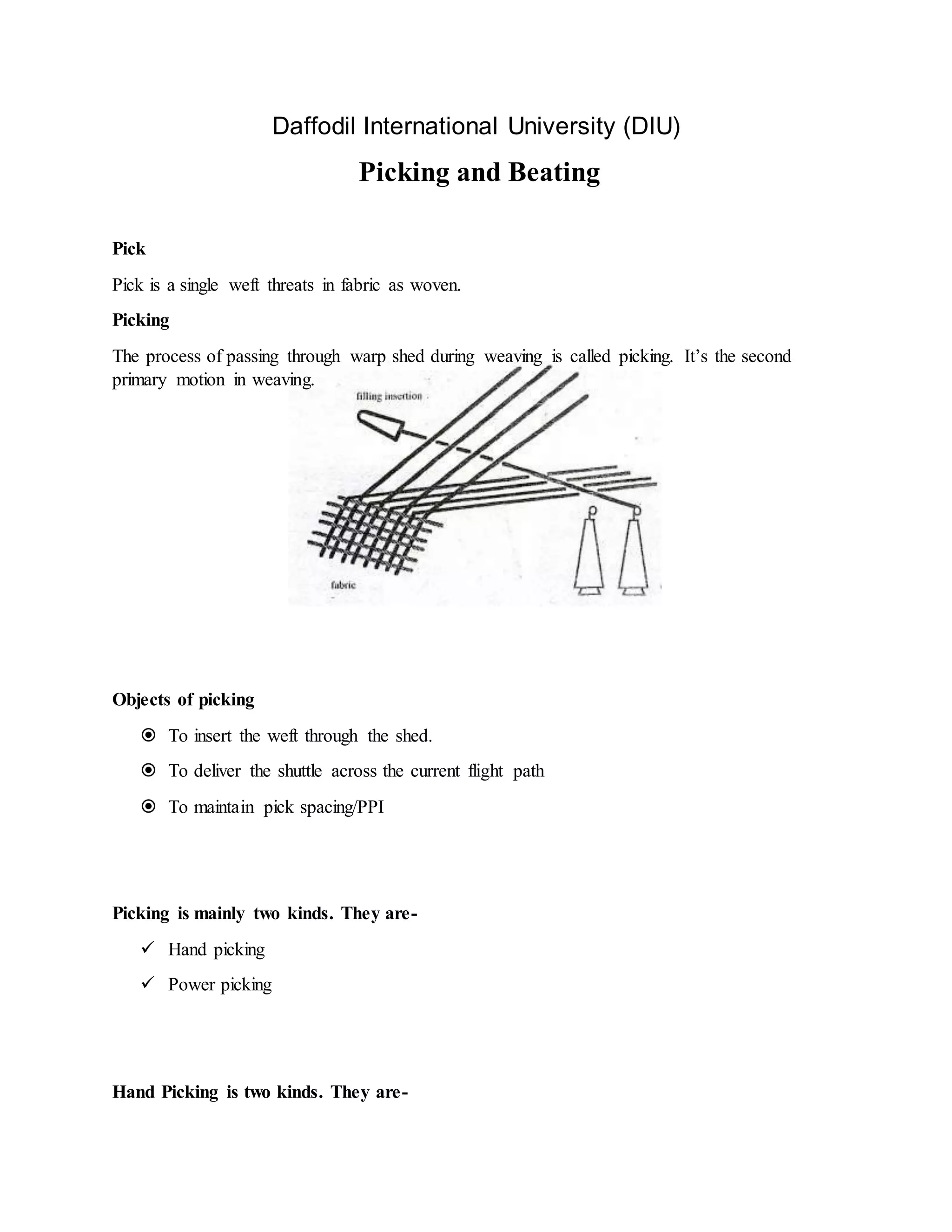
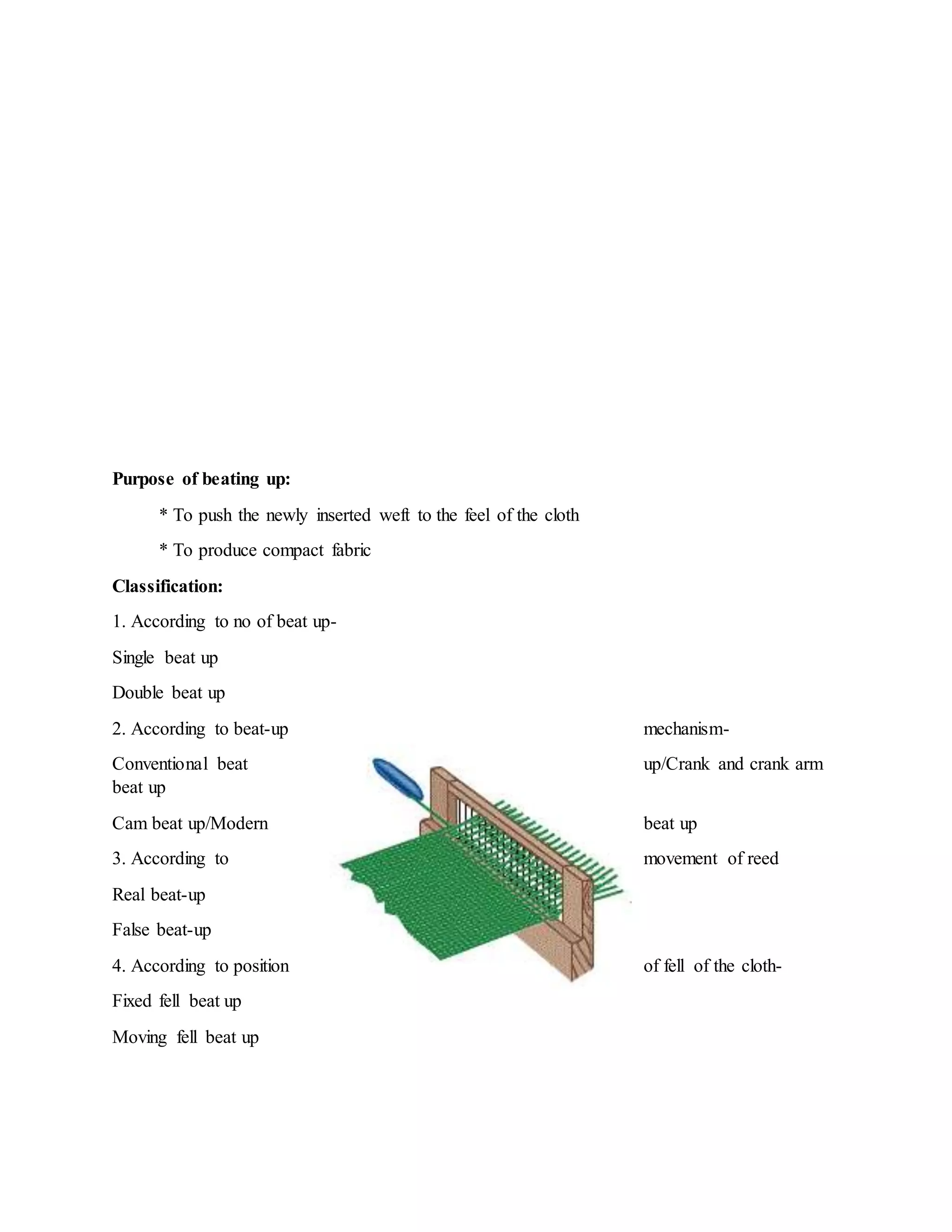
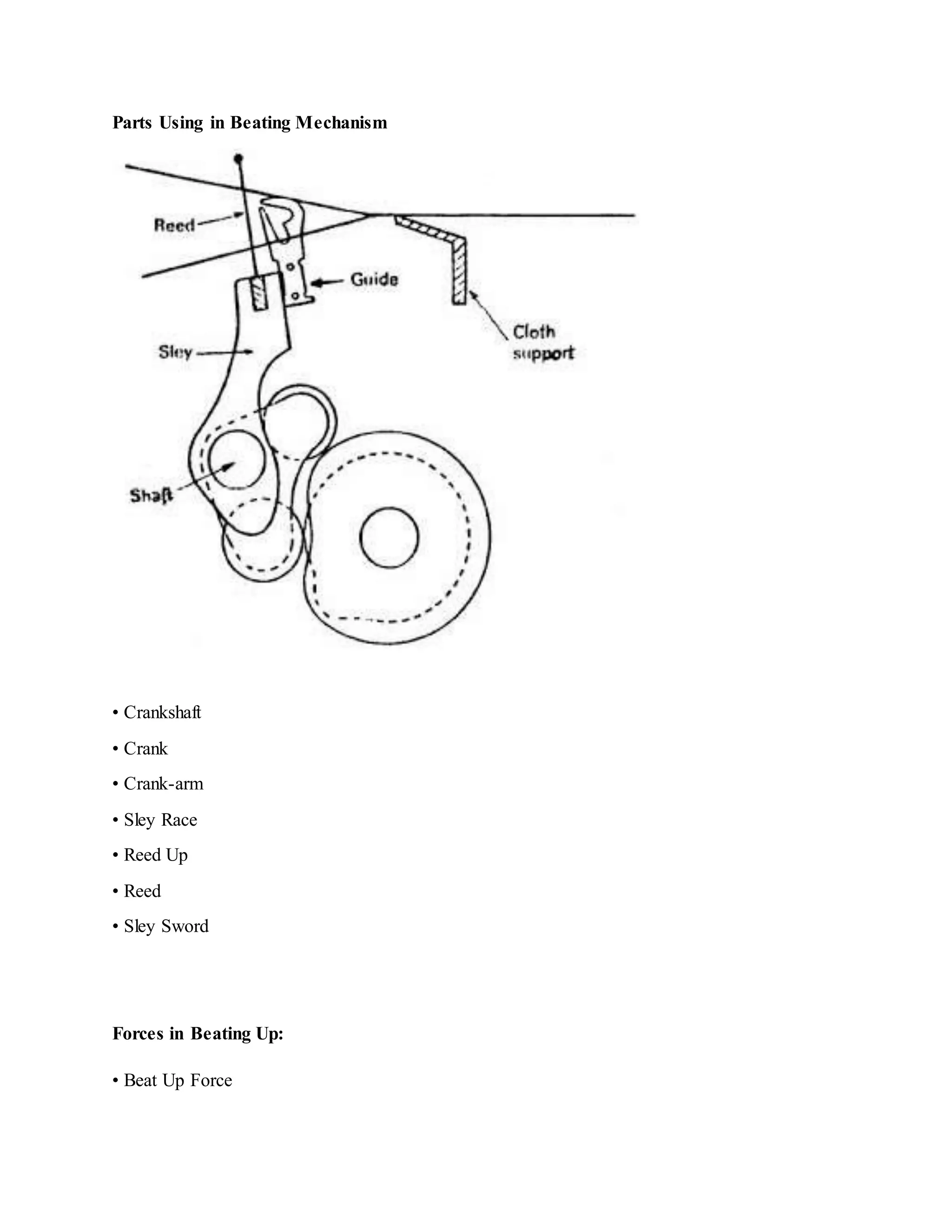
The document discusses the fundamentals of fabric manufacturing, specifically focusing on the processes of picking and beating in weaving. It details the mechanisms and types of picking, including hand and power picking, along with their advantages and differences between over and under pick mechanisms. Additionally, it elaborates on the beating process, its classification, components, and working principles, highlighting both single and double beat-up mechanisms.