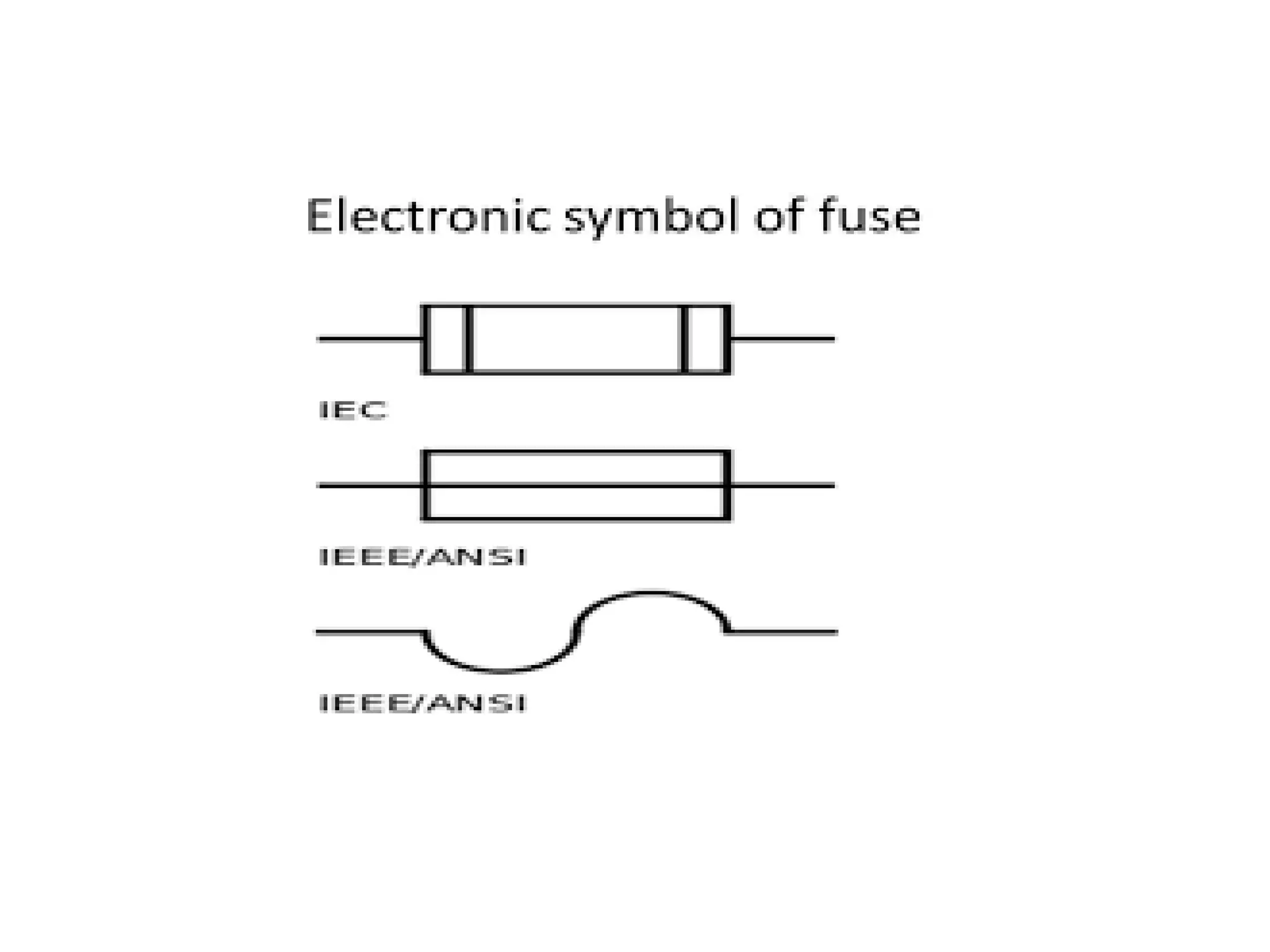
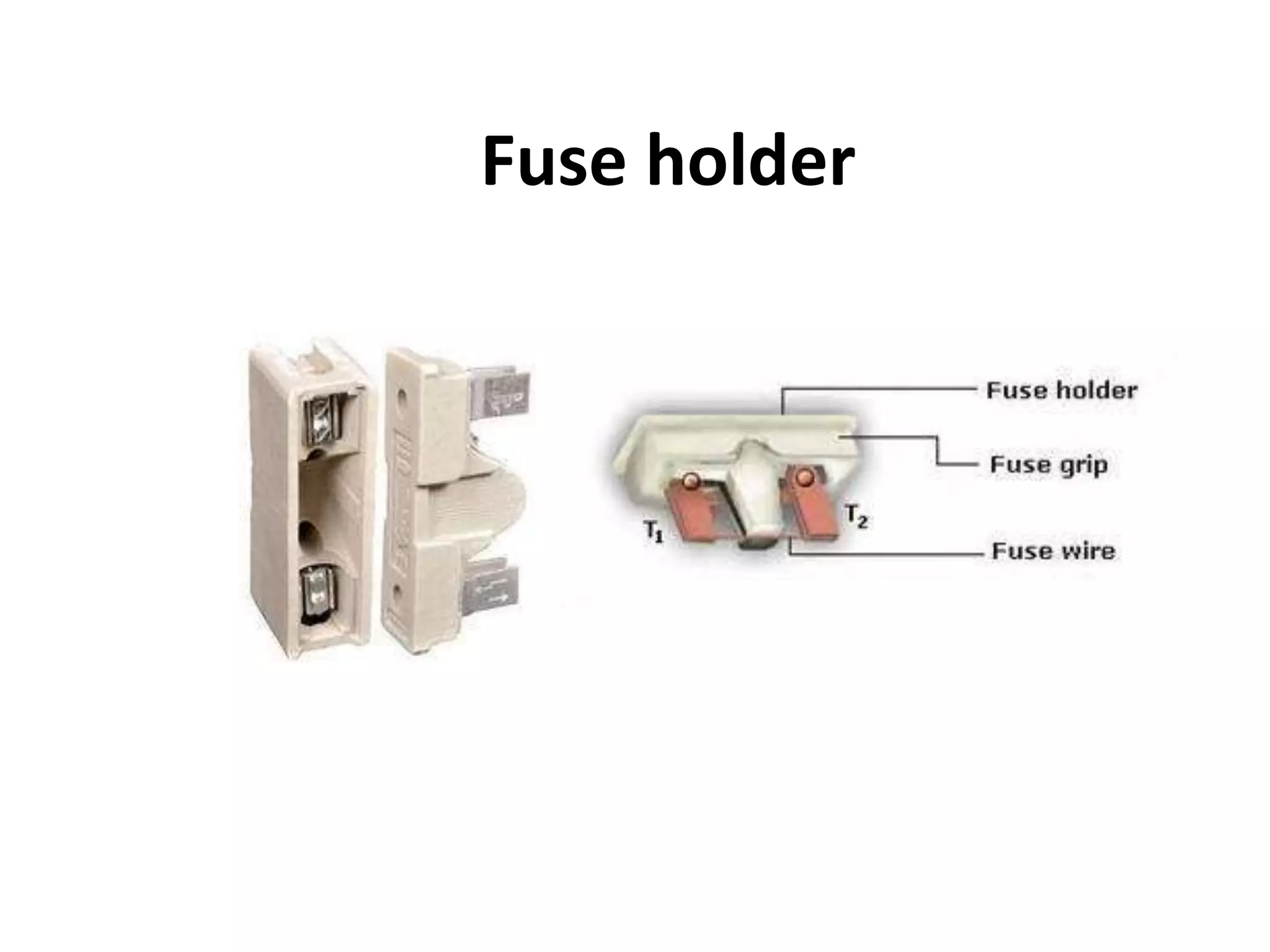
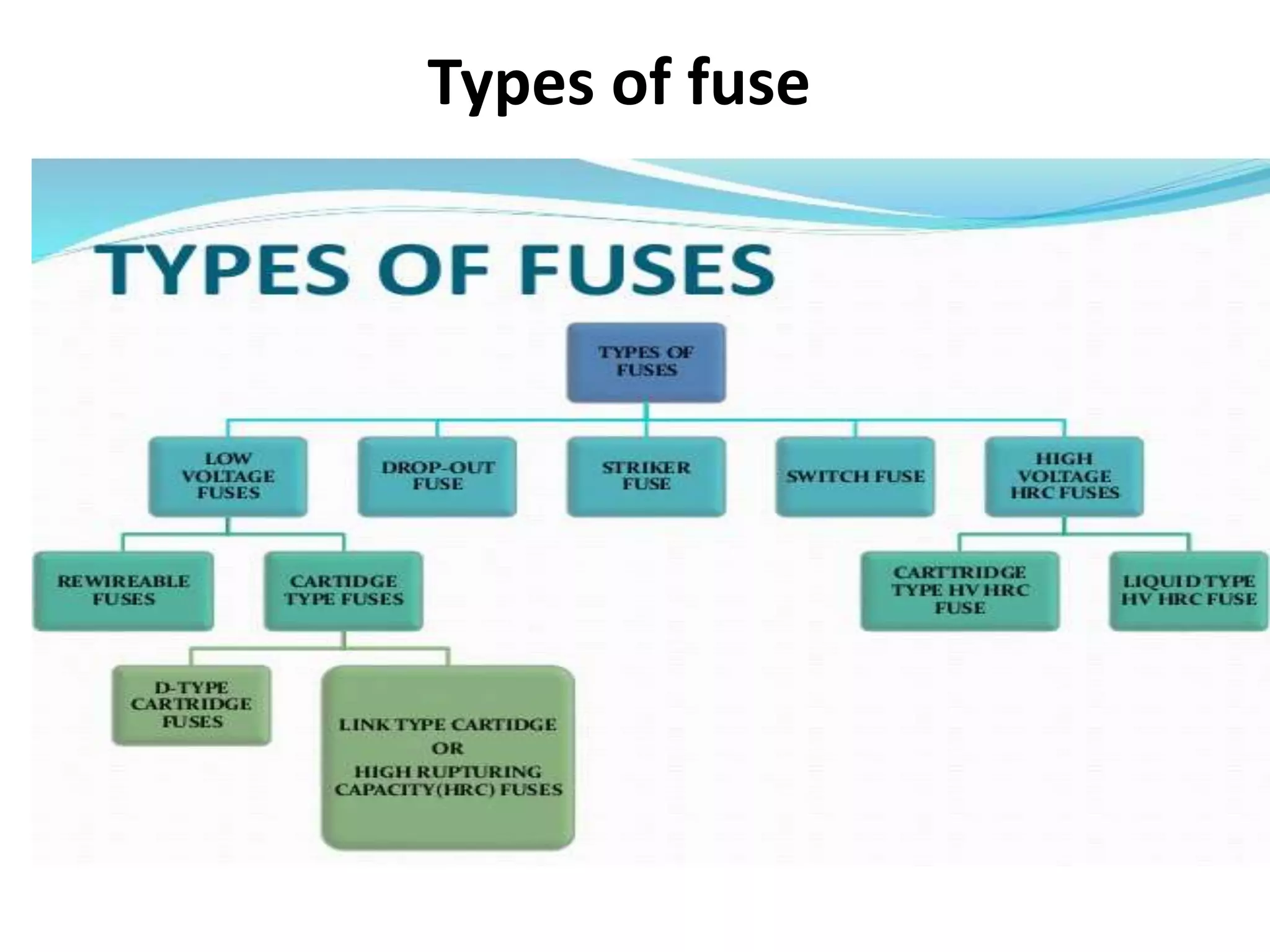
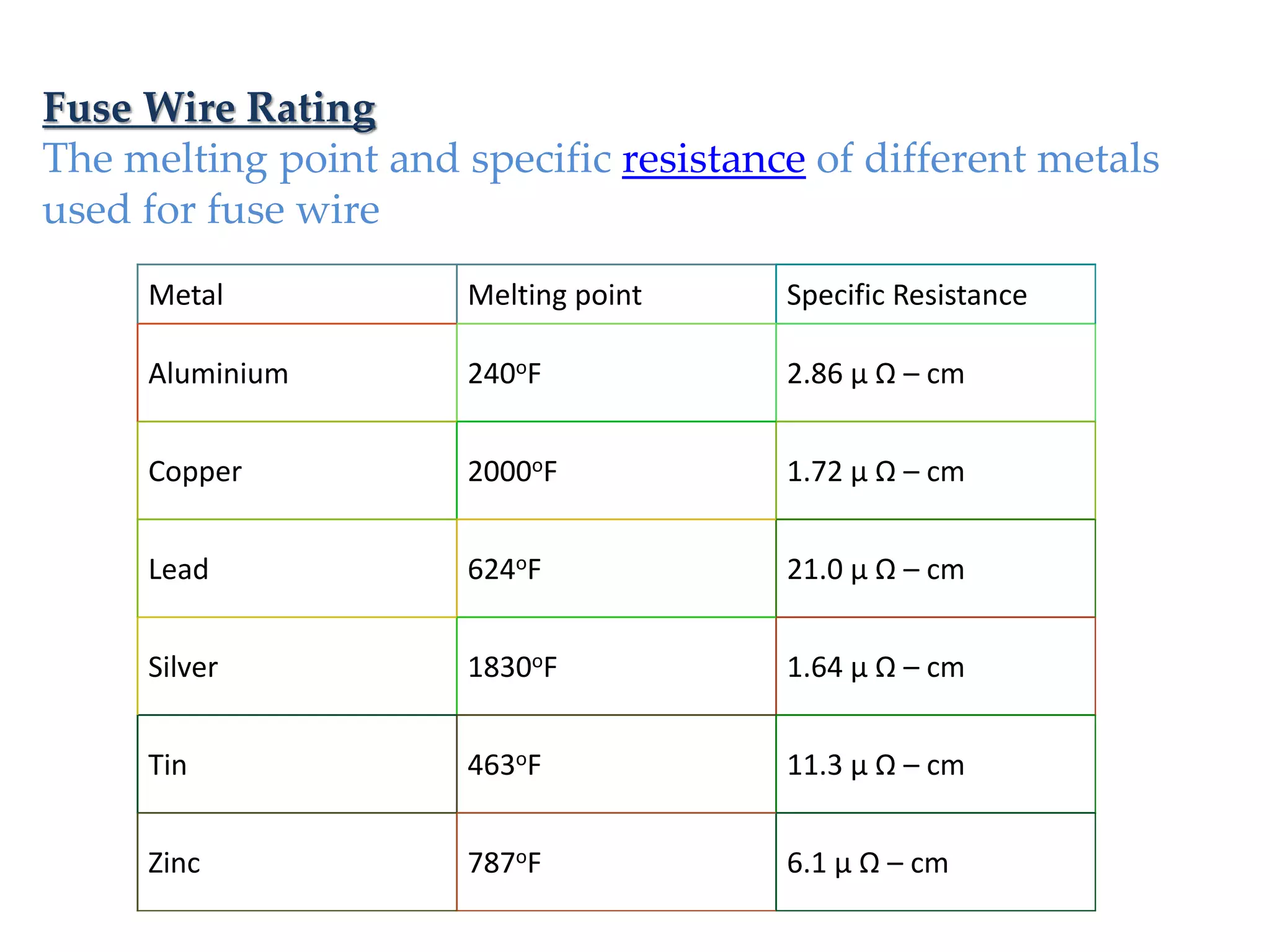
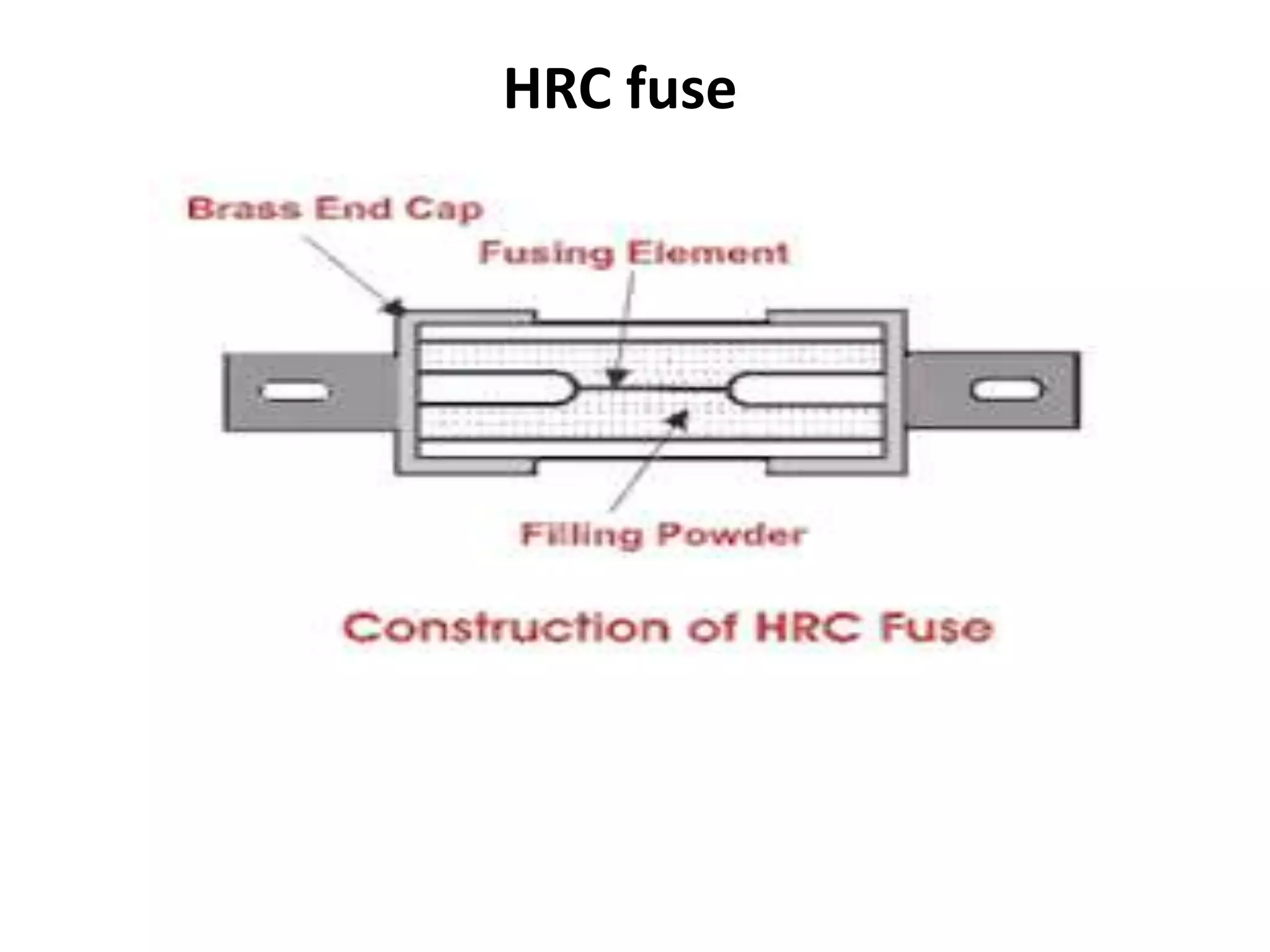
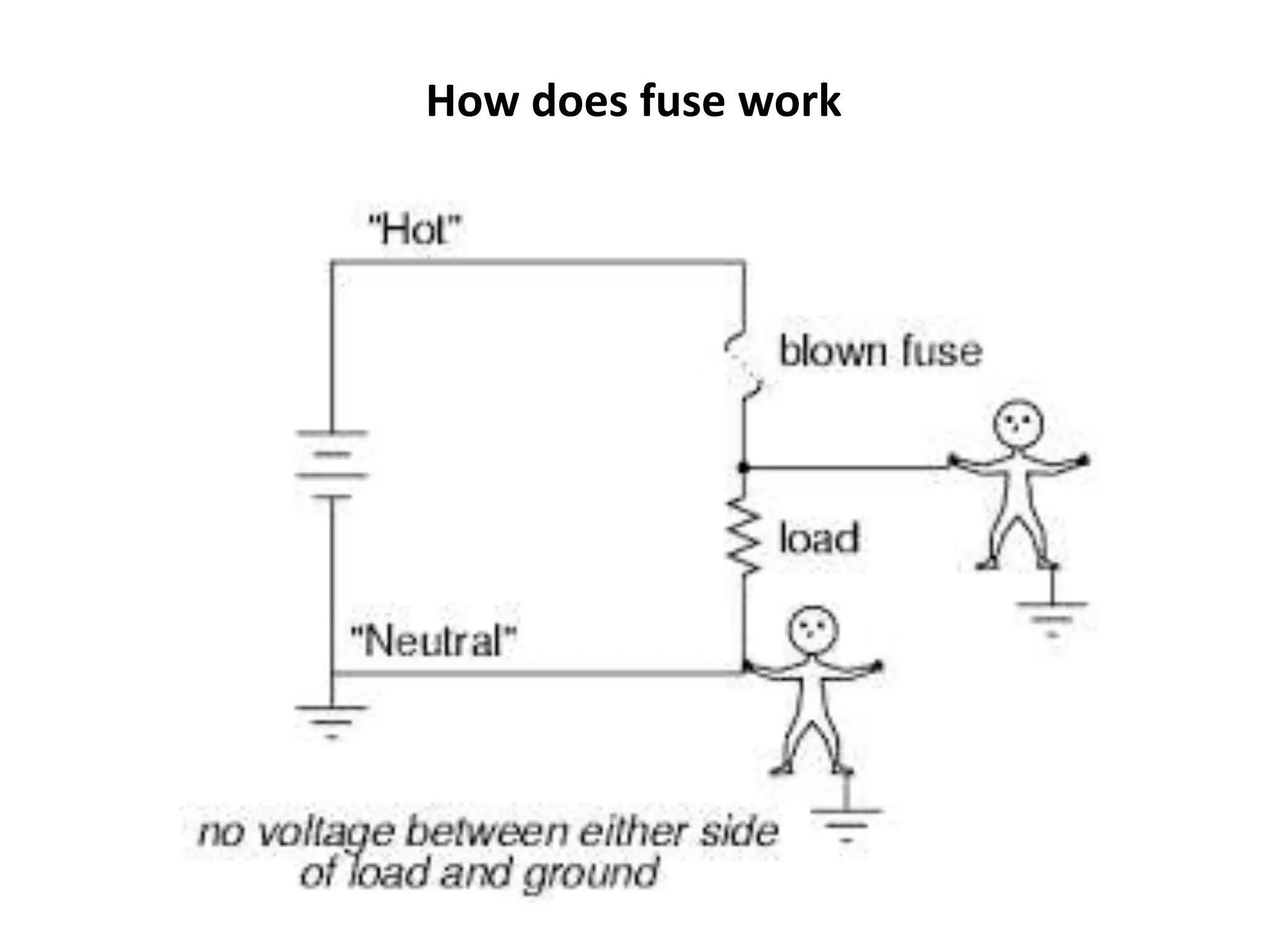
The document discusses electrical fuses, explaining their role in protecting electrical circuits by melting and breaking the connection when current exceeds a predetermined value. It covers various types of fuses, such as high rupturing capacity (HRC) fuses, and details the materials used for fuse wires along with their properties. The presentation emphasizes the importance of fuses in preventing damage to equipment during network faults.