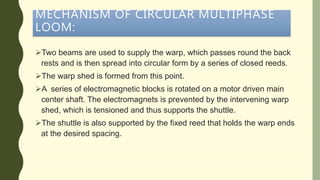
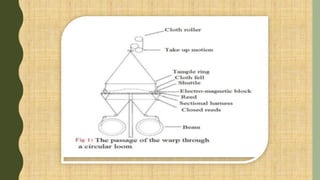
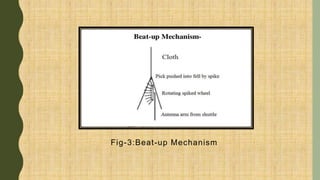
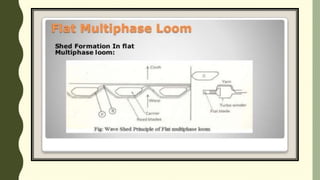
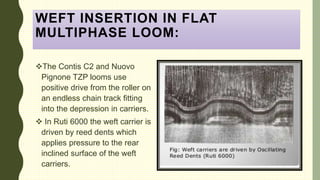
The document describes a multiphase loom assignment submitted by 6 students. It provides details on the mechanisms of circular and flat multiphase looms. Circular looms use two warp beams, closed reeds to spread the warp circularly, and electromagnetic shuttles that follow a circular path. Flat looms use positive weft carrier drives and rotating reeds for beat-up. The document also outlines features such as medium fabric production and use of split harnesses for shedding.