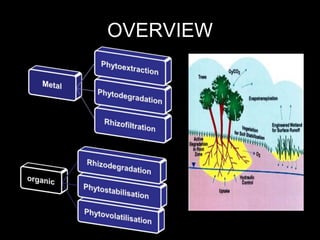
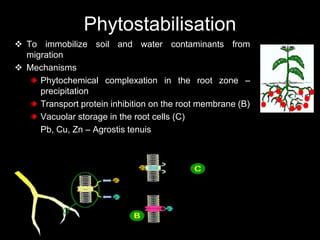
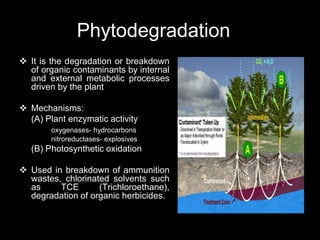
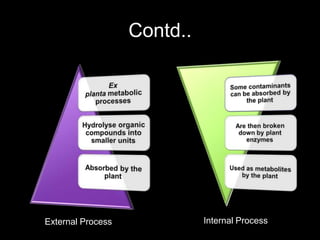
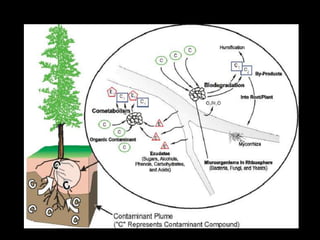
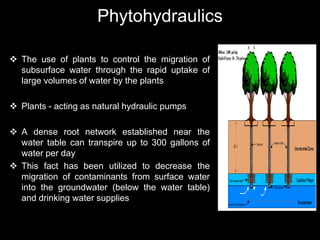
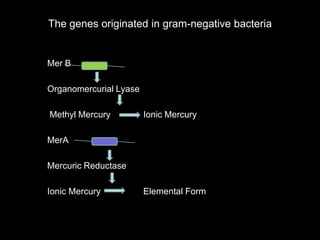
Phytoremediation uses plants to remove, transfer, stabilize, or destroy contaminants in soil, sediment, surface water and groundwater. It involves processes such as phytoextraction, rhizofiltration, phytostabilization, phytodegradation, rhizodegradation, phytovolatilization, and phytohydraulics. Genetic engineering can be used to enhance plants' natural abilities to remediate contamination. While phytoremediation is more environmentally friendly than traditional methods, it typically takes longer and plant growth conditions must be suitable for the contaminants present.