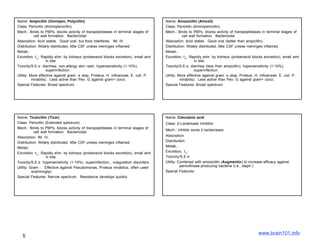
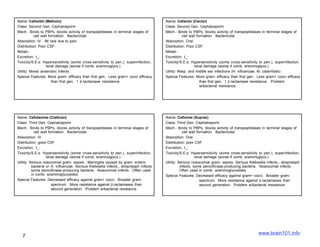
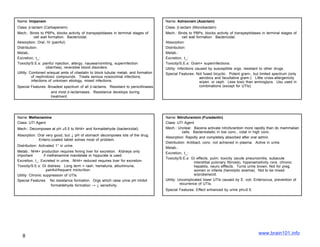
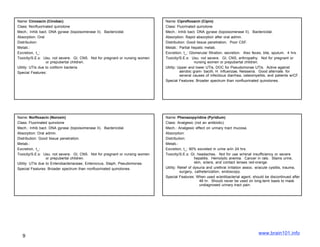
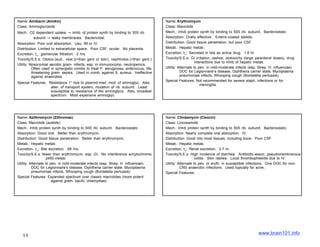
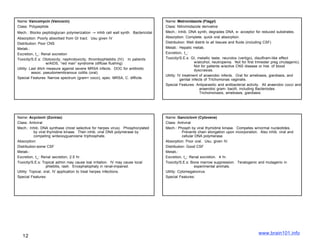
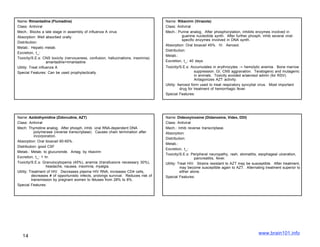
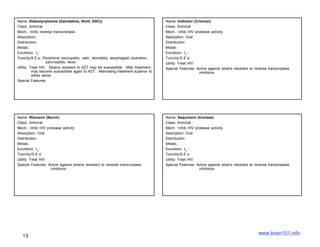
The document describes several sulfonamide antibiotics including their class, mechanism of action, absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, toxicity/side effects, and uses. Sulfonamides work by inhibiting the incorporation of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) into dihydropteric acid, thereby inhibiting folic acid synthesis and exerting a bacteriostatic effect. They are absorbed in the GI tract and distributed widely throughout the body, including crossing the placenta. Metabolism involves acetylation in the liver and excretion is primarily through renal filtration and secretion. Common side effects include hypersensitivity reactions, urinary tract disturbances, and hematopoietic disorders. Sulfonamides