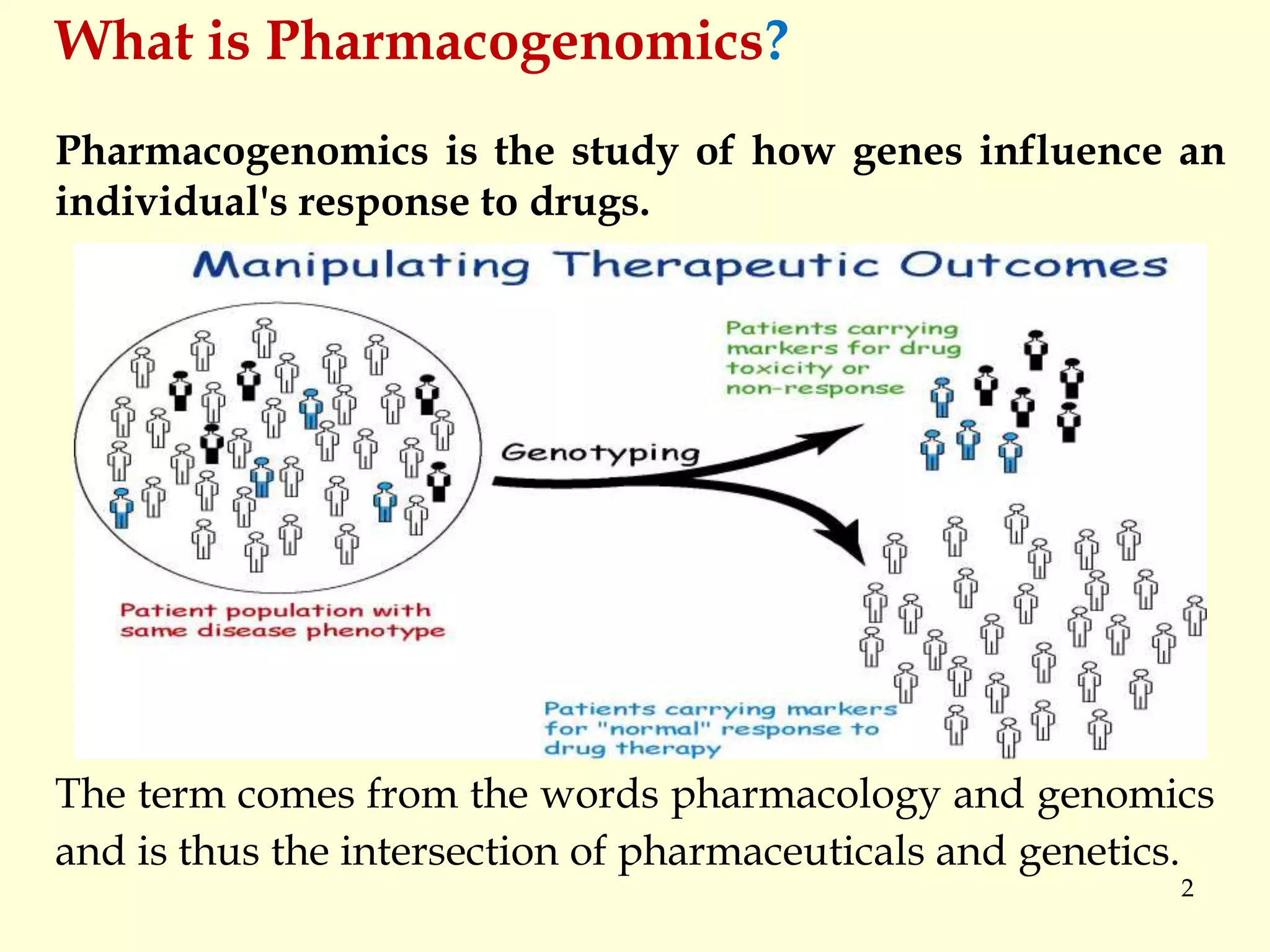
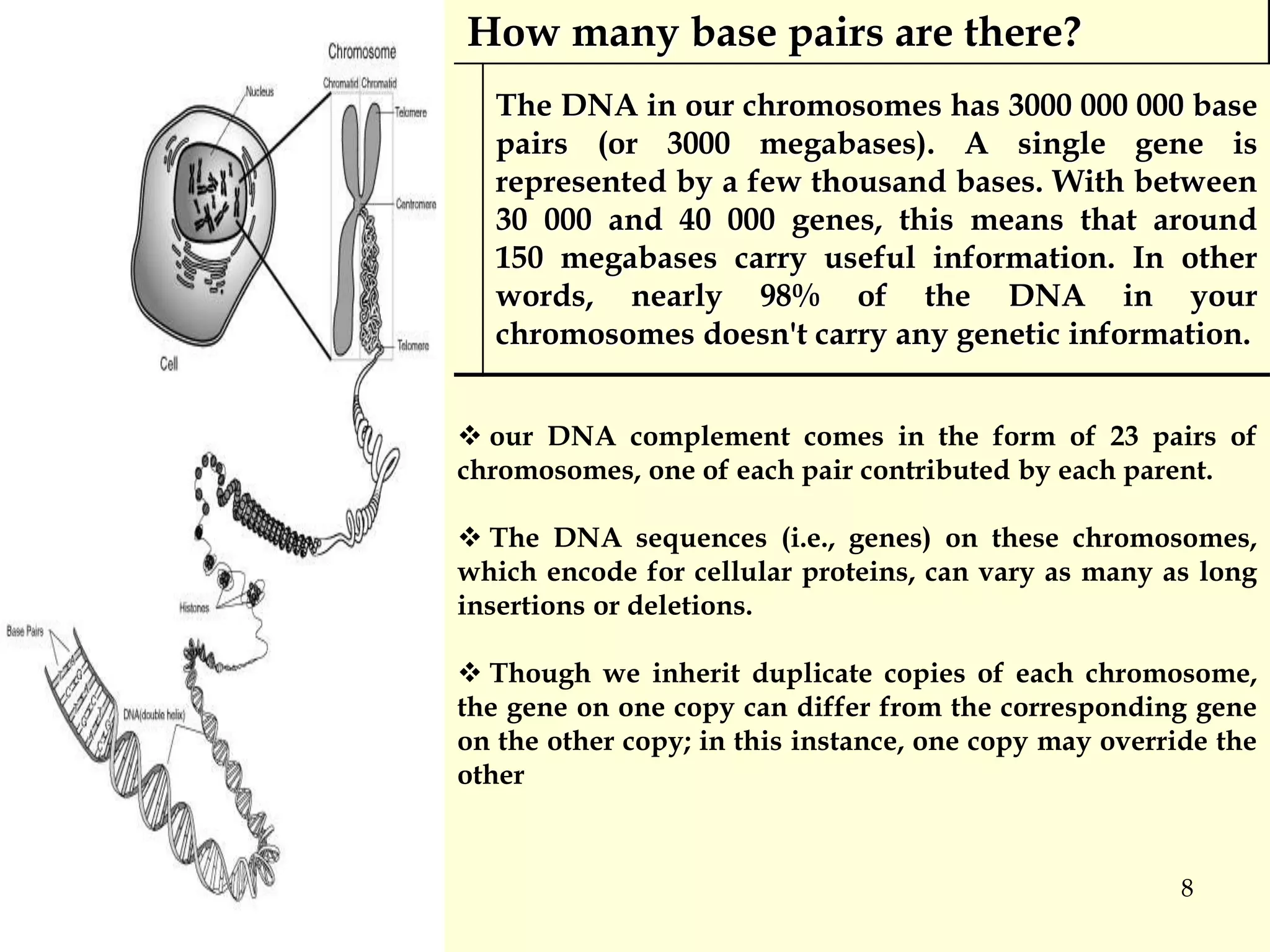
This document summarizes a seminar on pharmacogenomics presented by Mr. Madhan Mohan Elsani. Pharmacogenomics is the study of how genes influence individual responses to drugs. Understanding genetic variations between individuals can help explain differences in drug efficacy and risk of adverse reactions. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are variations in DNA sequences that can impact how the body processes and metabolizes drugs. Pharmacogenomic testing can help optimize drug selection and dosing for individual patients based on their genetic makeup. This could improve drug safety and reduce adverse reactions.