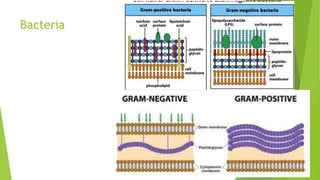
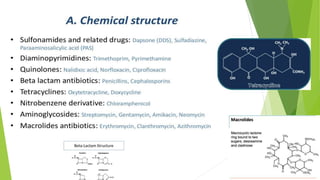
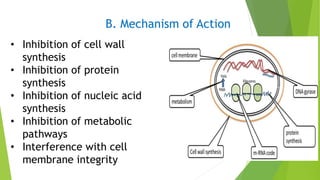
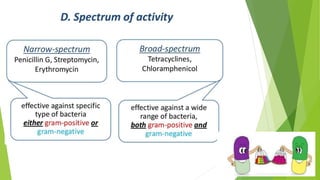
1. Chemotherapy involves using chemicals to treat diseases by killing cells or microorganisms like cancer cells or bacteria. Antibiotics are a type of chemotherapy used to treat infections caused by microorganisms.
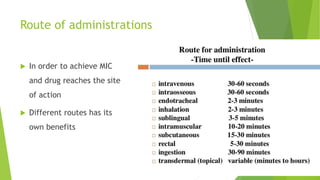
2. When selecting antimicrobial drugs, factors considered include the cost, safety, toxicity, and targeting the specific microorganism. The dose, duration, and route of administration are chosen to achieve the minimum inhibitory concentration needed.
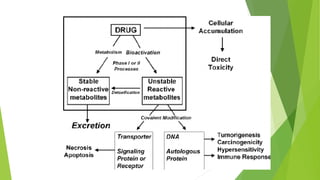
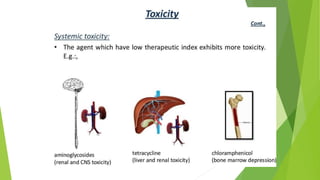
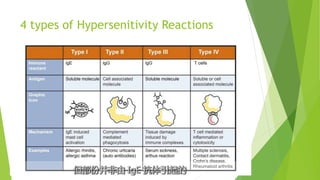
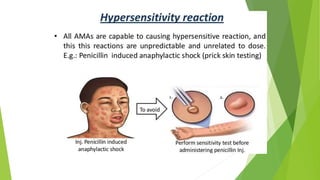
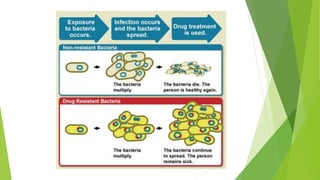
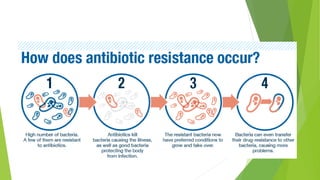
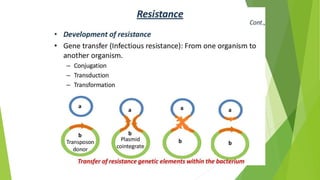
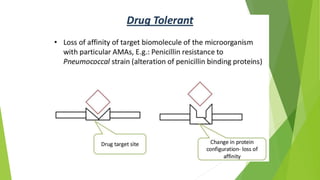
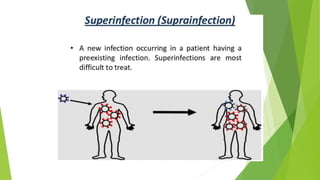
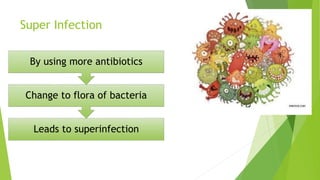
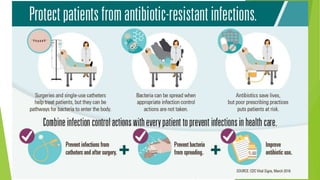
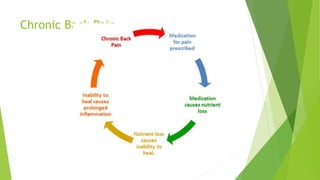
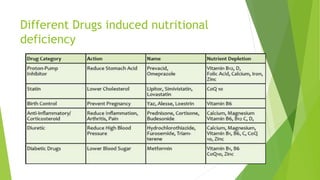
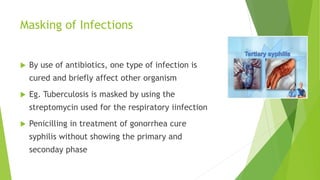
3. Adverse effects of antimicrobial agents include toxicity, hypersensitivity reactions, drug resistance, superinfections, and nutritional deficiencies. Proper use and completing treatment helps prevent these issues.