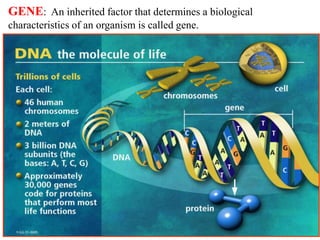
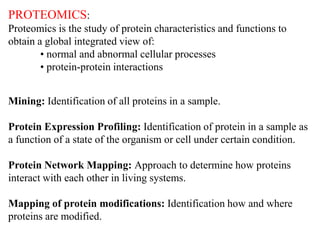
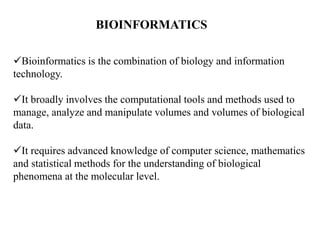
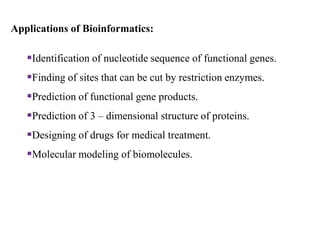
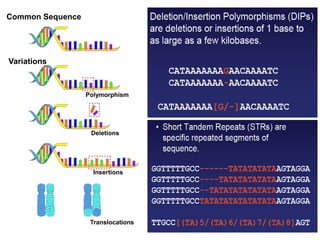
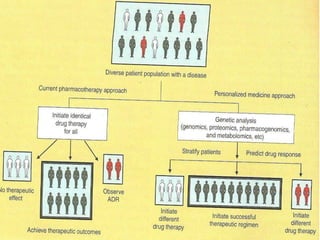
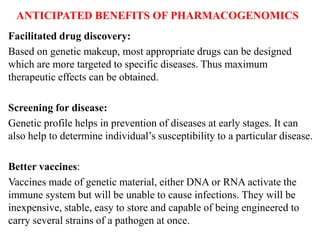
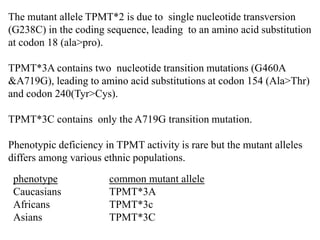
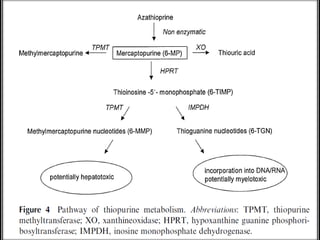
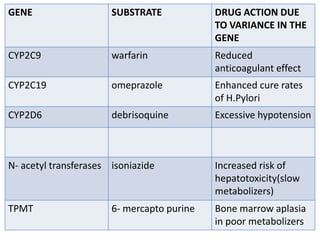
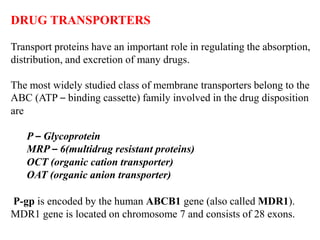
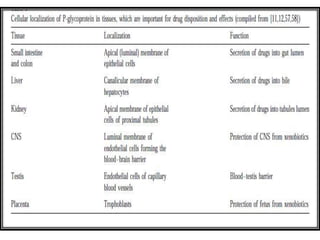
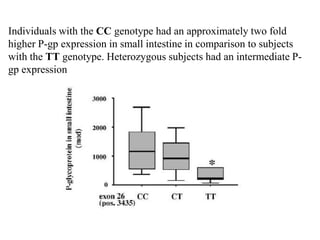
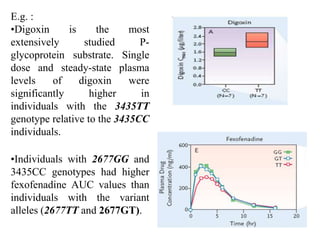
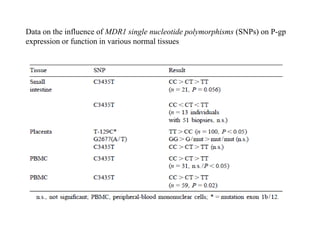
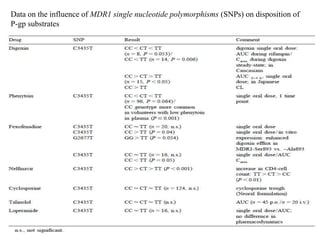
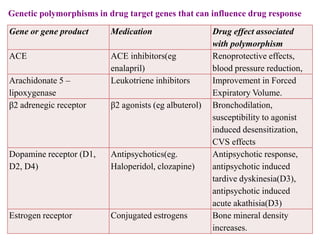
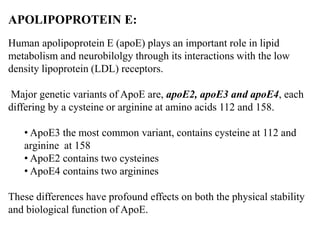
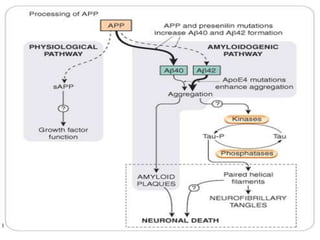
This document discusses genomics, proteomics, bioinformatics, pharmacogenomics, and the human genome project. It provides information on how genetic polymorphisms can influence drug disposition by affecting metabolizing enzymes and transporters. The human genome project mapped the entire human genome sequence to further the goals of personalized medicine based on an individual's genetic profile. Single nucleotide polymorphisms are particularly important for understanding how individuals respond differently to drugs.