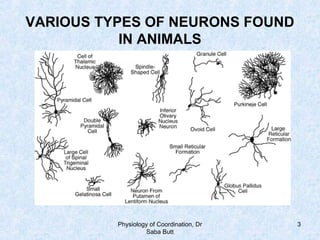
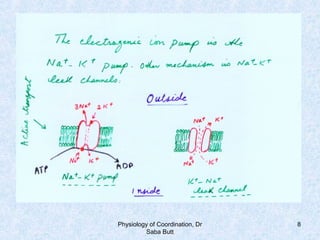
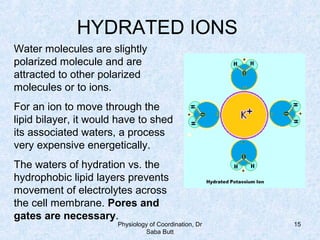
This document discusses the physiology of coordination in the nervous system. It describes the different types of neurons found in animals and the functional divisions of the nervous system. The resting membrane potential is explained, which is normally around -90 mV due to mechanisms like the sodium-potassium pump and Donnan equilibrium. Ion concentrations differ inside and outside cells, with higher potassium and lower sodium and chloride inside. Ion permeability is selective, with potassium able to pass more easily than hydrated sodium ions. Diseases can impact ion concentrations and membrane potentials.