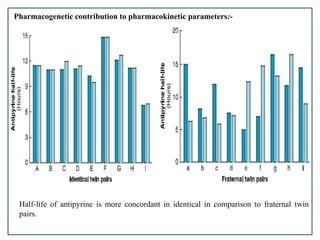
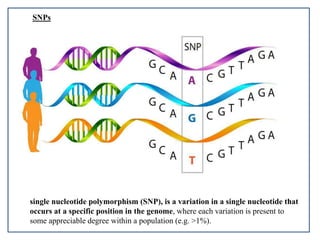
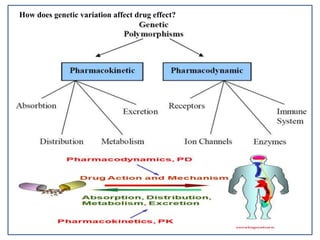
Pharmacogenetics is the study of genetic basis of variation in drug response. It aims to maximize drug efficacy and minimize toxicity. Genetic and exogenous factors contribute to differences in how individuals respond to drugs. Pharmacogenetics can help identify patient subgroups likely to respond to a drug, which aids drug development and allows for customized prescriptions to improve outcomes. It offers advantages like predicting responses, reducing adverse events, and improving rational drug design.