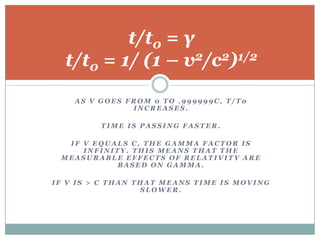The document discusses several topics in physics including:
1) The stars of the Big Dipper constellation and their properties such as temperature, distance, and luminosity.
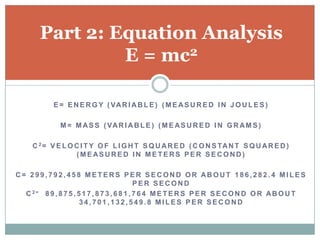
2) Einstein's mass-energy equivalence equation E=mc2 and what it means that mass and energy are different forms of the same thing.
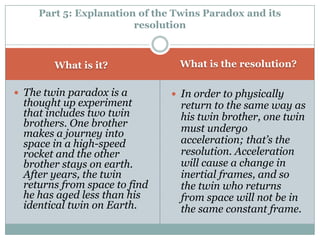
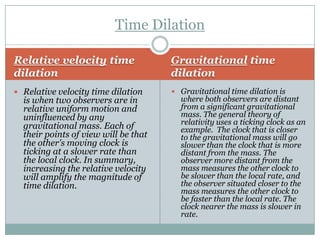
3) The twin paradox thought experiment and how the resolution is that one twin undergoing acceleration causes them to experience different frames of reference and amounts of aging.
4) Factors that could explain Fermi's paradox such as life being unsuitable for Earth conditions or advanced civilizations not existing yet.