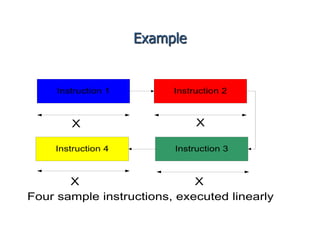
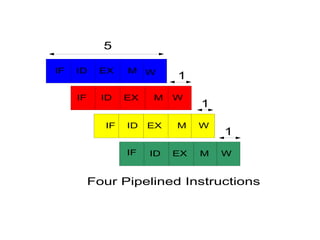
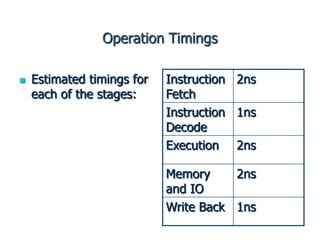
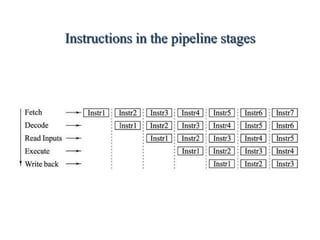
Pipelining is a technique where a microprocessor can begin executing the next instruction before finishing the previous one. It works by dividing instruction processing into discrete stages - fetch, decode, execute, memory, and write back. When an instruction enters one stage, the next instruction can enter the following stage so that multiple instructions are in different stages at the same time, improving efficiency. The pipeline allows for faster overall processing but hazards can occur if instructions depend on previous ones, disrupting the smooth flow.