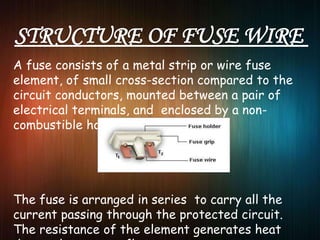
A fuse is a device that protects electrical systems by interrupting excessive currents. It contains a fuse element, usually a metal wire, that melts and breaks the circuit when too much current passes through. This prevents damage to the wider system. Fuses come in different types for alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) systems. They can be single-use, requiring manual replacement after melting, or resettable to reuse. The fuse element works as a sacrificial part that safely disconnects power in a surge, rather than allowing components further down the line to overheat or catch fire.