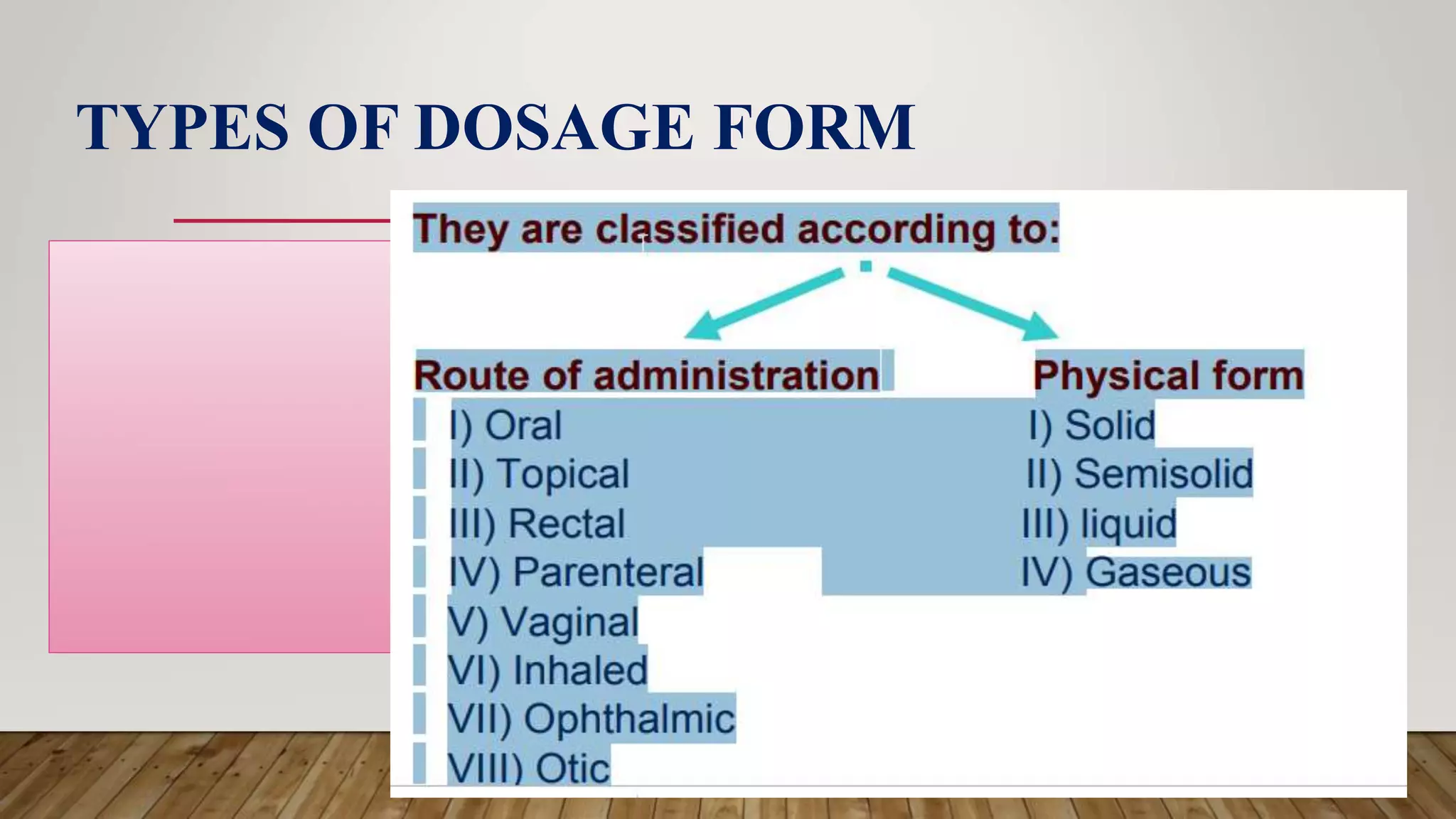
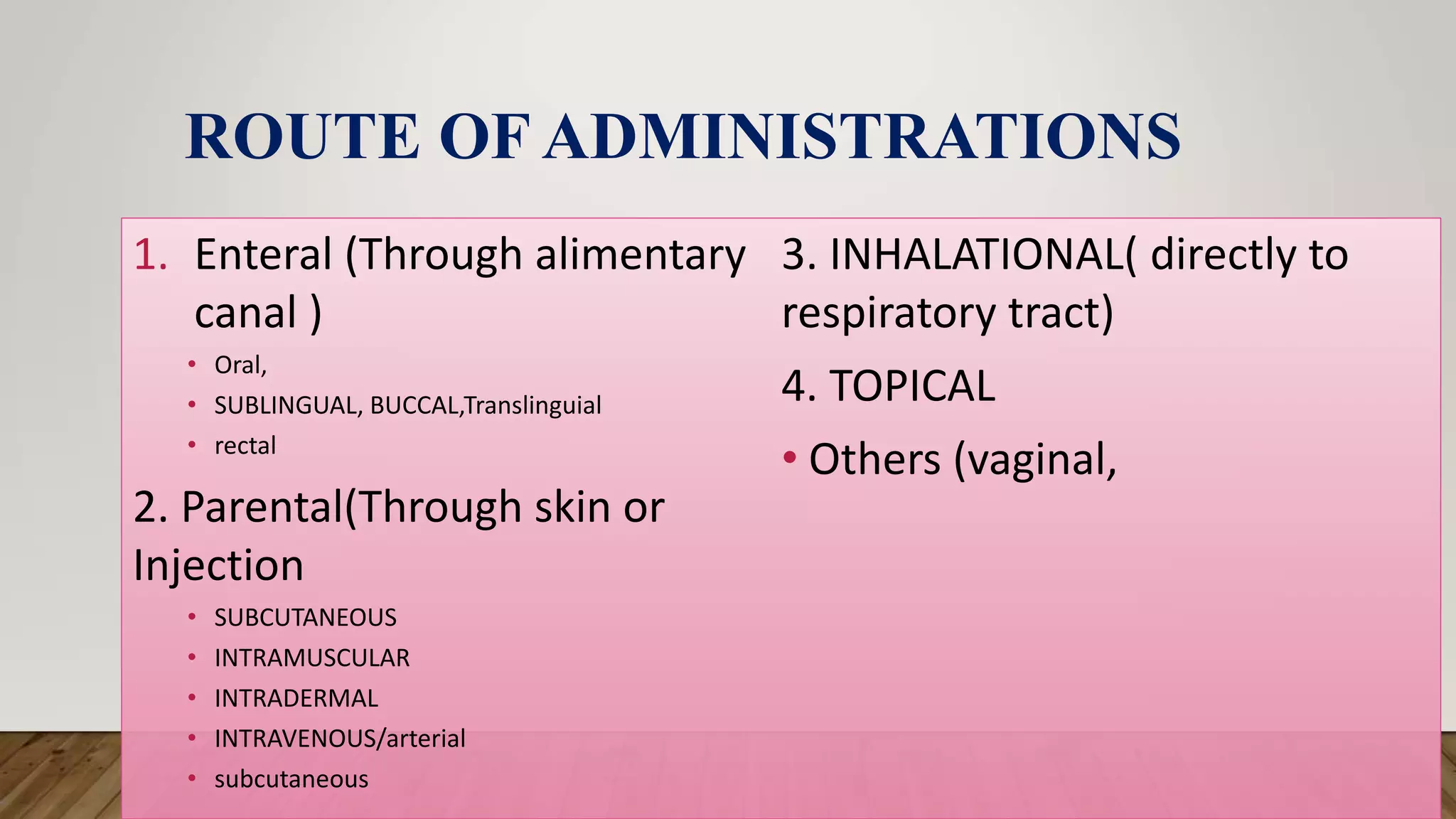
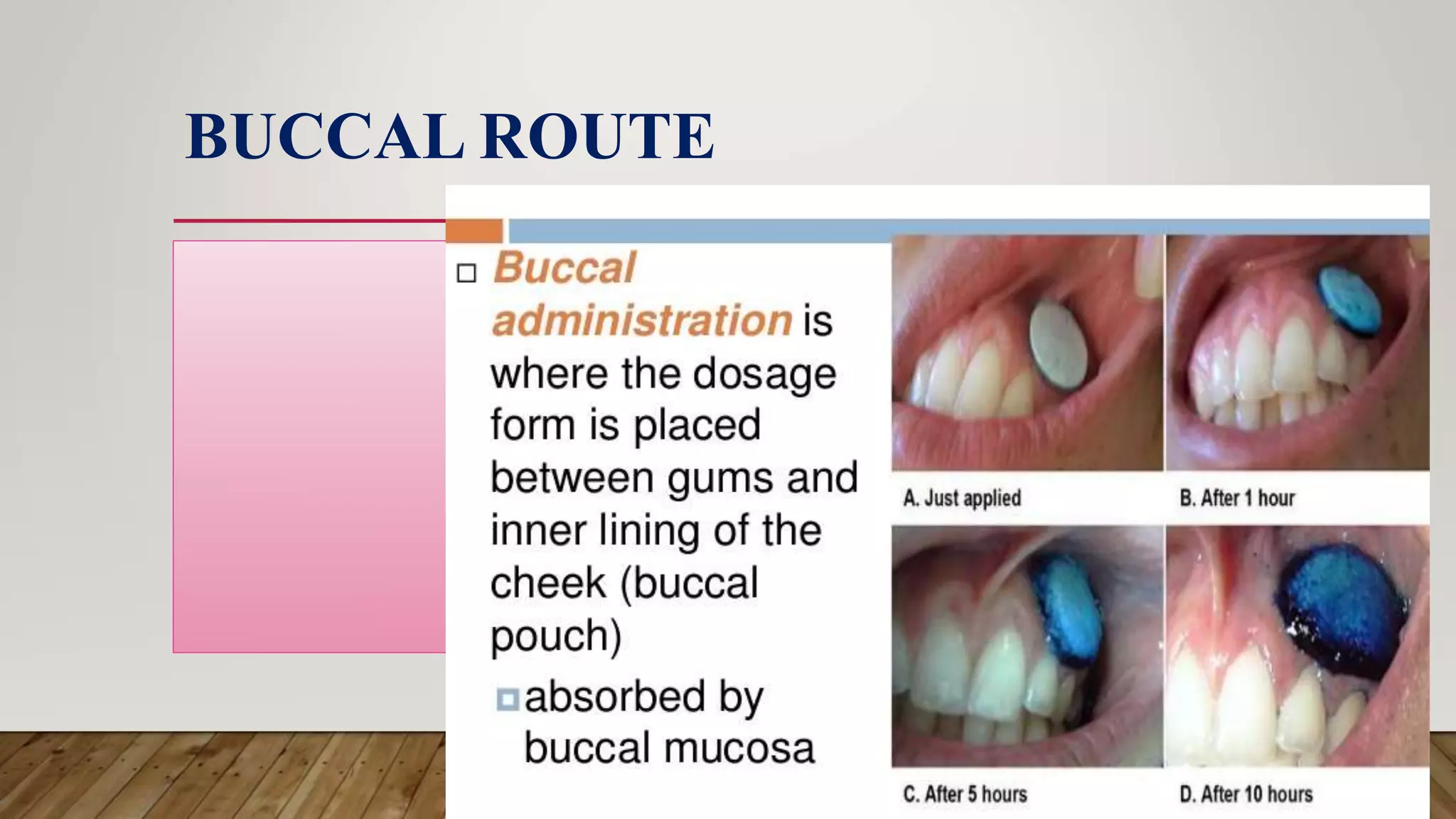
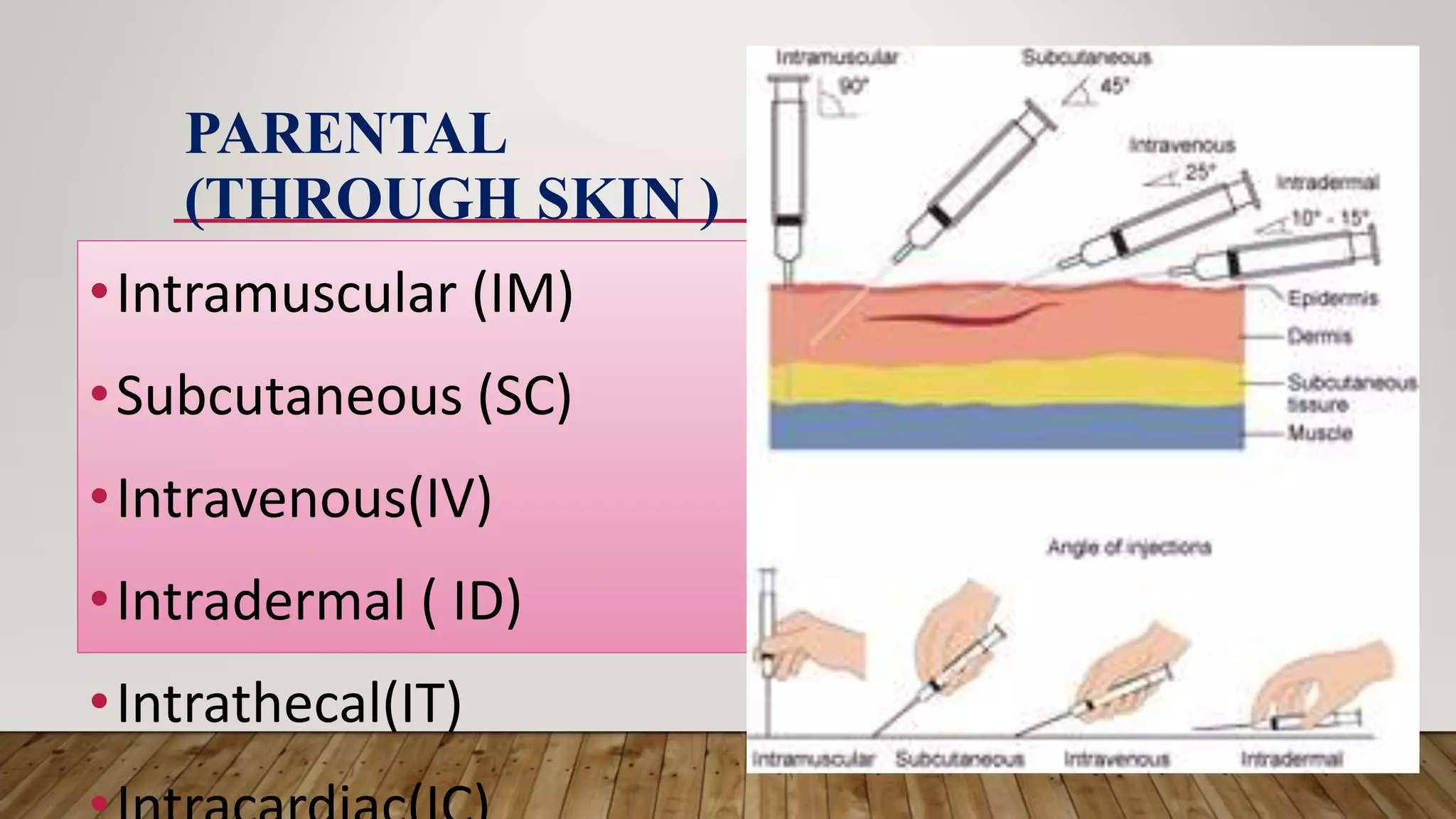
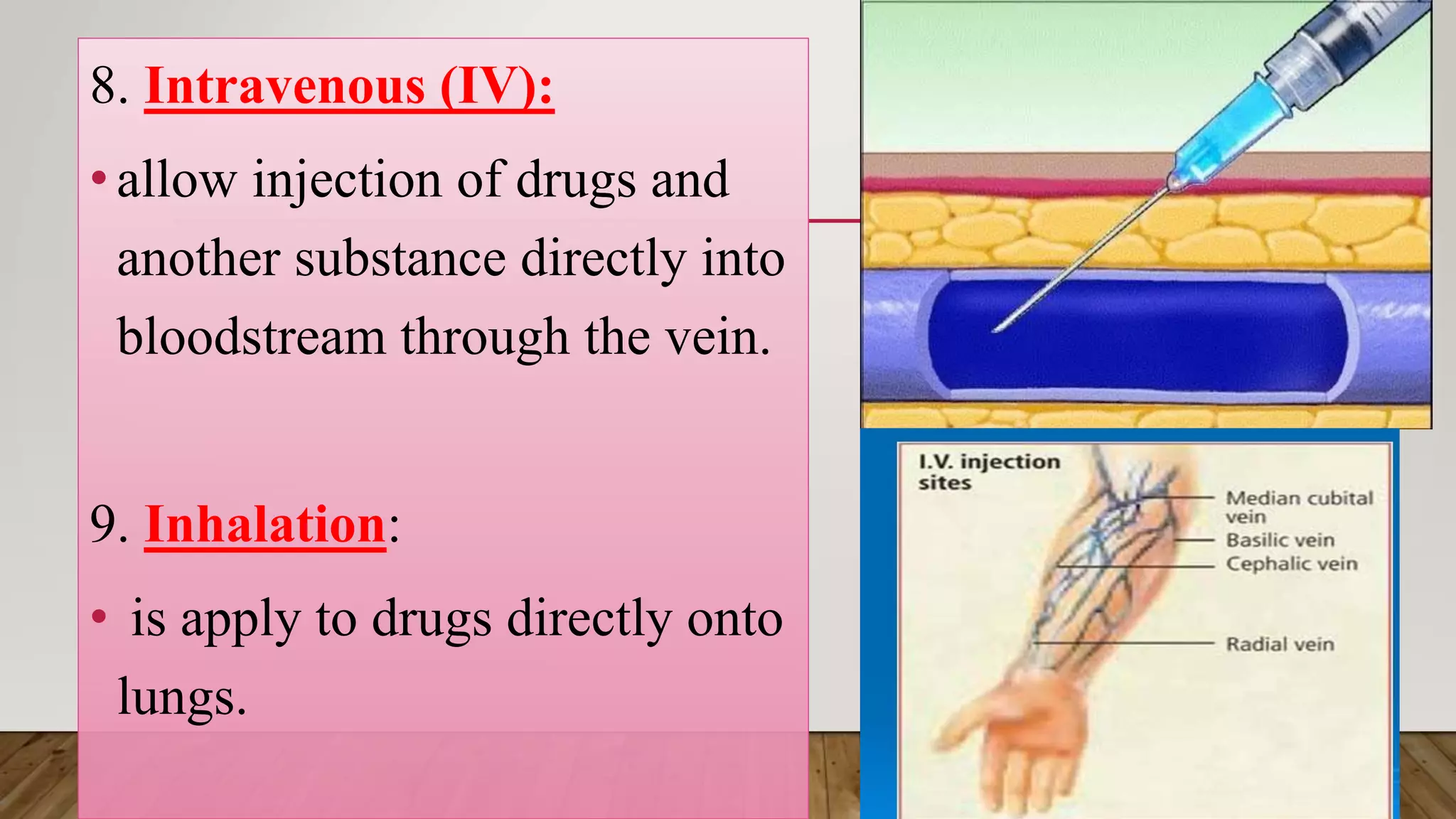
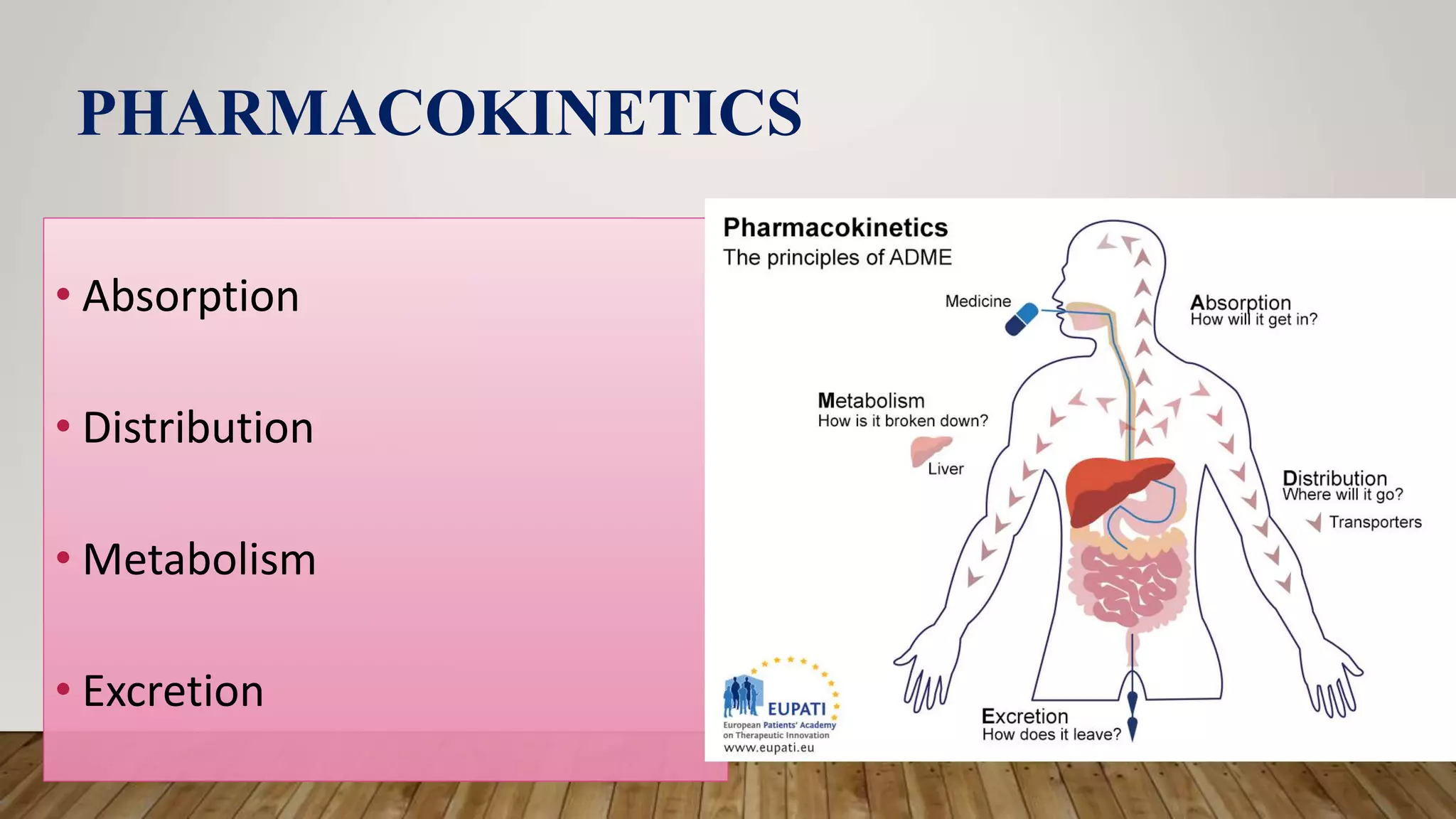
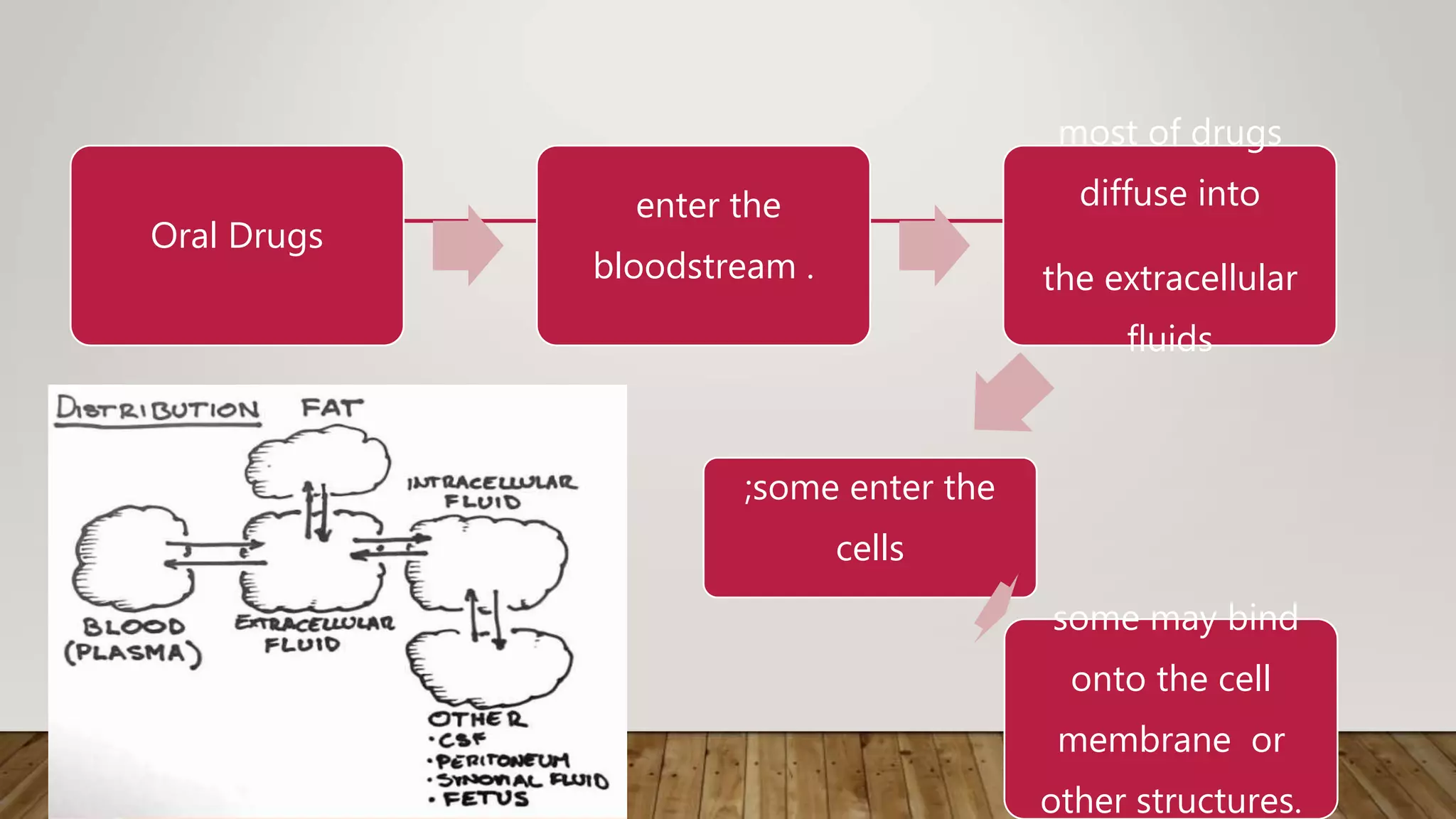
This document provides an introduction to pharmacology. It discusses key topics including branches of pharmacology such as pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacotherapeutics. Pharmacokinetics refers to what the body does to drugs and includes absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Pharmacodynamics is what drugs do to the body and how they produce their effects. Pharmacotherapeutics is the use of drugs to treat diseases. The document also covers drug terminology, sources and names of drugs, routes of drug administration, factors affecting drug response, and common pharmaceutical dosage forms.