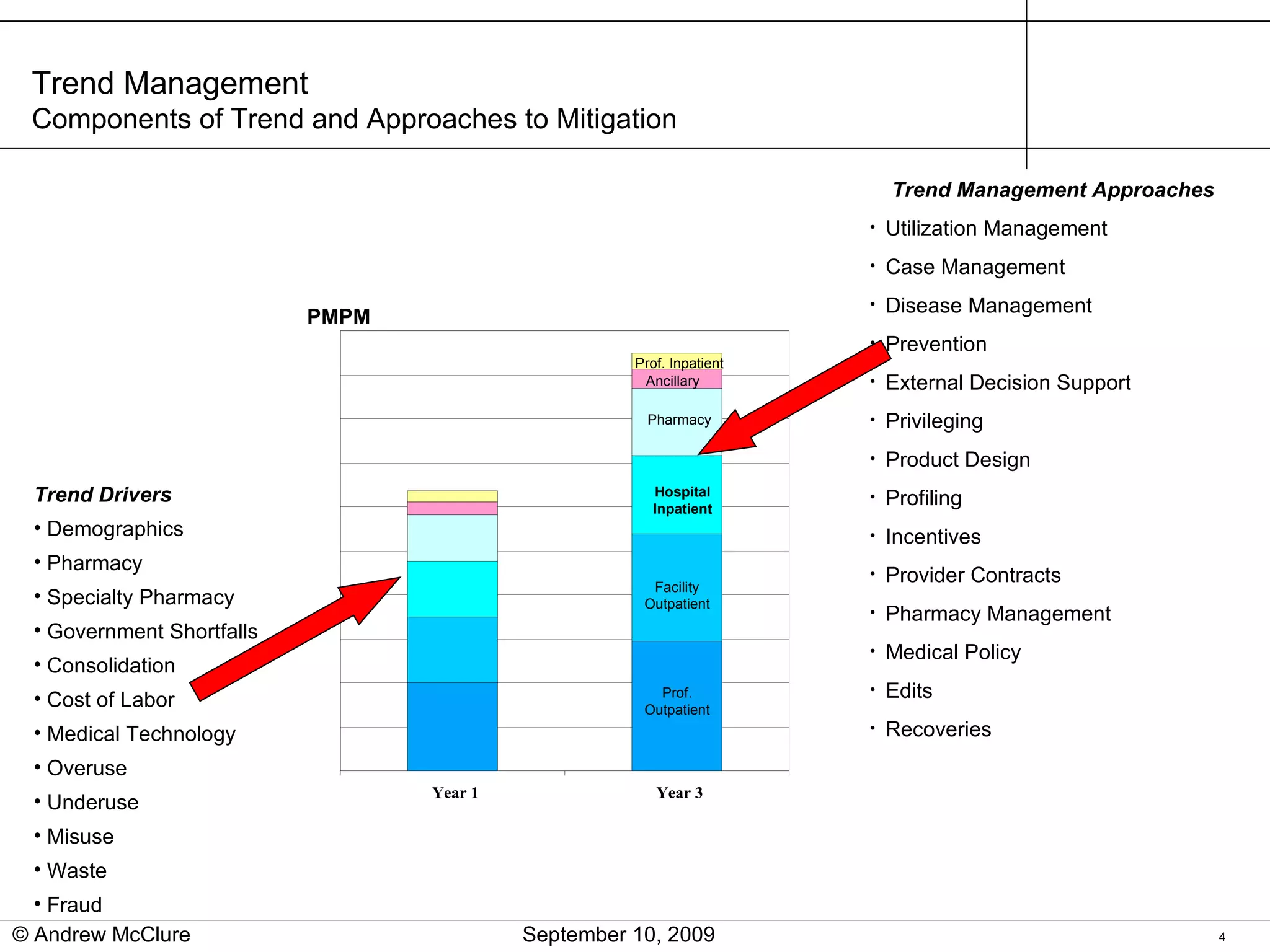
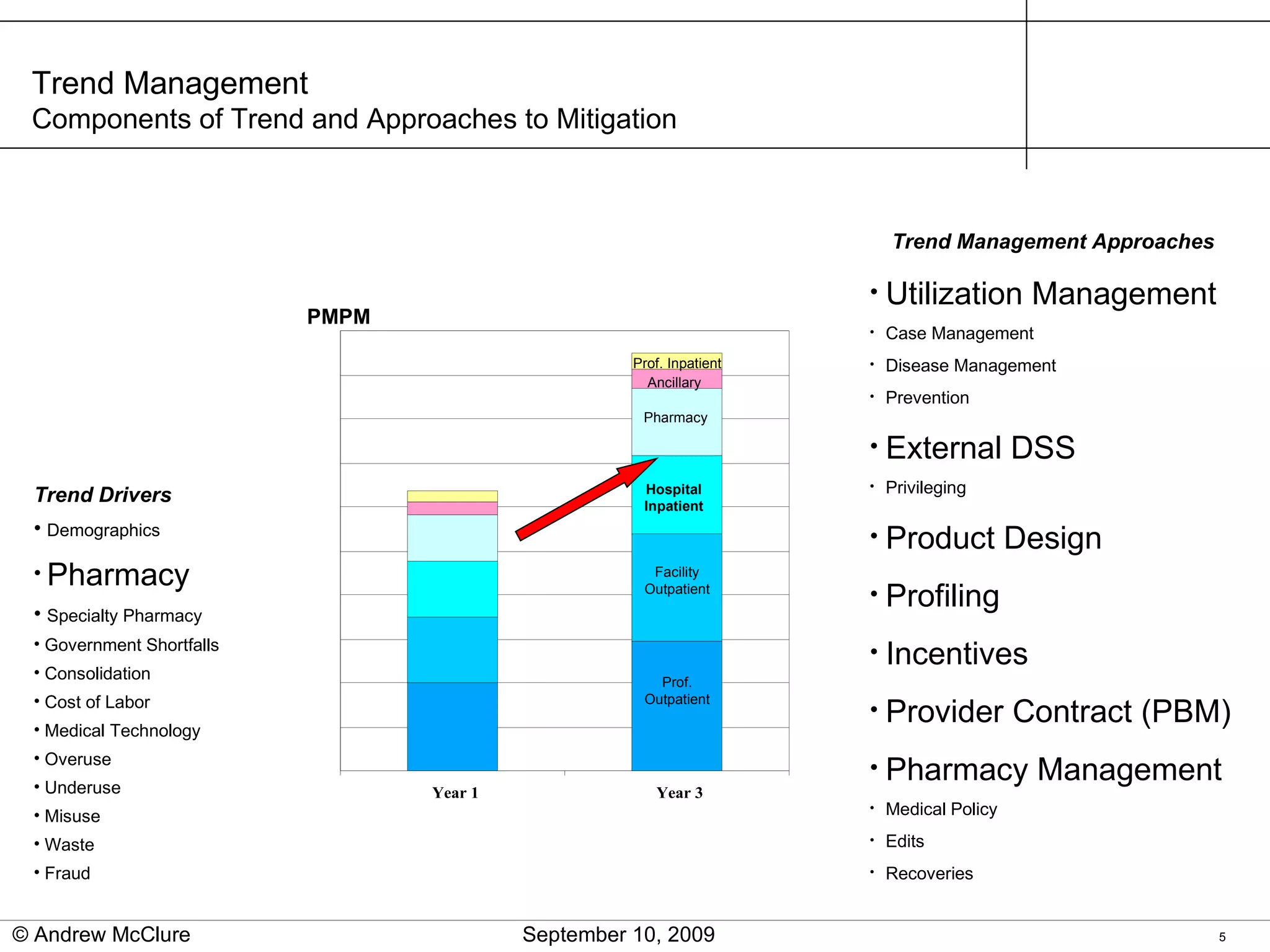
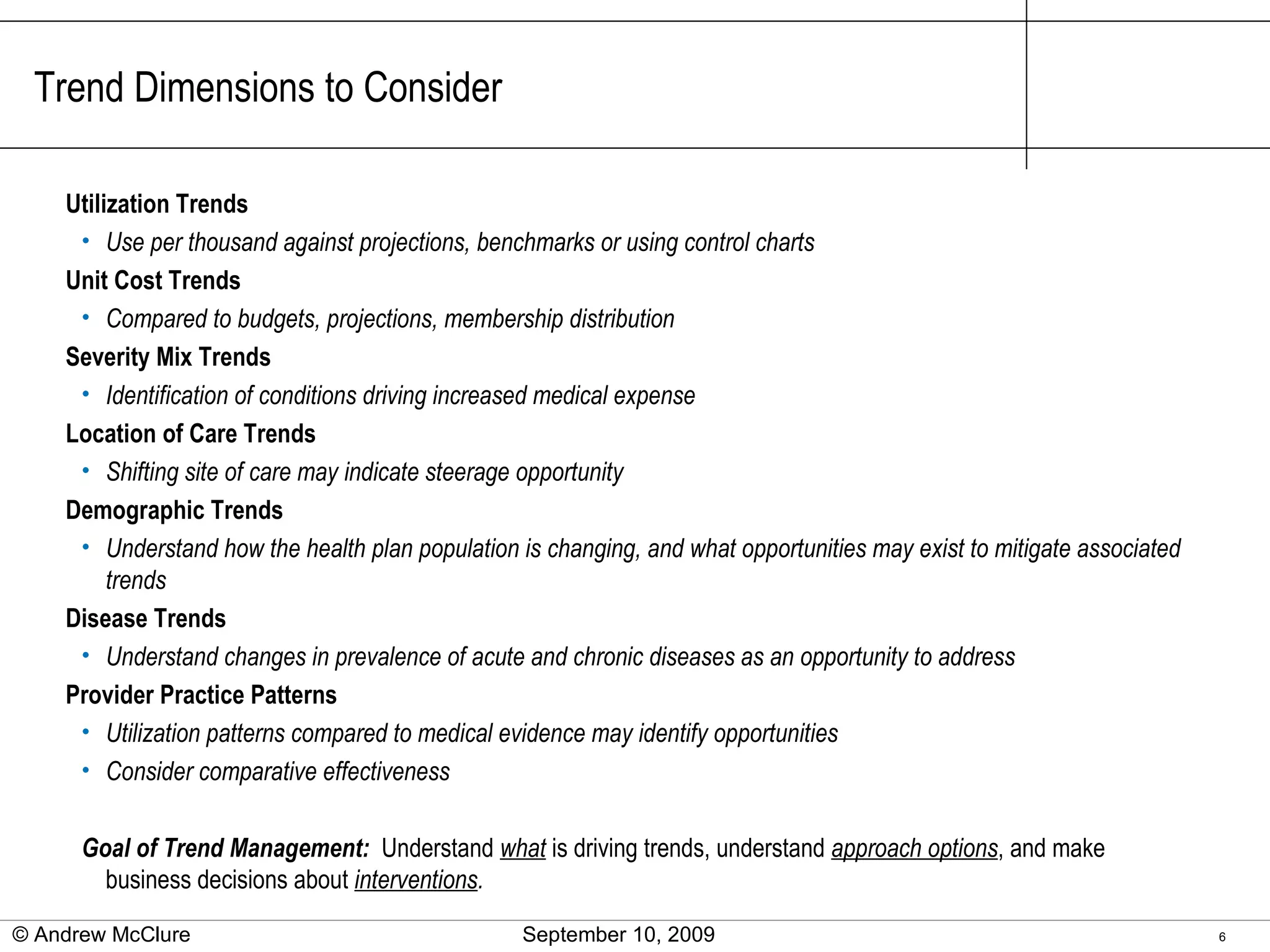
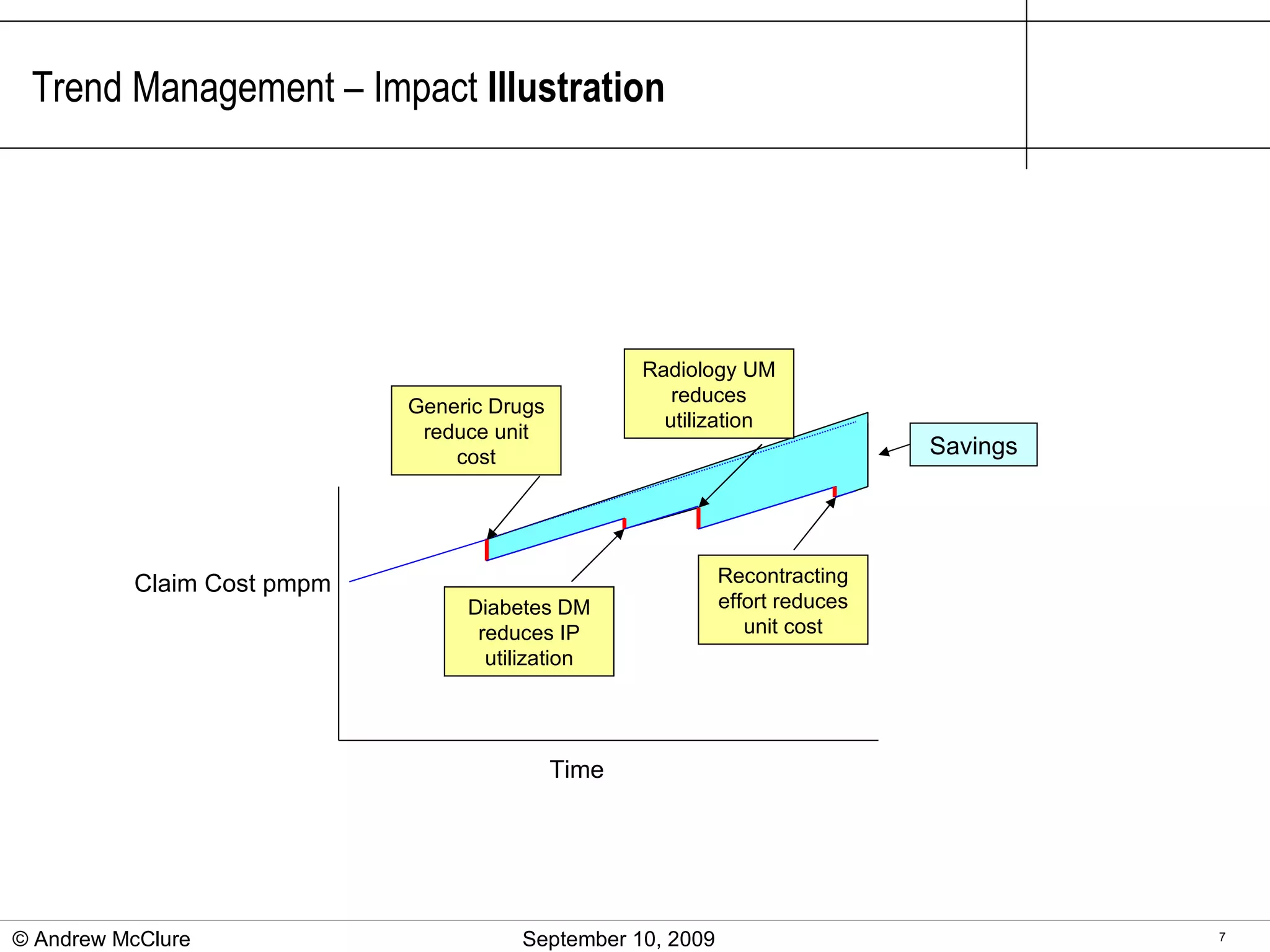
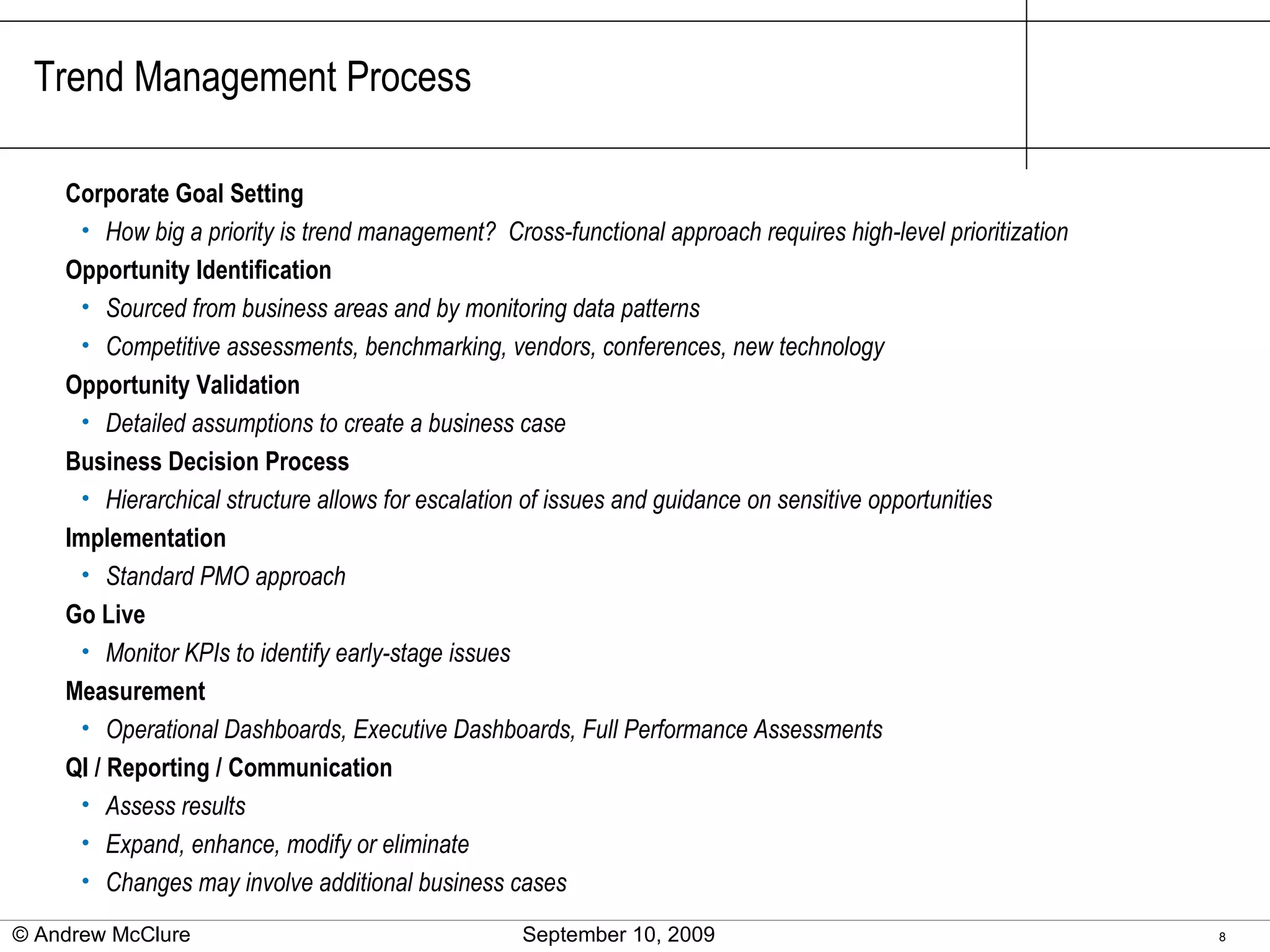
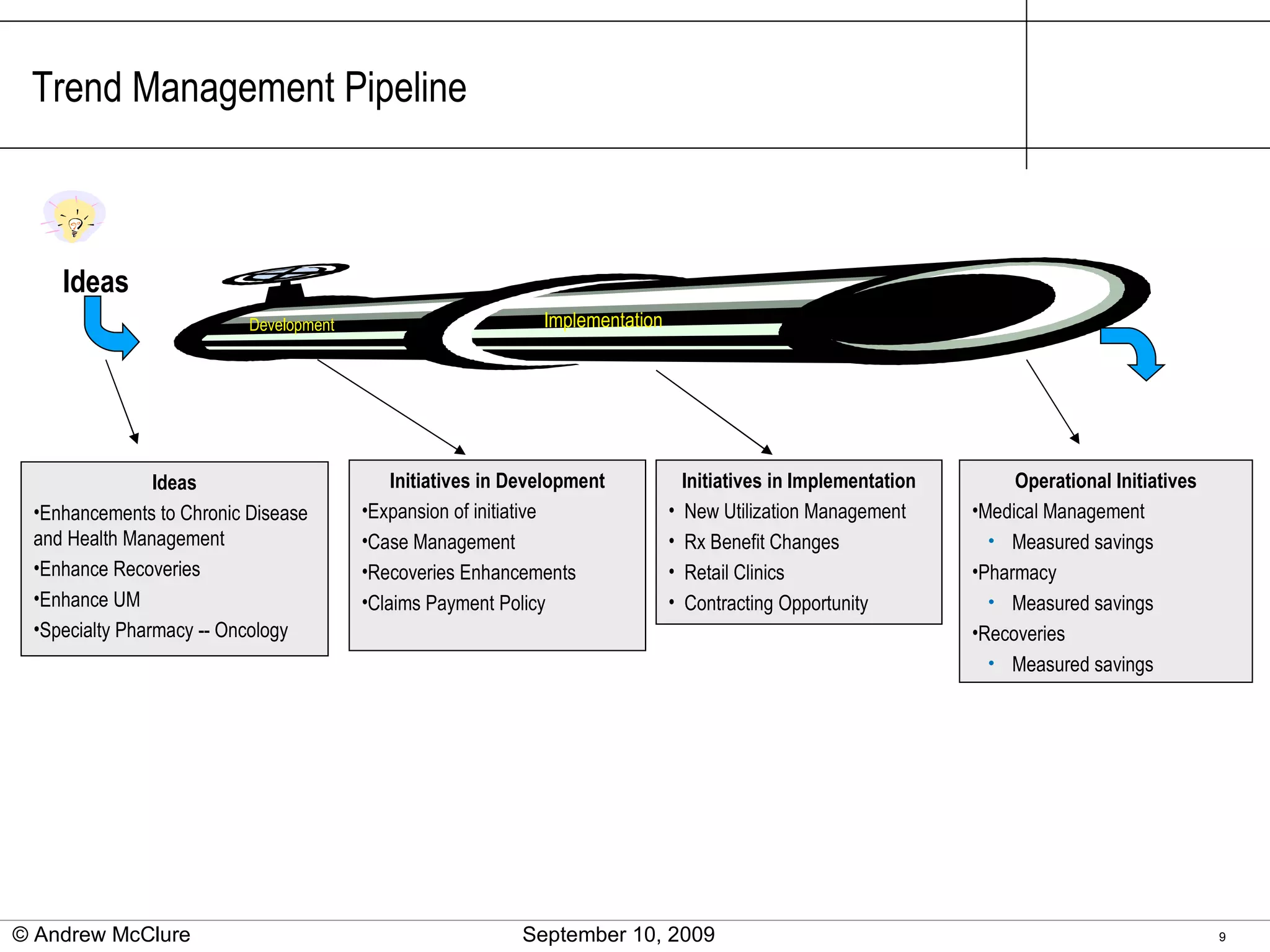
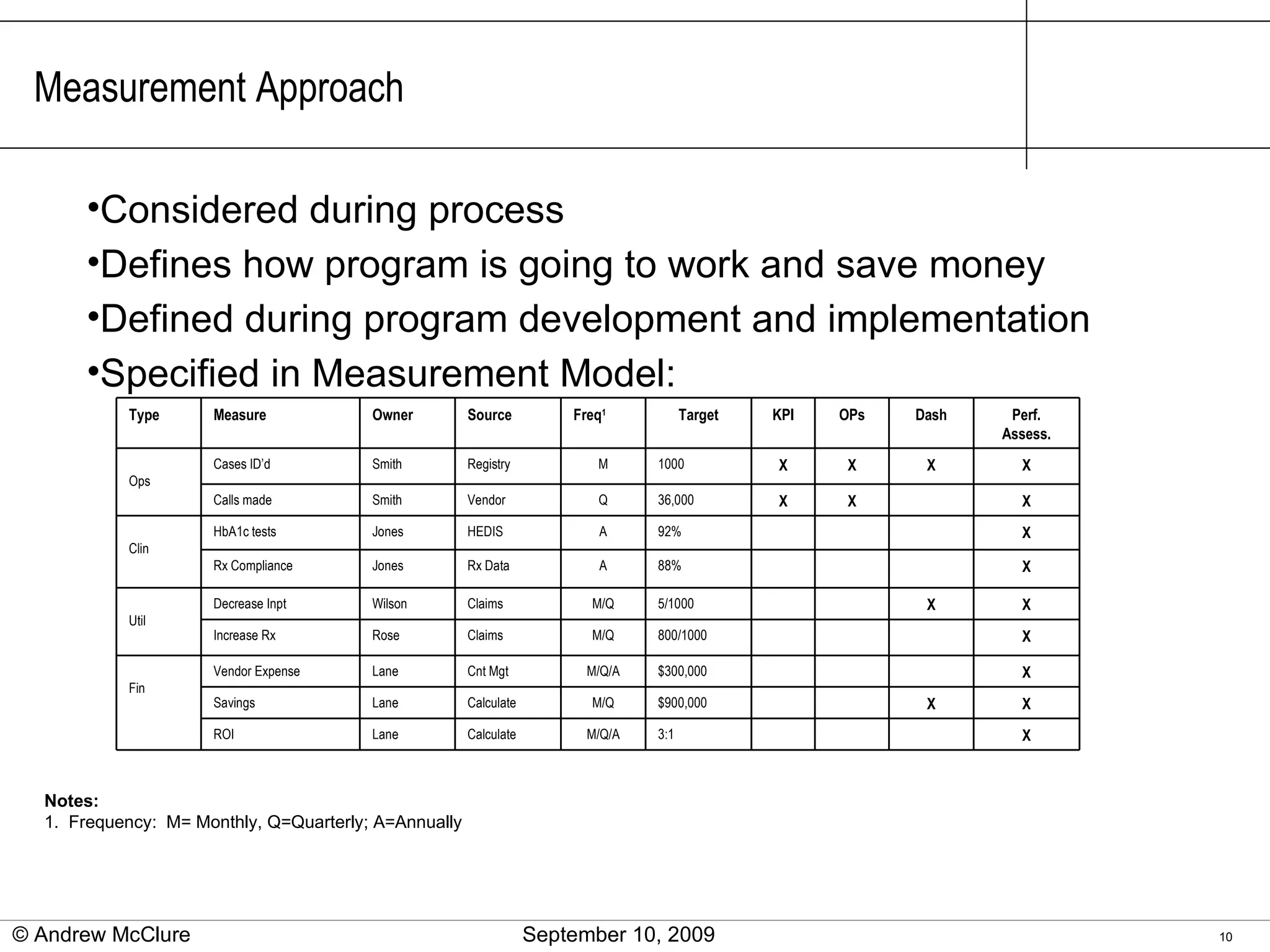
The document provides an overview of trend management methodologies, emphasizing its critical success factors and components such as utilization management, disease management, and provider contracts. It highlights the importance of understanding trend drivers, utilizing measurements to monitor progress, and having a structured approach for opportunity identification and implementation. The effective management of trends can help mitigate costs and improve healthcare outcomes by enabling informed decision-making and data-driven strategies.