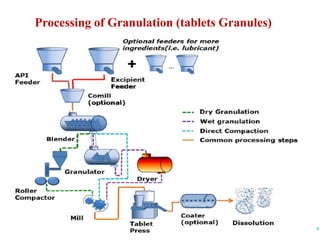
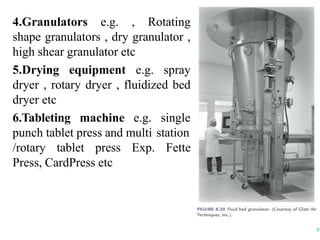
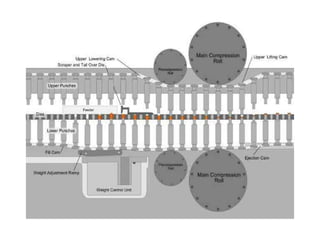
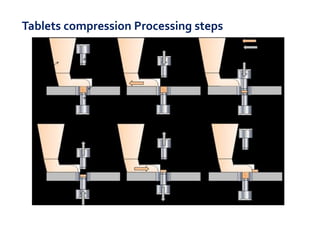
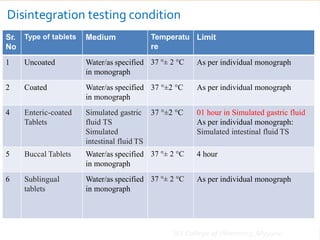
This document discusses the process of manufacturing tablets. It begins by defining tablets and outlining the main steps in tablet formation, which include weighing, milling, mixing, granulation, drying, compression, coating and packaging. It then describes the goals and categories of tablets and provides more detail on specific unit operations like granulation processing, compression, and evaluation methods. The document also lists common equipment used in each step and discusses packaging and storage considerations. The overall manufacturing process involves accurately weighing ingredients, reducing particle size, blending powders, granulating to improve flow, compressing into tablets, optionally coating, and automated packaging.