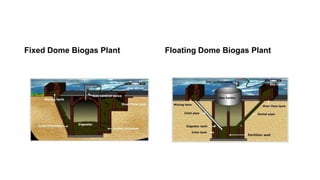
Biogas is formed from the natural degradation of organic matter in anaerobic conditions. It contains 50-70% methane and can be used as a fuel for cooking, heating, lighting, and electricity generation. There are two main types of biogas plants - fixed dome and floating gas holder. Biogas plants produce biogas through a three step process of hydrolysis, acidogenesis, and methanogenesis and the sludge produced can be used as fertilizer. While biogas technologies have potential benefits, high initial costs and lack of adequate organic waste inputs have limited adoption in many developing countries.