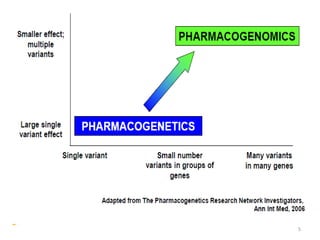
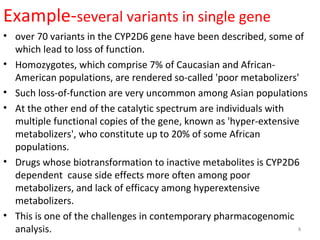
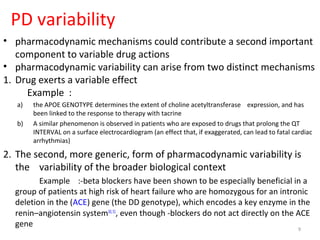
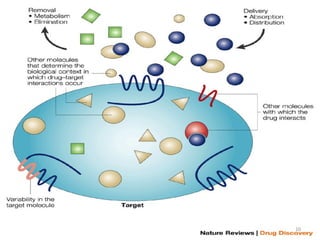
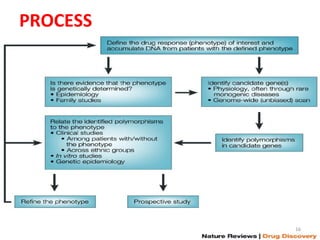
This document provides an introduction to pharmacogenomics. It defines pharmacogenomics as the study of how genetic variations affect drug response and metabolism. It discusses key concepts like interracial and individual variability in drug metabolism due to single nucleotide polymorphisms and variable number tandem repeats. Case studies on tamoxifen metabolism and alcohol metabolism are presented. Challenges to implementing pharmacogenomics in clinical practice are noted. Applications to drug development and personalized medicine are mentioned.