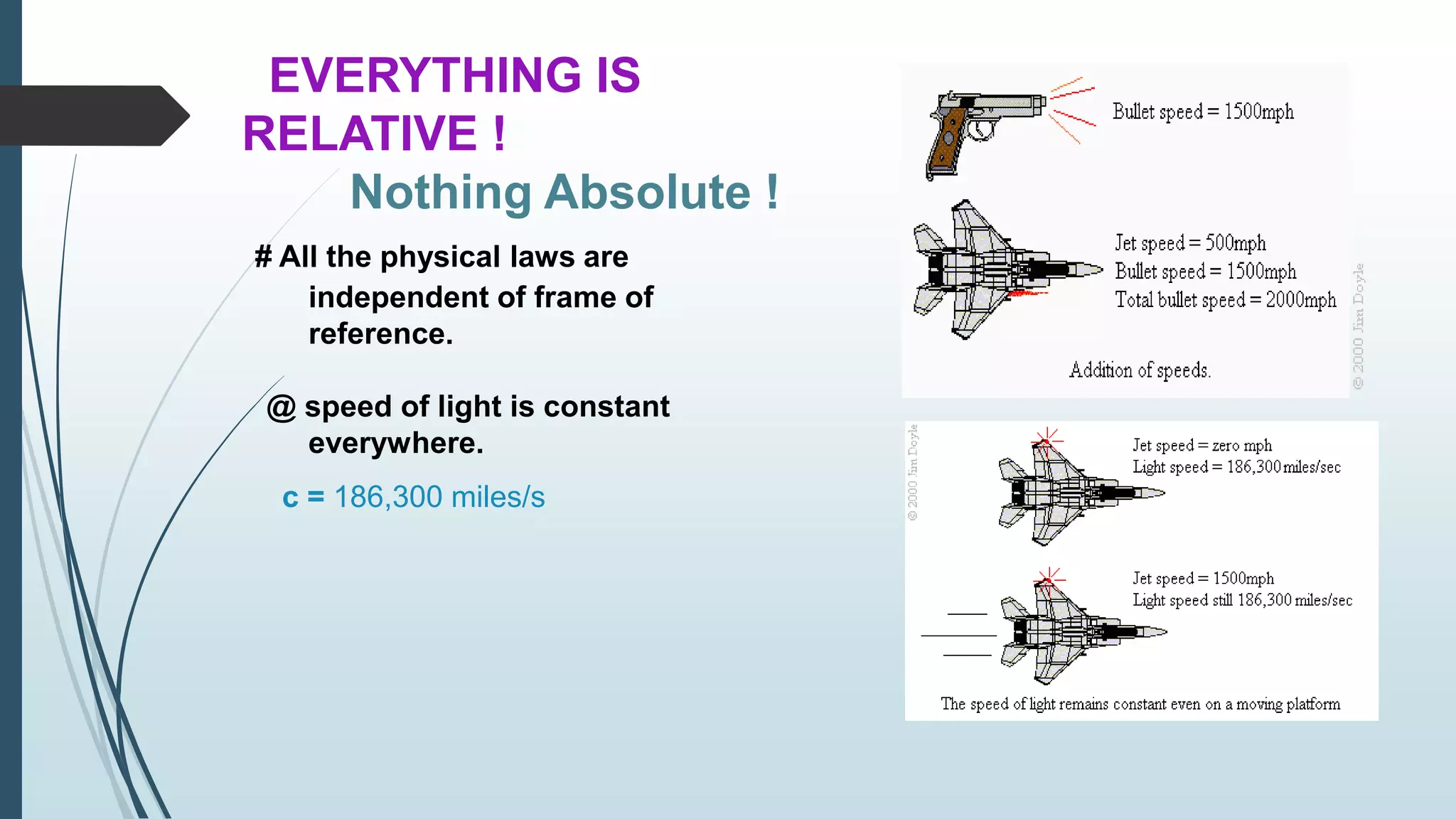
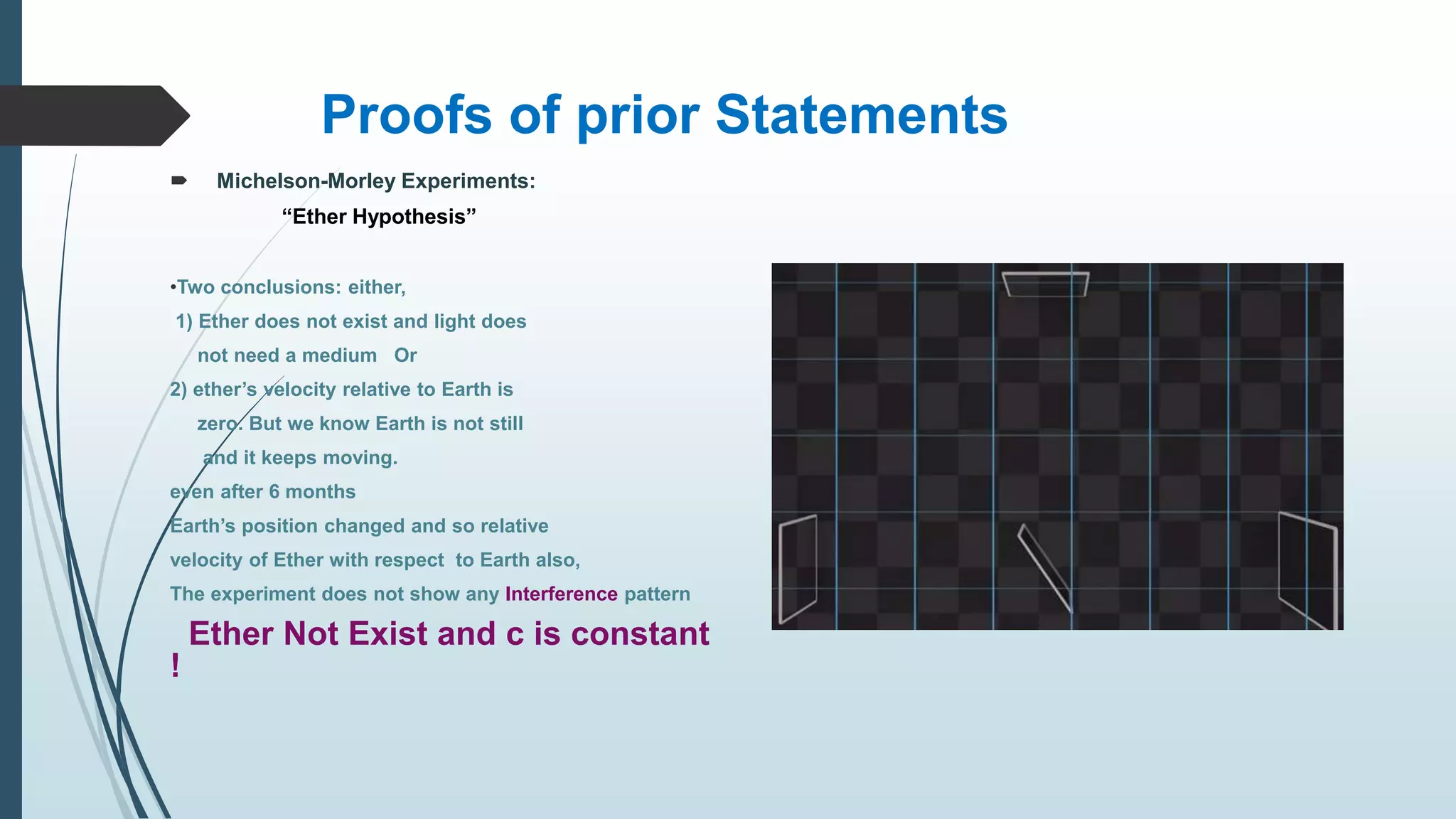
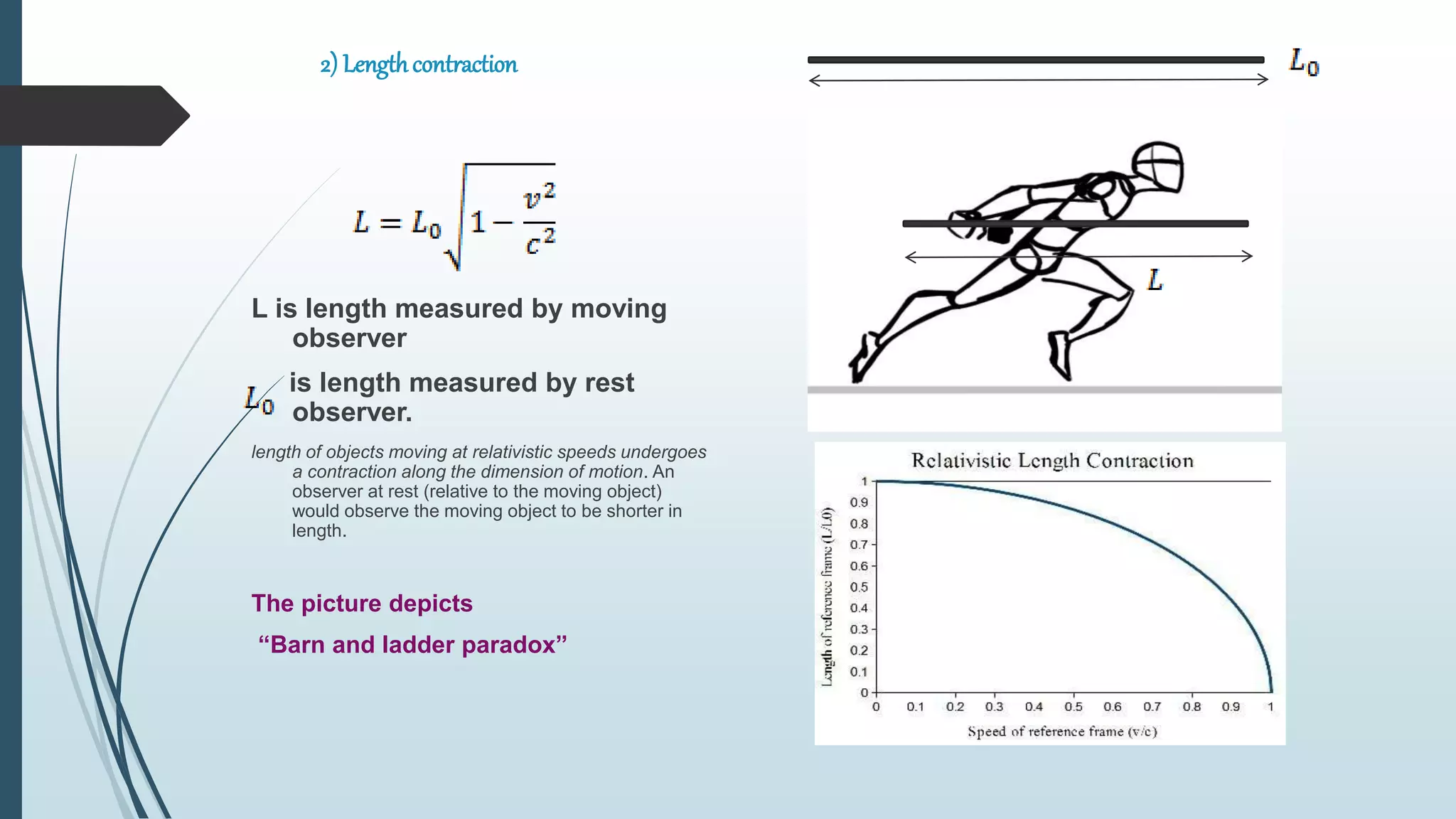
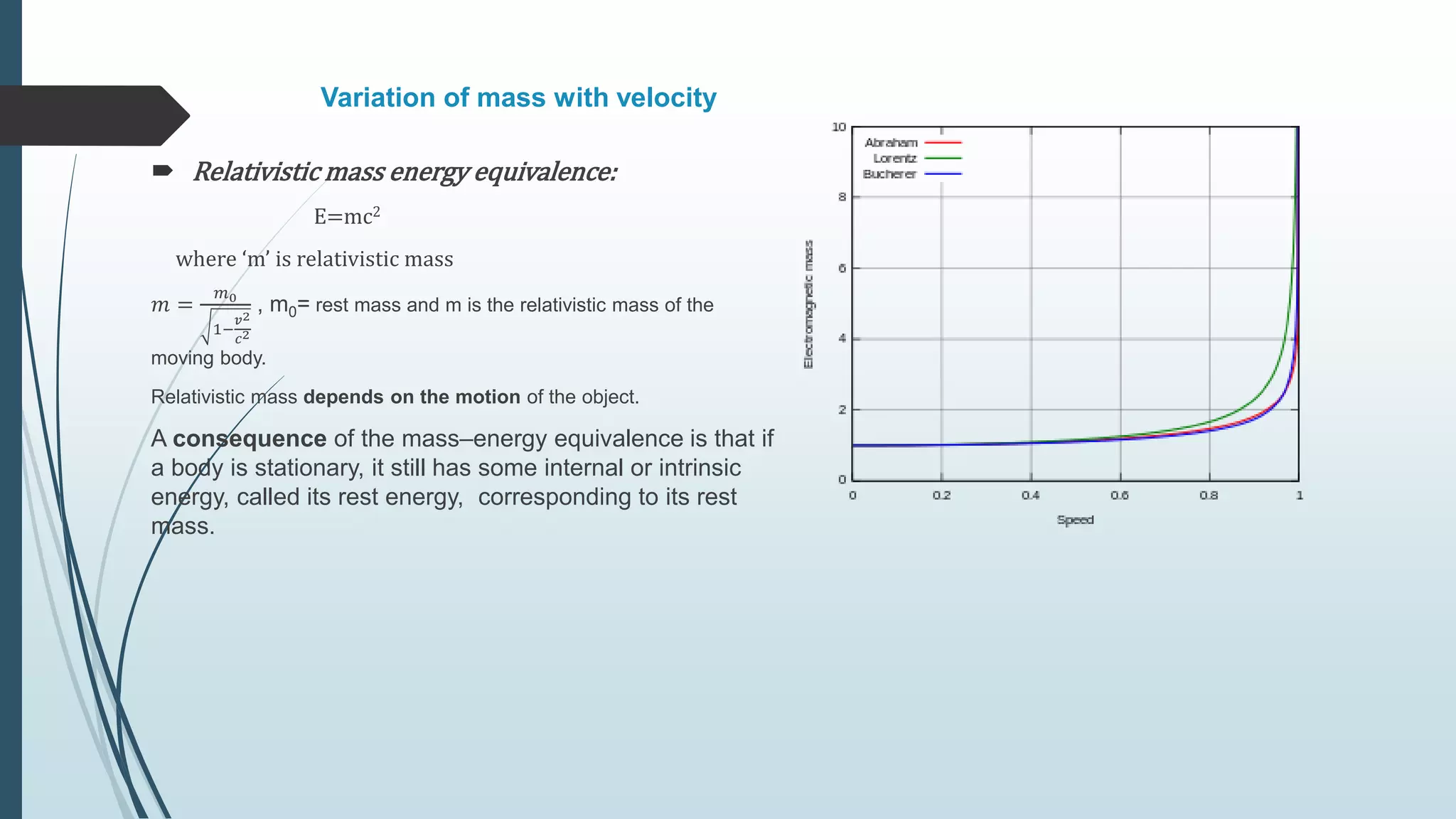
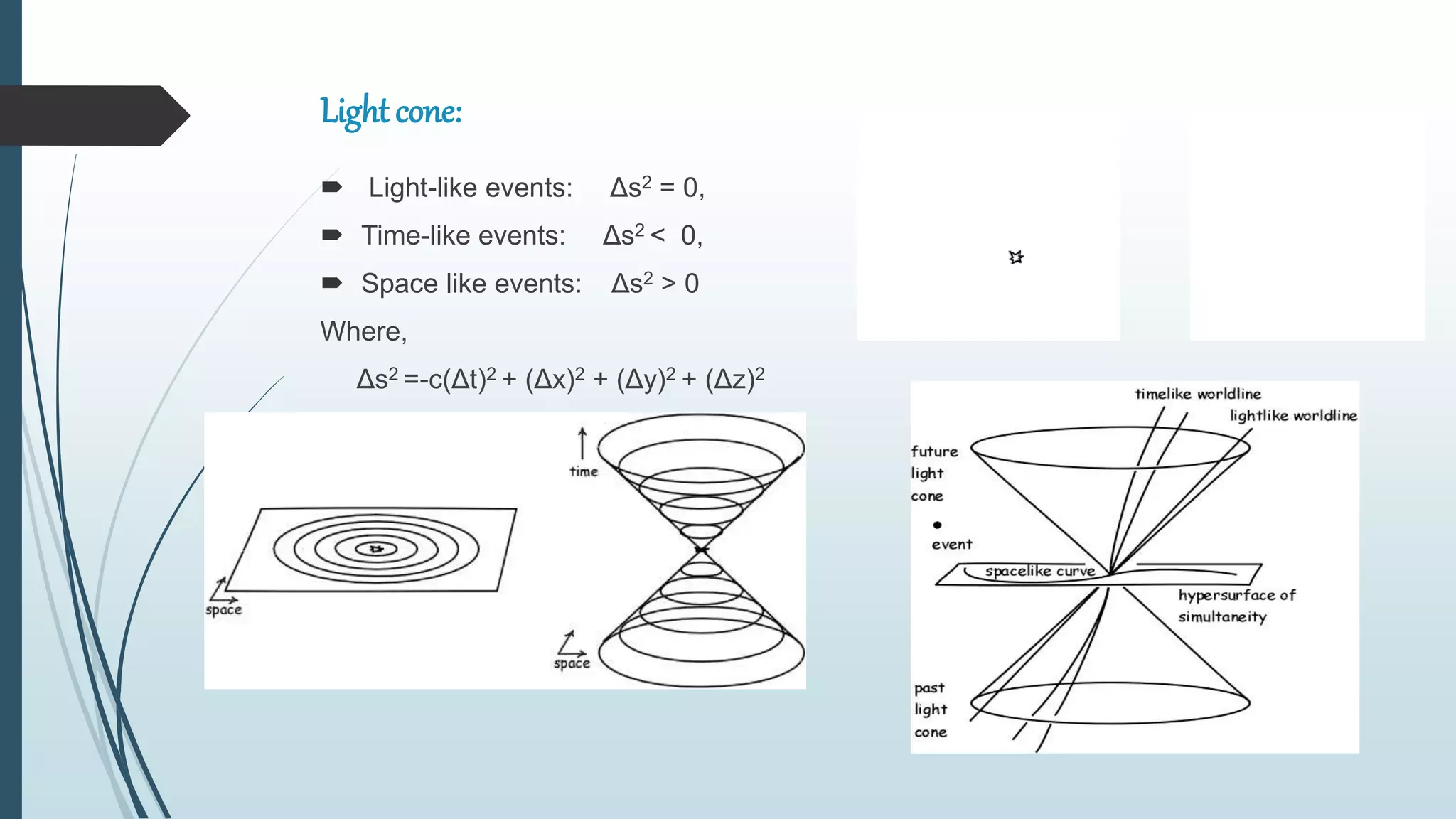
This document summarizes key concepts from Einstein's special and general theories of relativity presented in a seminar. It discusses that all physical laws are independent of reference frame and the speed of light is constant. It also covers time dilation, length contraction, relativity of simultaneity, and the twin paradox from special relativity. For general relativity, it describes gravity as the warping of spacetime, the equivalence principle, gravitational time dilation, bending of light by gravity, gravitational redshift, black holes, and experimental tests supporting the theories.