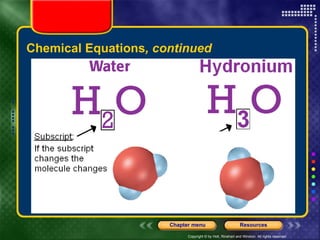
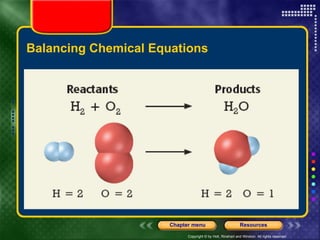
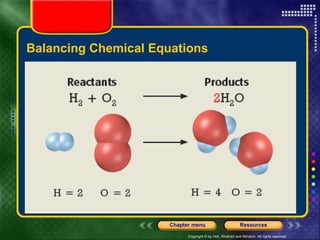
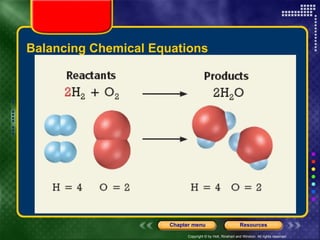
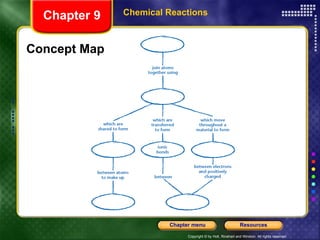
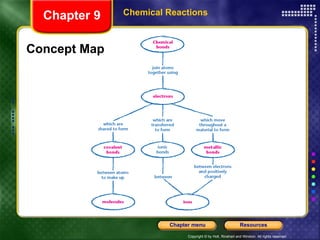
To view the presentation as a slideshow, select "View" and click "Slide Show." Click the right arrow or space bar to advance slides. Click on resources or lessons in the menus to go directly to those sections. Press Esc to exit the slideshow. The presentation covers chemical reactions, including formulas, equations, and conservation of mass. Signs of reactions and energy changes are also discussed.