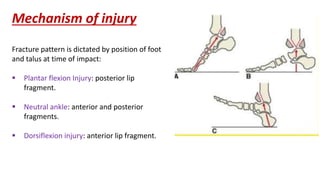
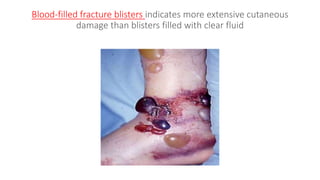
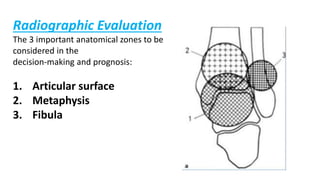
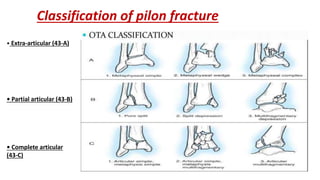
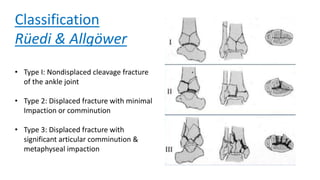
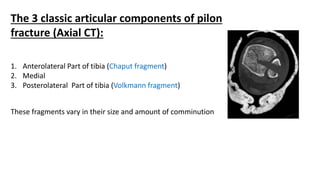
Pilon fractures involve the distal articular surface of the tibia. They account for 7-10% of tibial fractures and usually result from high-energy injuries. Classification systems categorize pilon fractures as extra-articular, partial articular, or complete articular, with complete fractures having significant articular comminution. Treatment goals are anatomical reduction, axial alignment, joint stability, and union. Options include casting, external fixation, limited internal fixation, and open reduction with staged procedures to address soft tissue status. Complications can include skin necrosis, nonunion, stiffness, infection, and arthritis.