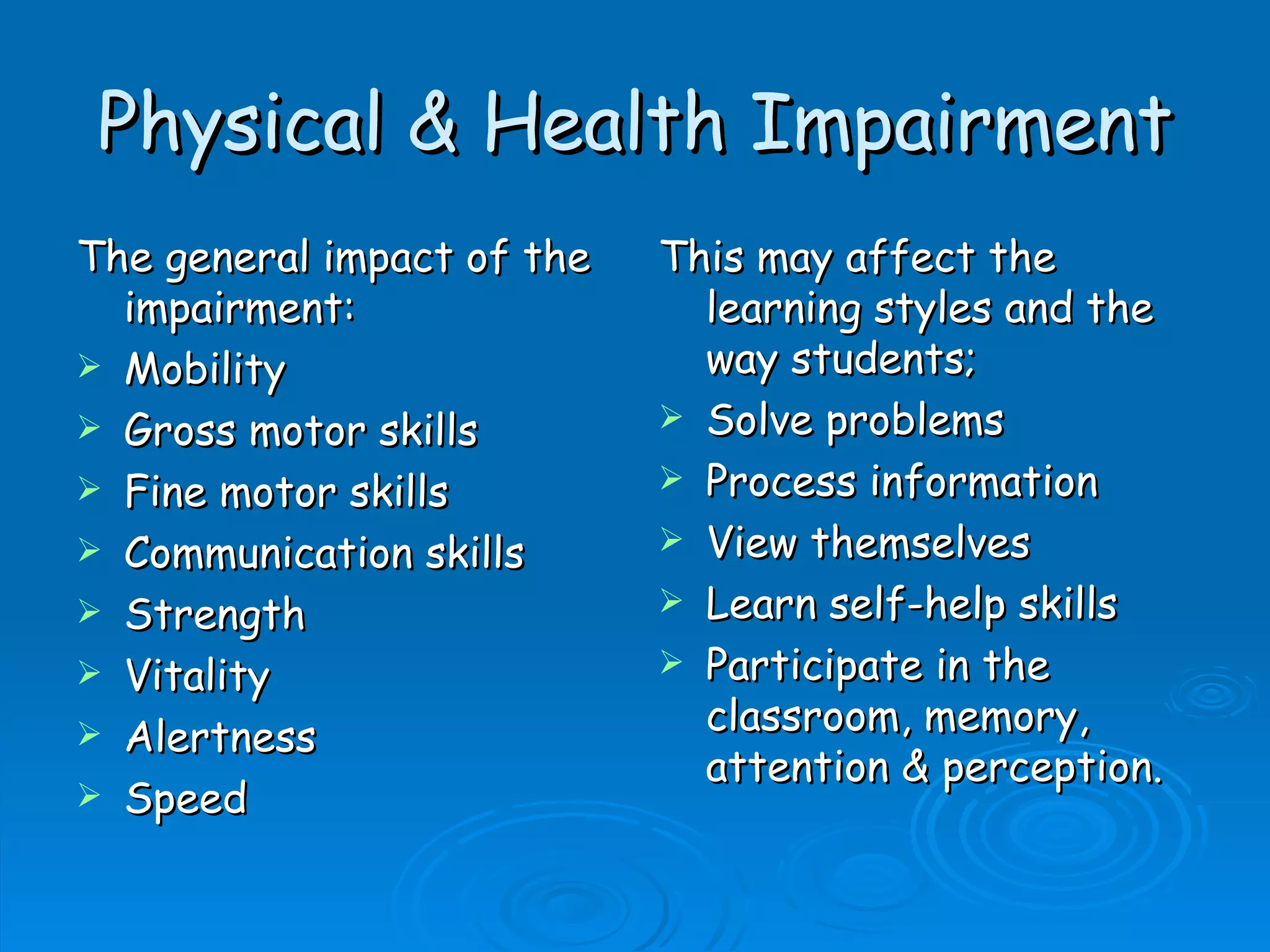
The document discusses physical disabilities and impairments, noting that there is no direct link between intelligence and severity of physical limitations. It aims to alter environments so children with physical disabilities can function. Having a physical impairment alone does not require special education placement; environmental and functional demands determine handicaps. The document outlines categories of physical disabilities including orthopedic, neurological, musculoskeletal and other health impairments. It discusses assessing students' abilities and needs, curriculum considerations, educational programming and potential IEP goals for students with physical or health impairments.