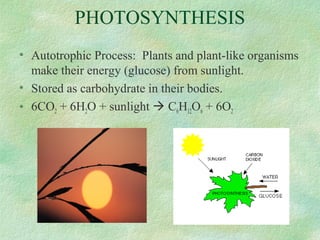
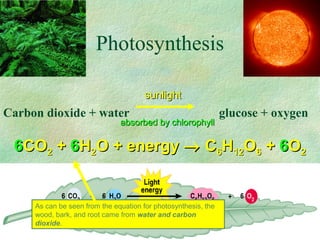
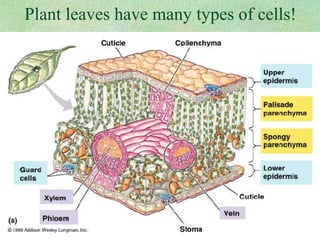
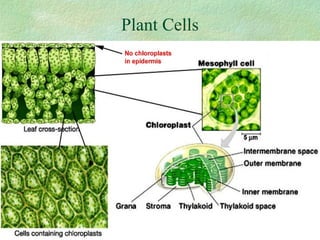
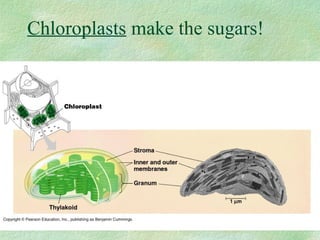
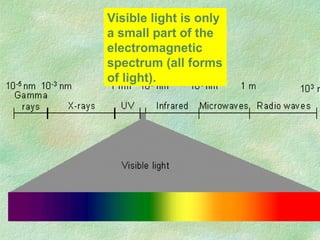
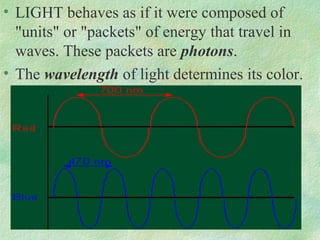
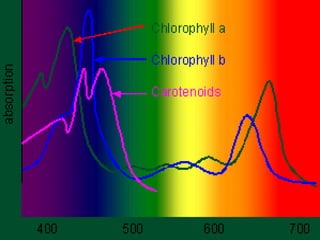
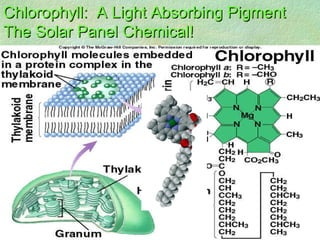
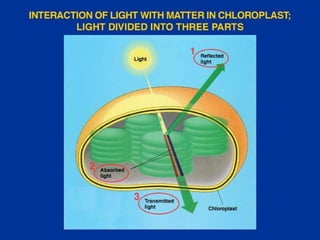
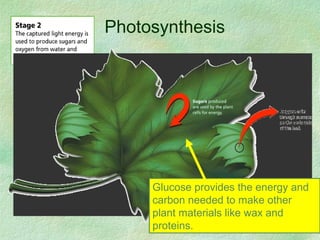
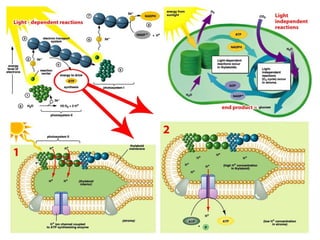
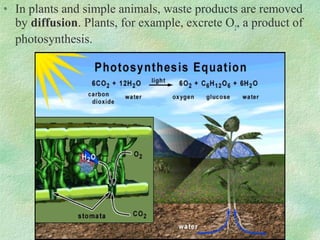
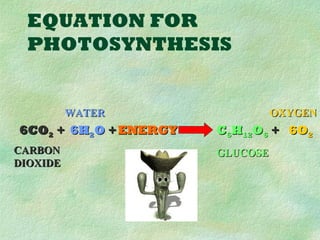
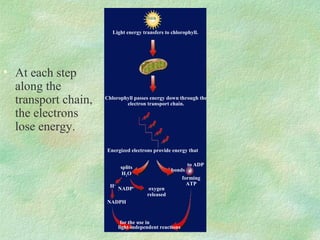
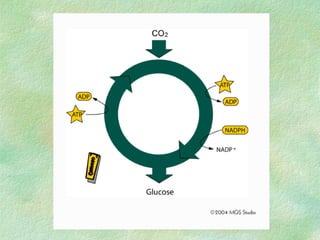
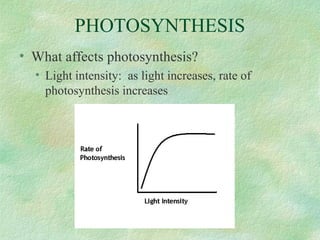
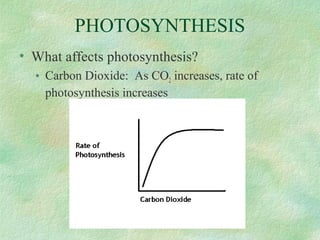
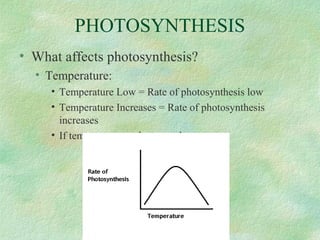
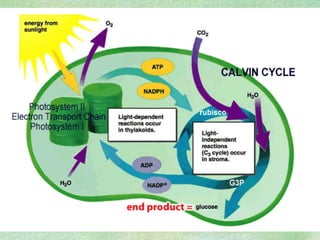
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in two phases - the light-dependent reaction that converts solar energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent reaction that uses this chemical energy to fix carbon and produce glucose. Photosynthesis is essential for all life as it produces the oxygen and food/energy upon which all organisms ultimately depend.