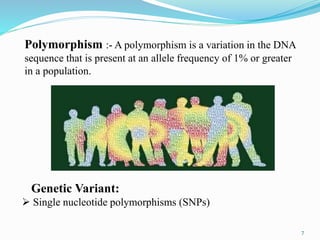
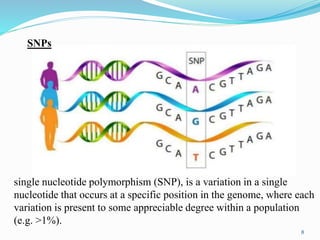
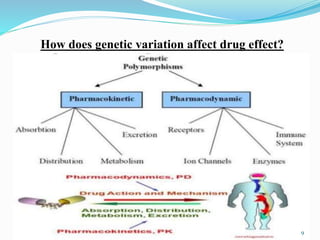
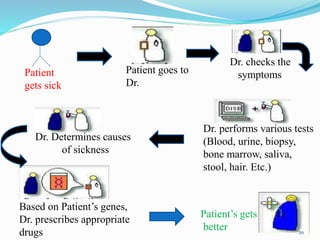
The document discusses pharmacogenetics, which is the study of how genetic factors affect individual responses to drugs. It begins by defining pharmacogenetics and explaining why it is important. Then it outlines the goals of pharmacogenetics, which include maximizing drug efficacy and minimizing toxicity. It also discusses how genetic variations like single nucleotide polymorphisms can impact how individuals metabolize and respond to certain drugs. The document notes the roles of pharmacogenetics in drug development, clinical practice, and precision medicine. It concludes by stating that pharmacogenetics has potential to optimize drug therapy and enable more personalized treatment approaches.