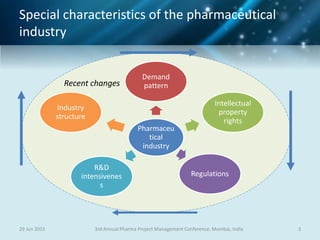
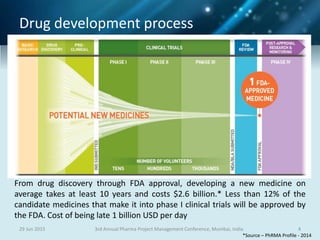
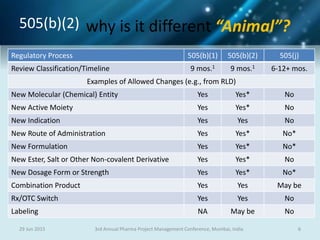
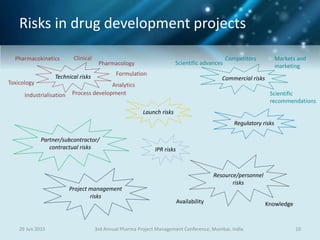
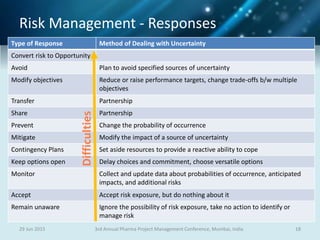
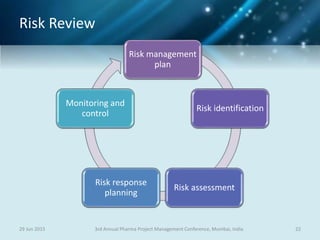
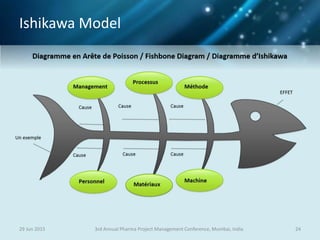
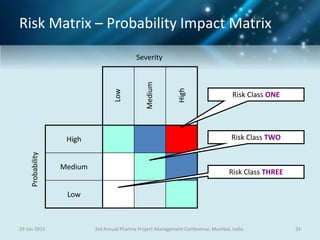
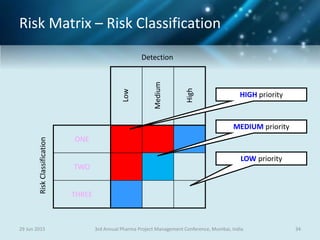
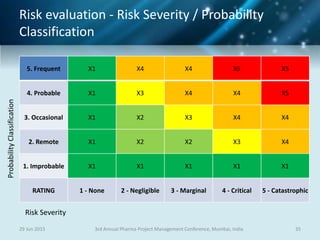
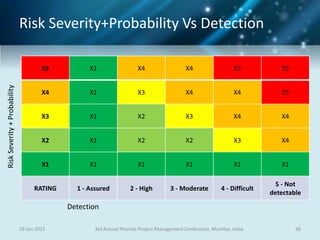
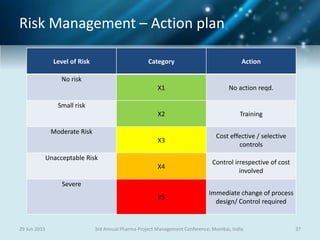
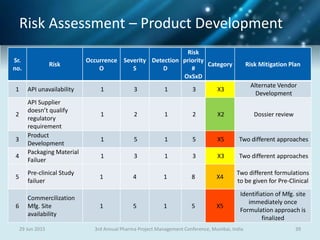
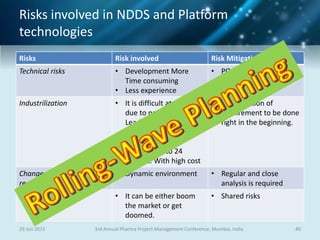
The document discusses risk management for pharmaceutical projects. It begins by outlining the characteristics of the pharmaceutical industry and drug development process. The drug development process takes an average of 10 years and $2.6 billion to develop a new drug. The presentation then covers risk management processes, tools and techniques for identifying, analyzing, and responding to risks in drug development projects. A case study on risk assessment for product development is presented to demonstrate how to evaluate risks and prioritize mitigation actions.