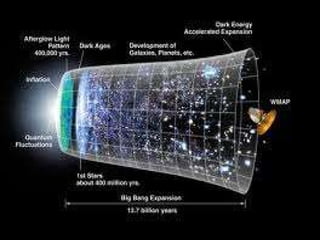
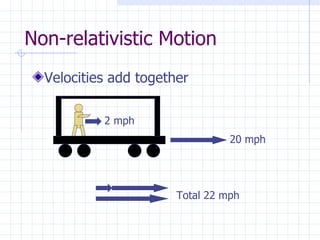
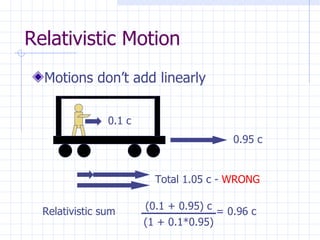
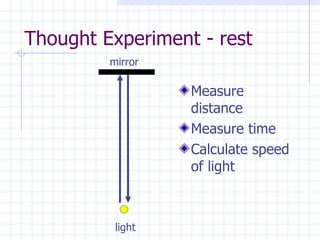
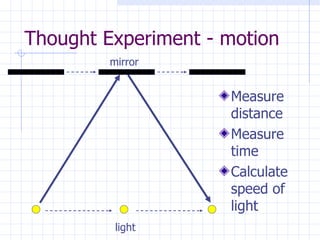
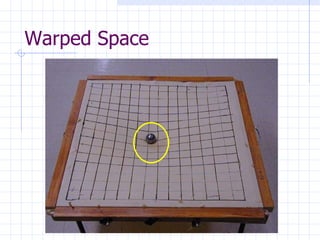
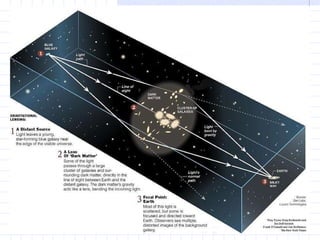
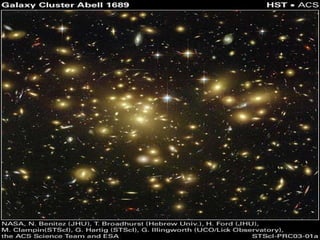
The document discusses how space and time can be warped based on one's frame of reference and motion. It introduces concepts from special and general relativity such as length contraction, time dilation, gravitational time dilation, and how matter warps space-time. It explains how the expansion of space causes galaxies to appear to move away from each other, providing evidence for the Big Bang theory that the universe has expanded over billions of years from a hot, dense state.