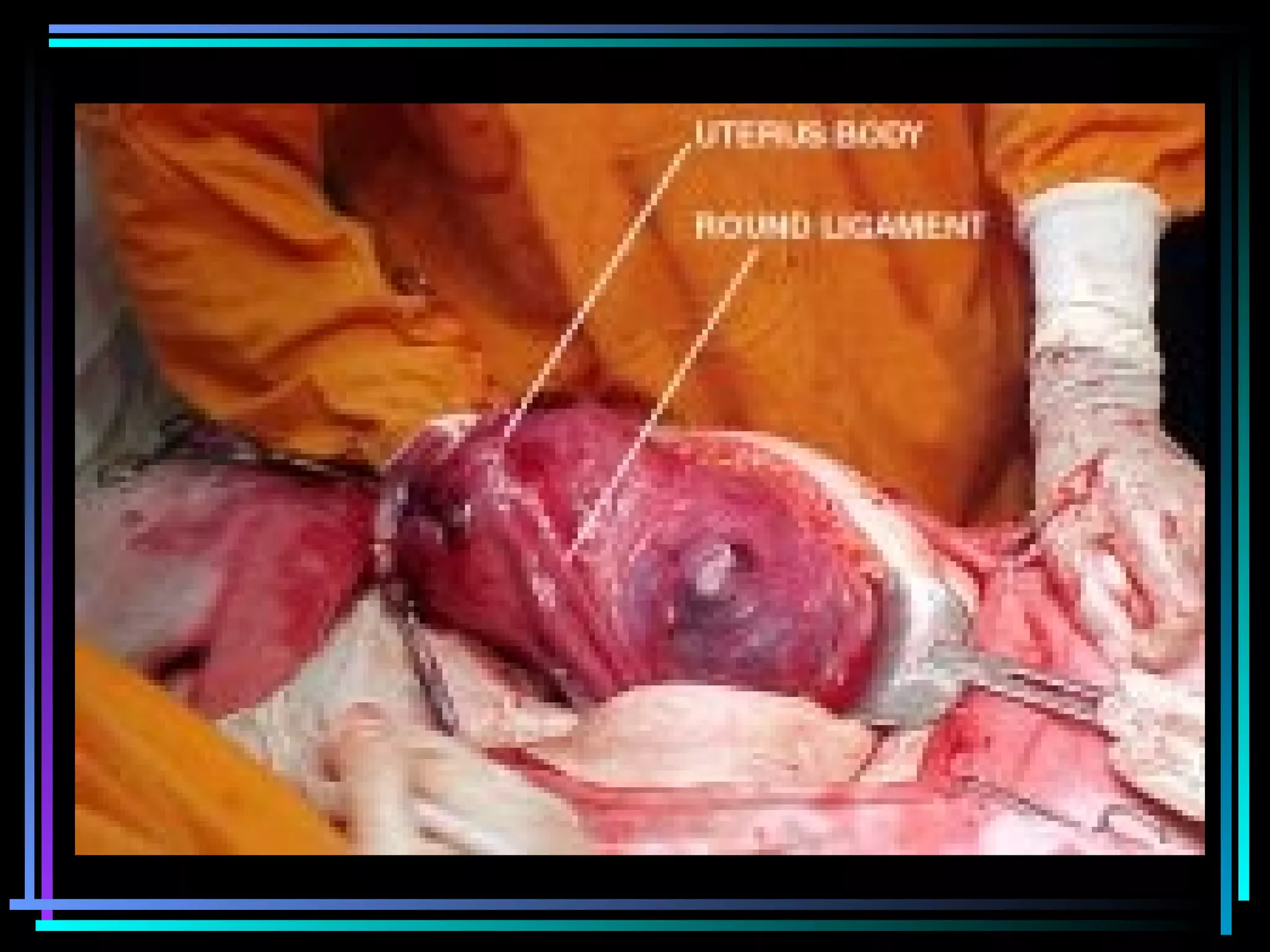
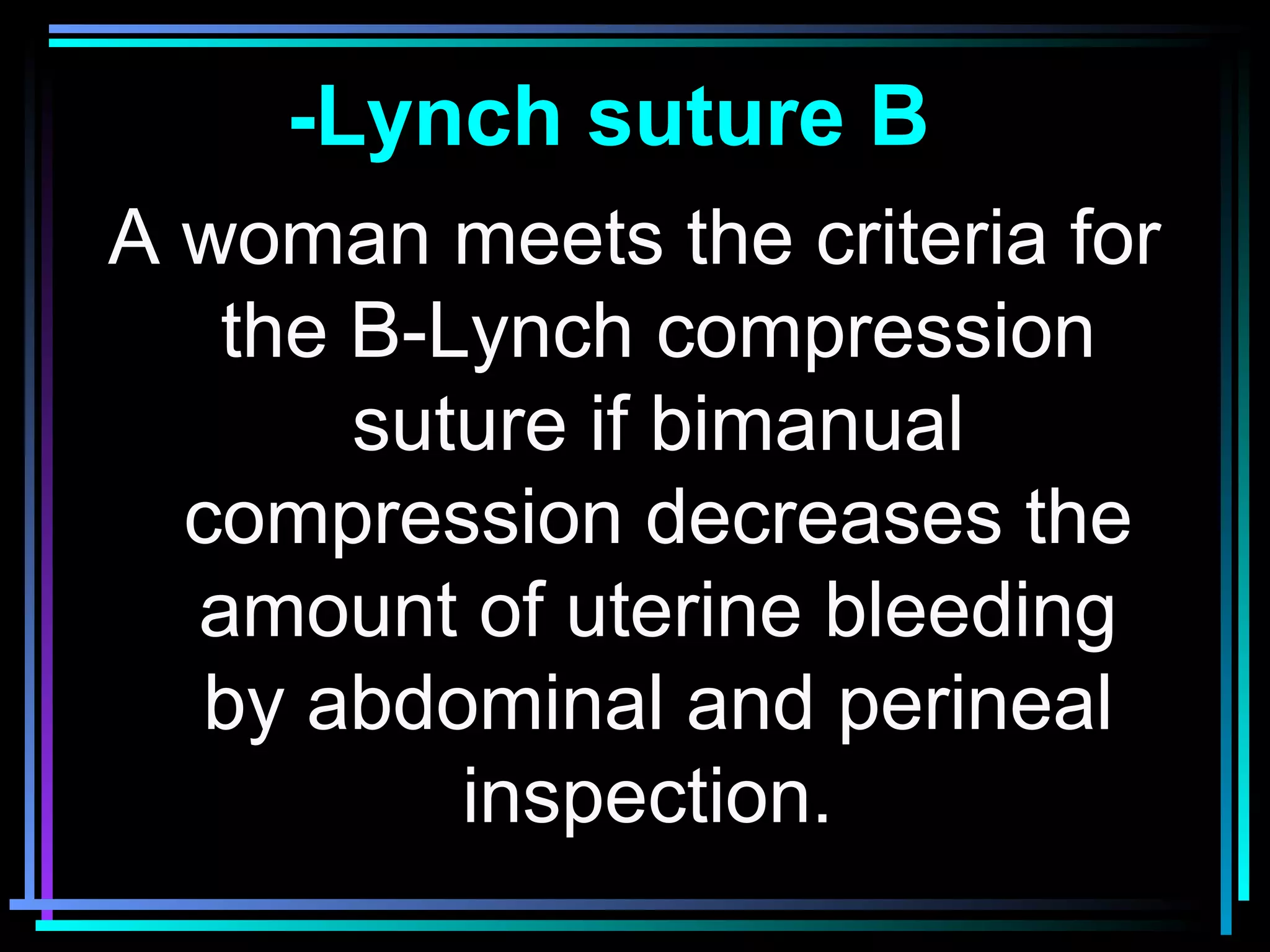
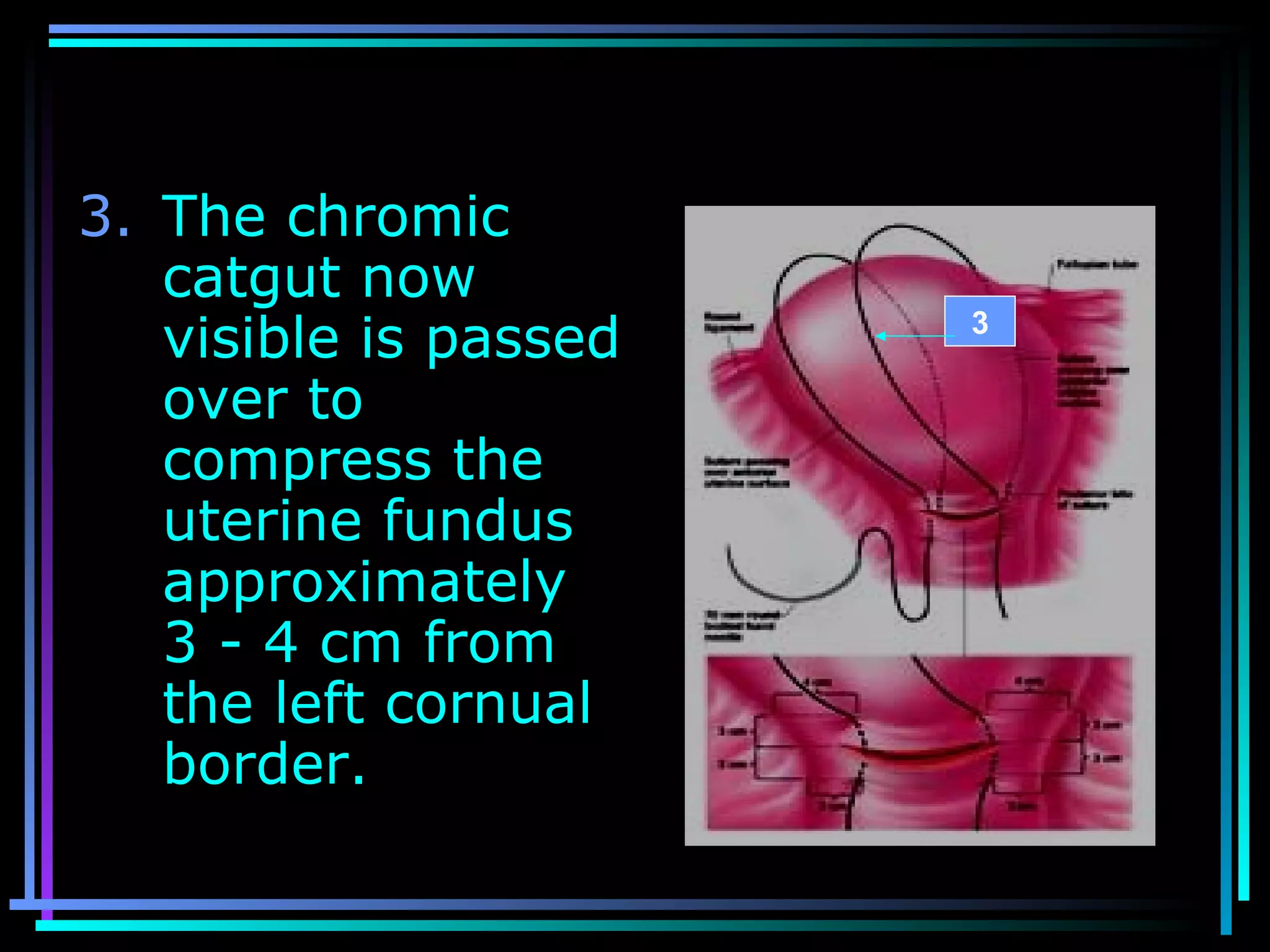
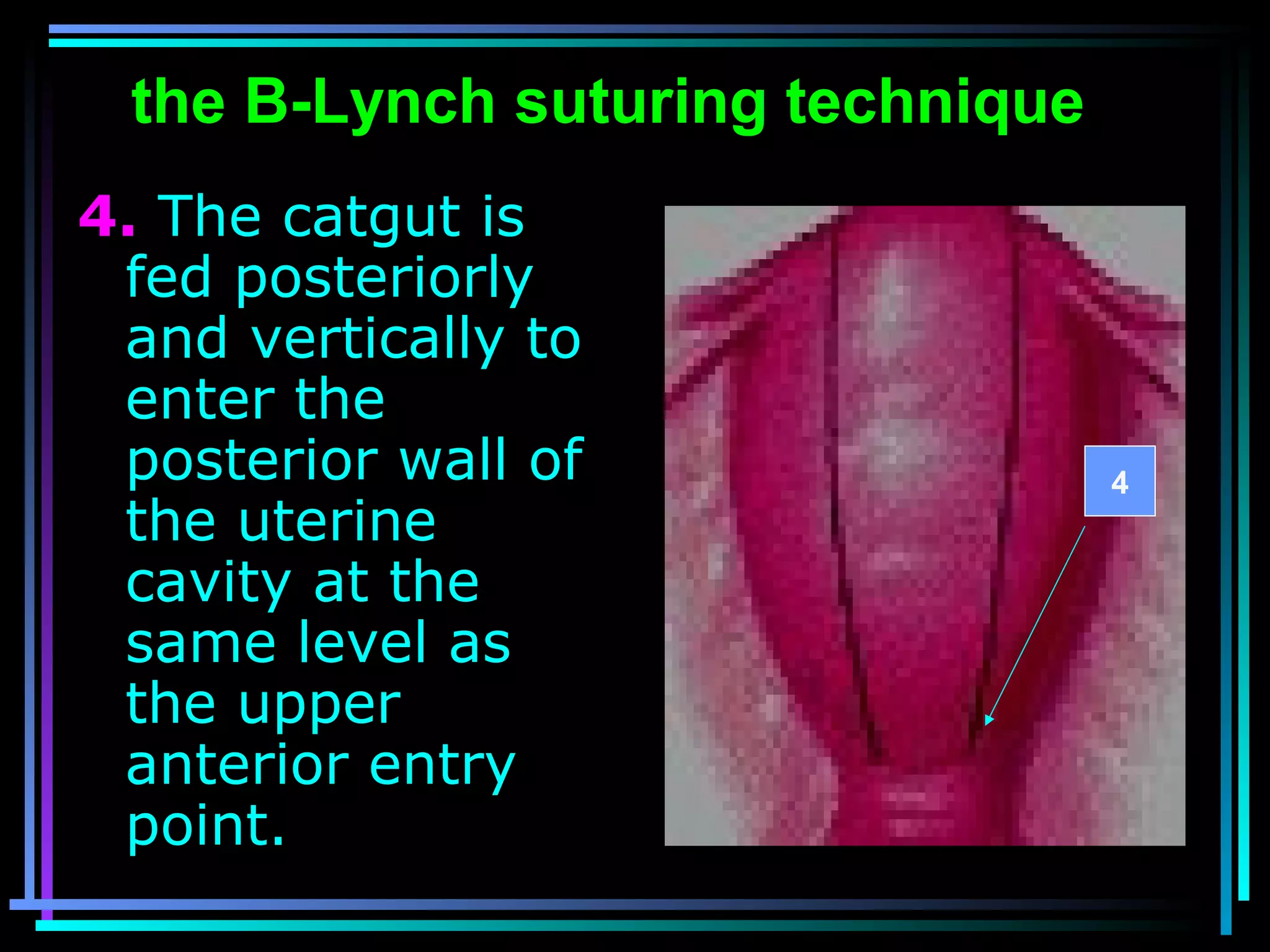
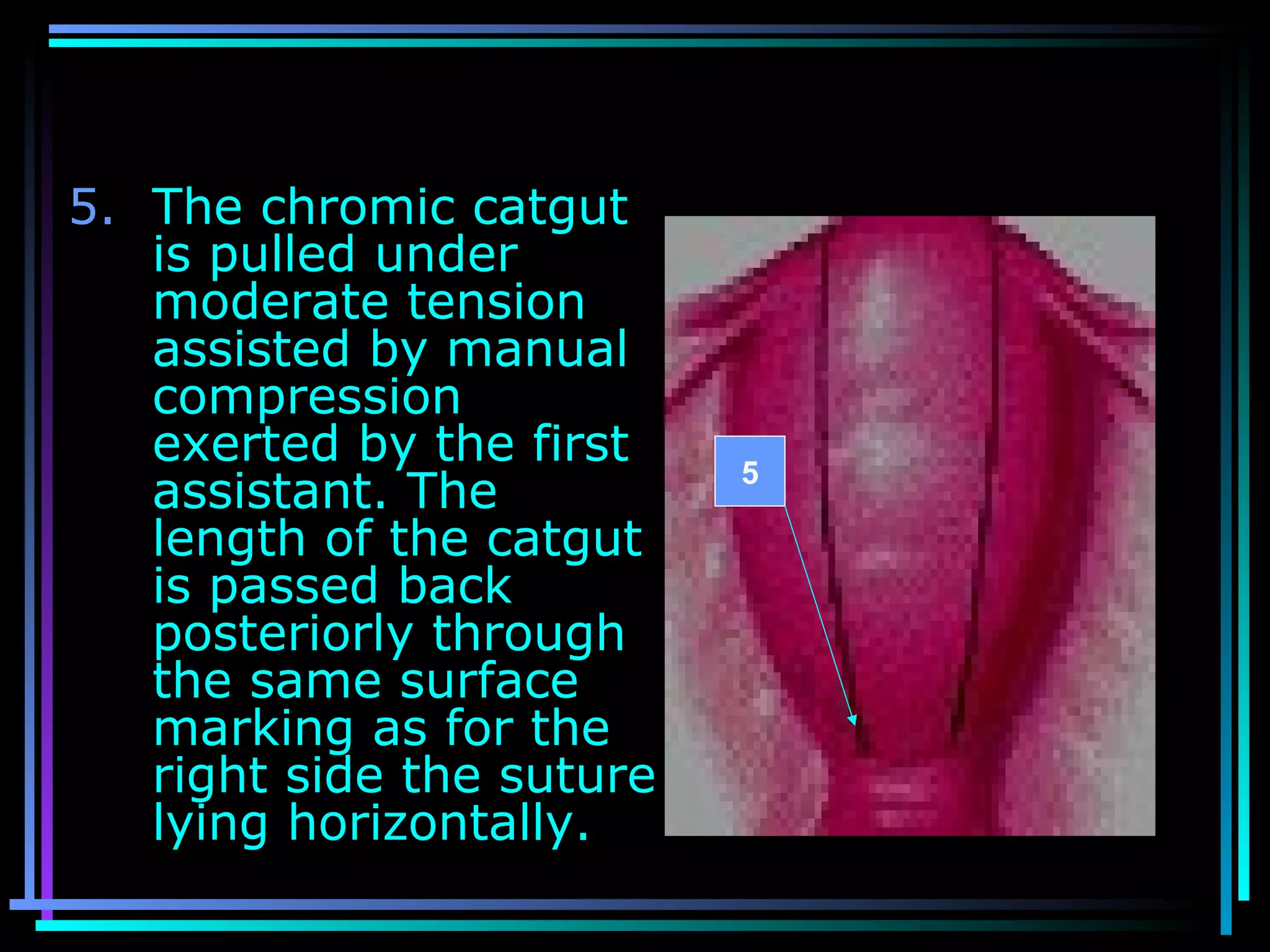
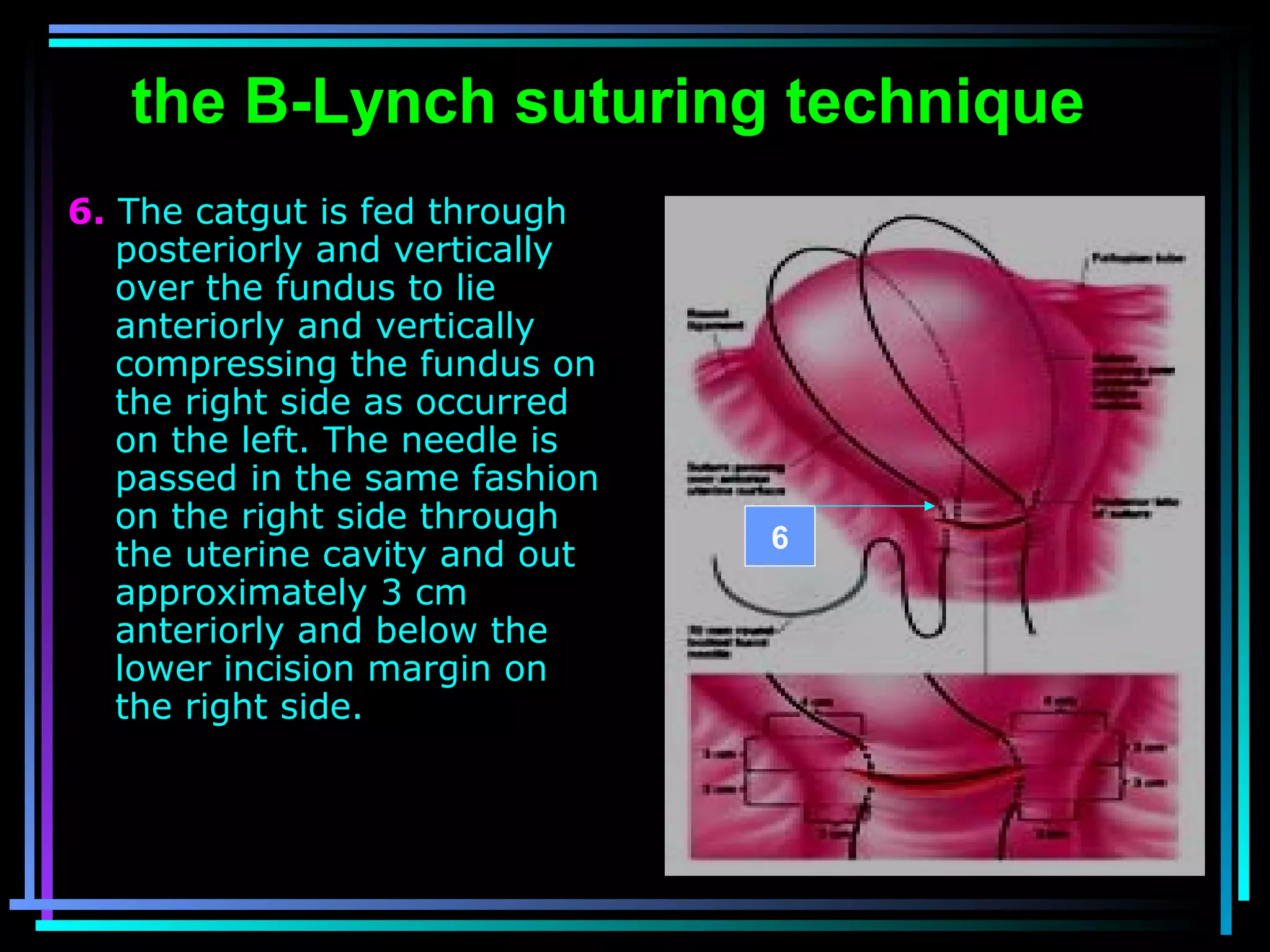
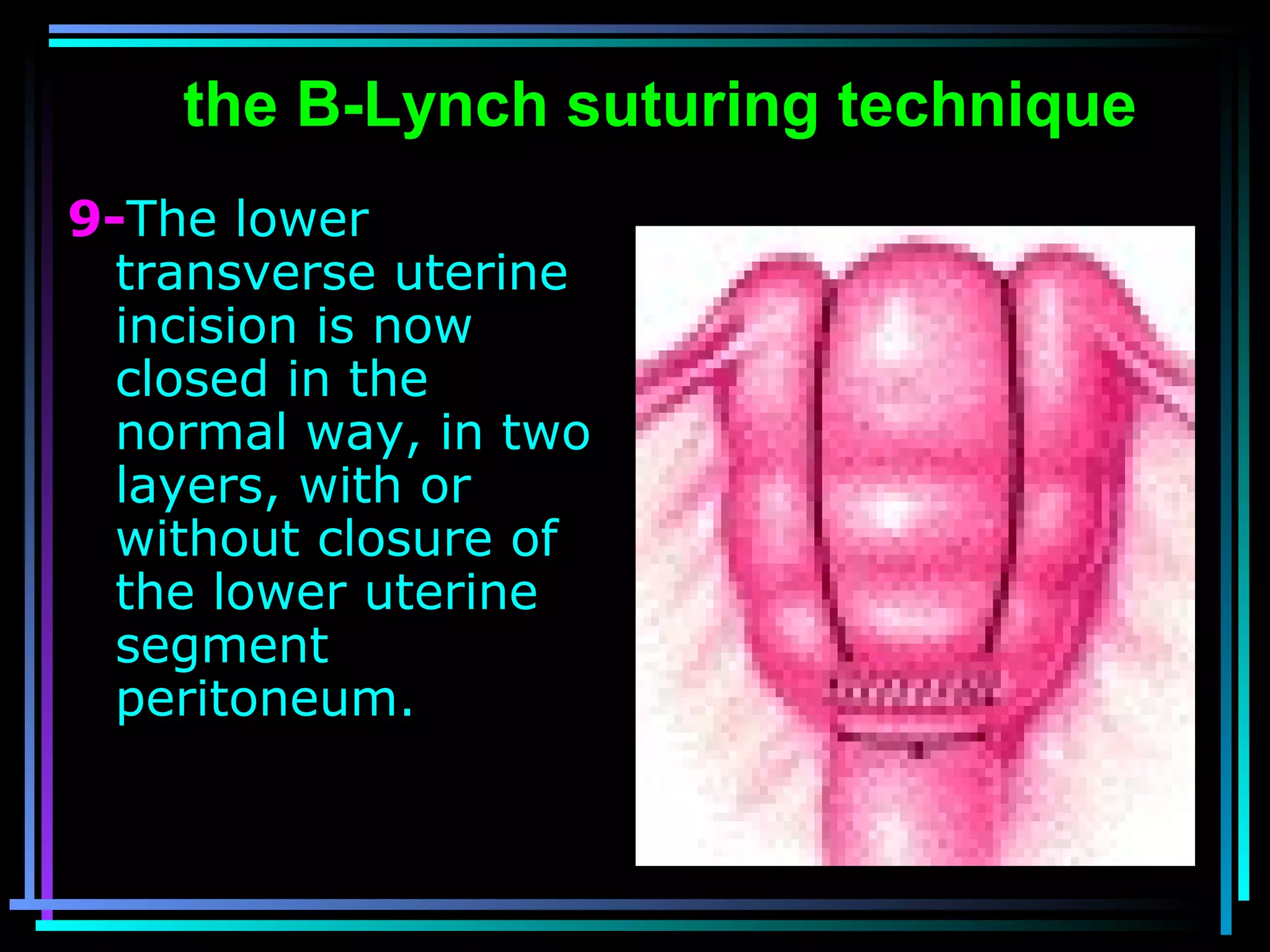
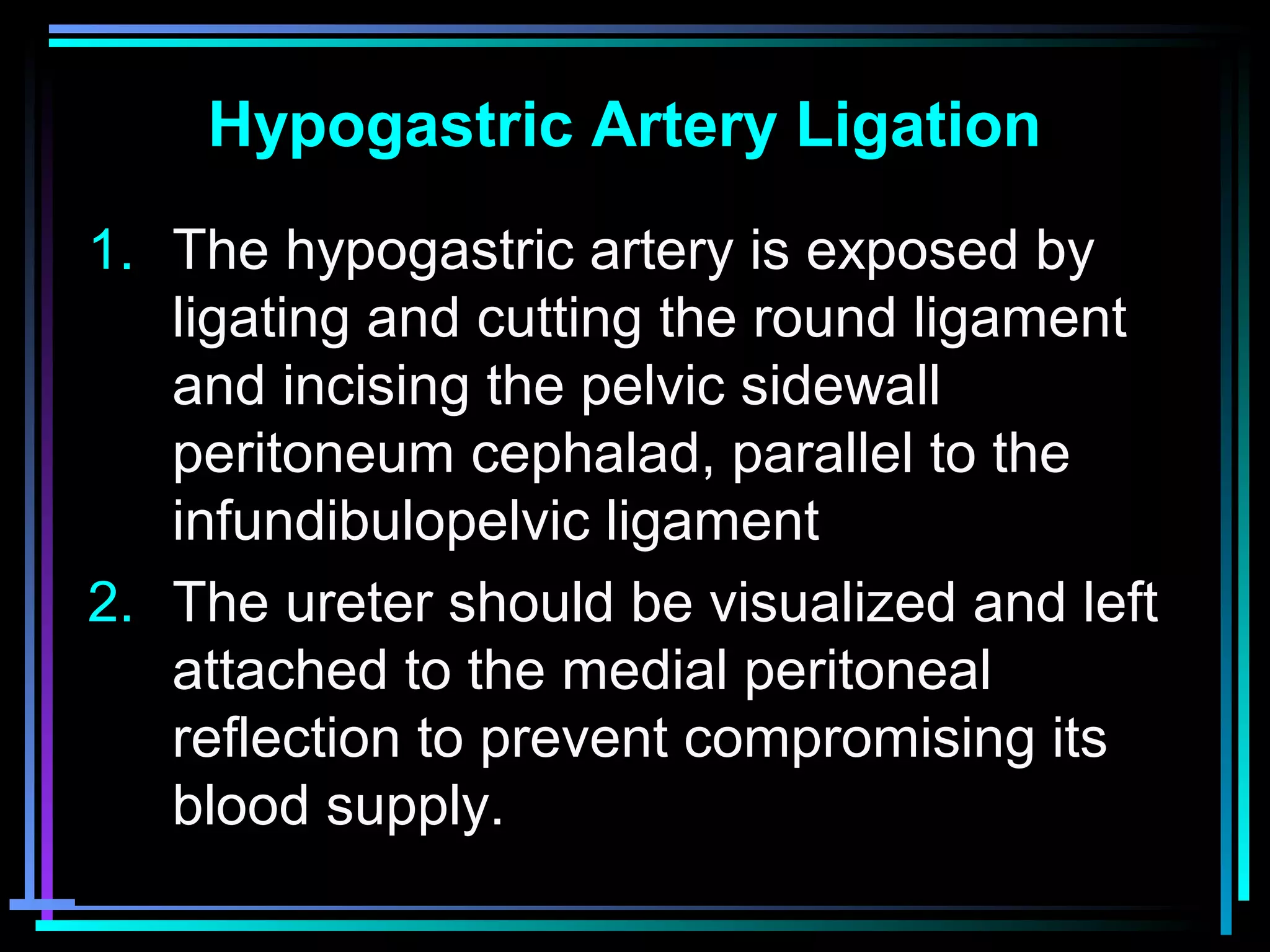
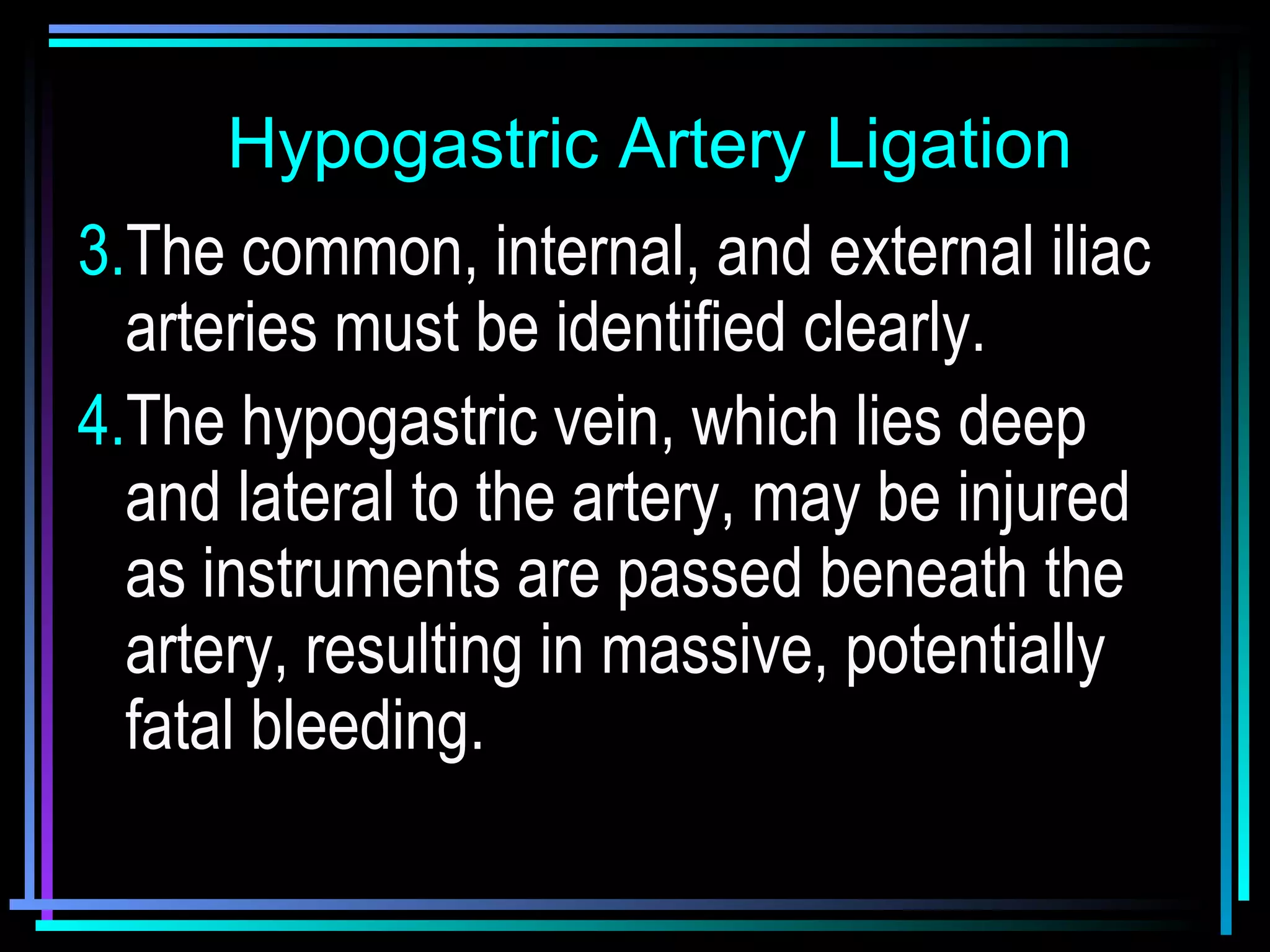
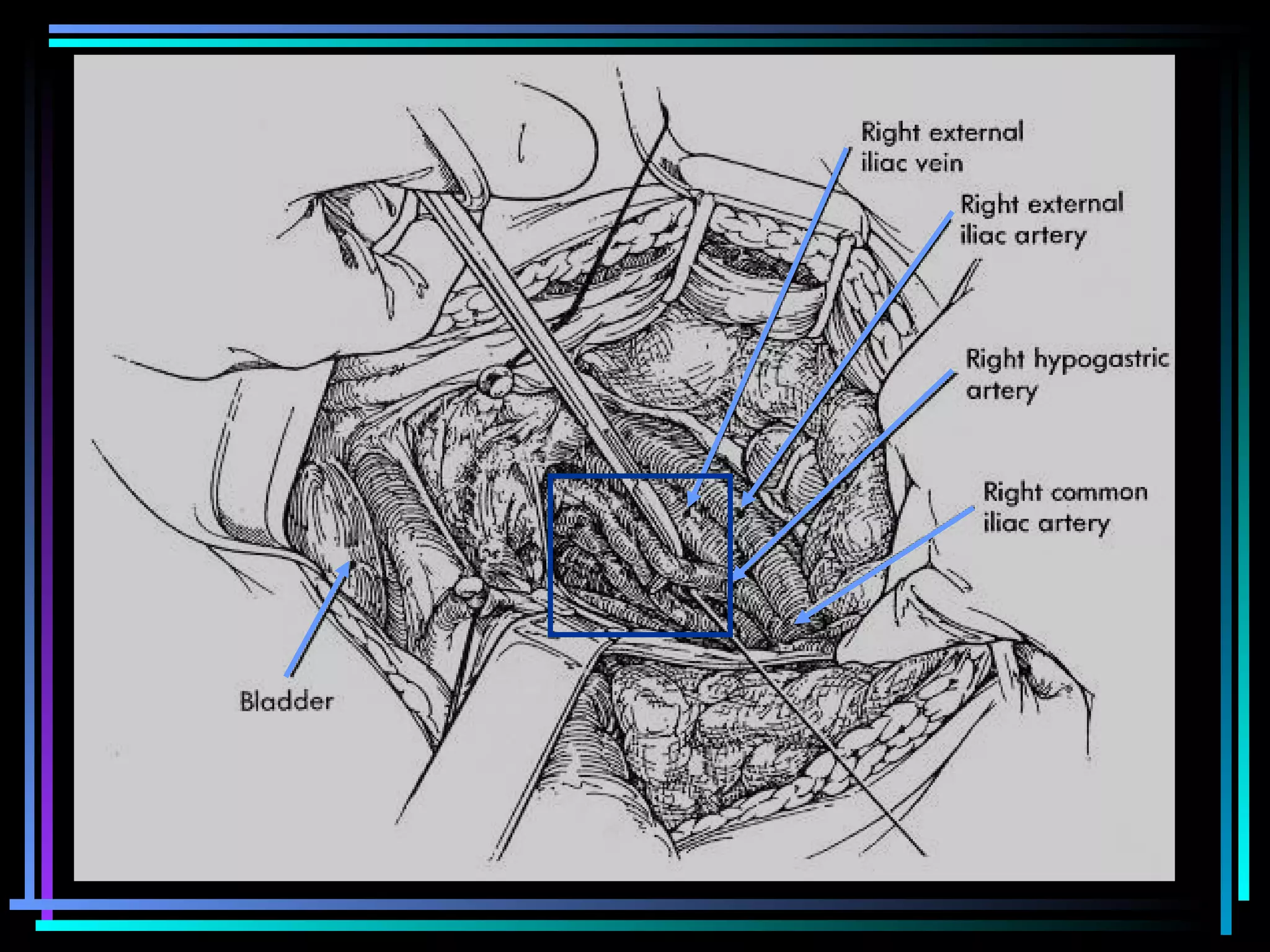
The document discusses placenta accreta, a condition where the placenta invades and attaches abnormally to the uterine wall. It has increased in incidence 10-fold over the past 50 years due to rising cesarean delivery rates. Risk factors include placenta previa, prior uterine surgery, and increasing maternal age and parity. Ultrasound and MRI can be used to diagnose placenta accreta prenatally based on signs like lack of a hypoechoic zone between the placenta and uterus. Management options for severe postpartum hemorrhage from placenta accreta include uterine packing, arterial ligation, hysterectomy, and the B-Lynch compression suture




























![45
misoprostol
• * Keep five 200-[micro]g tablets of
misoprostol in the delivery or operating
room.
• * If uterine atony occurs and doesn't
respond to oxytocin or ergometrine (or if
ergometrine is contraindicated), place
the patient in the frog-leg position, and
while assessing the extent of vaginal
bleeding, place five tablets in her
rectum.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/placenta-accreta-101121022048-phpapp02/75/Placenta-accreta-45-2048.jpg)










![70
9. The condom catheter was kept for 24-48
hours and then was deflated gradually
over (10-15 minutes) and removed.
10.Patient was kept under triple antibiotic
coverage (amoxicillin [500 mg every 6
hrs] + metronidazole [500 mg every 8 hrs]
+ gentamicin [80 mg every 8 hrs])
administered intravenously for 7 days.
Use of a Condom to Control Massive
Postpartum Hemorrhage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/placenta-accreta-101121022048-phpapp02/75/Placenta-accreta-70-2048.jpg)