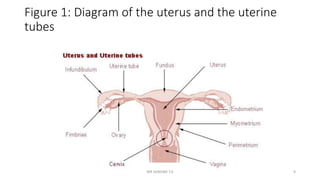
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a serious infection of the upper reproductive tract caused by sexually transmitted bacteria, predominantly affecting women under 25. Key factors for PID include the presence of chlamydia or gonorrhea, with symptoms varying from mild to severe and leading to serious complications like infertility and ectopic pregnancy. Management involves antibiotics, patient education, and supportive nursing care aimed at alleviating symptoms and preventing further complications.