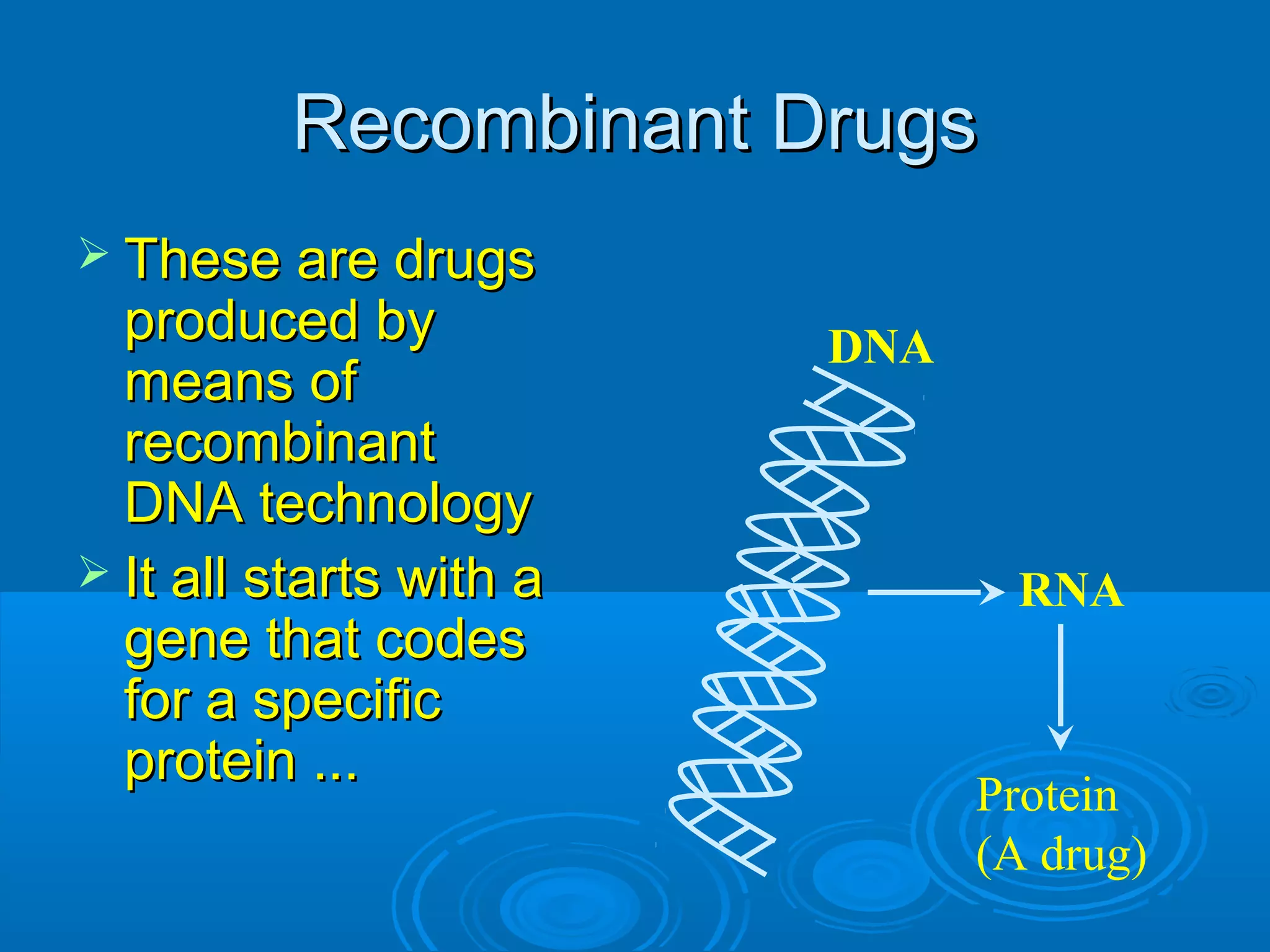
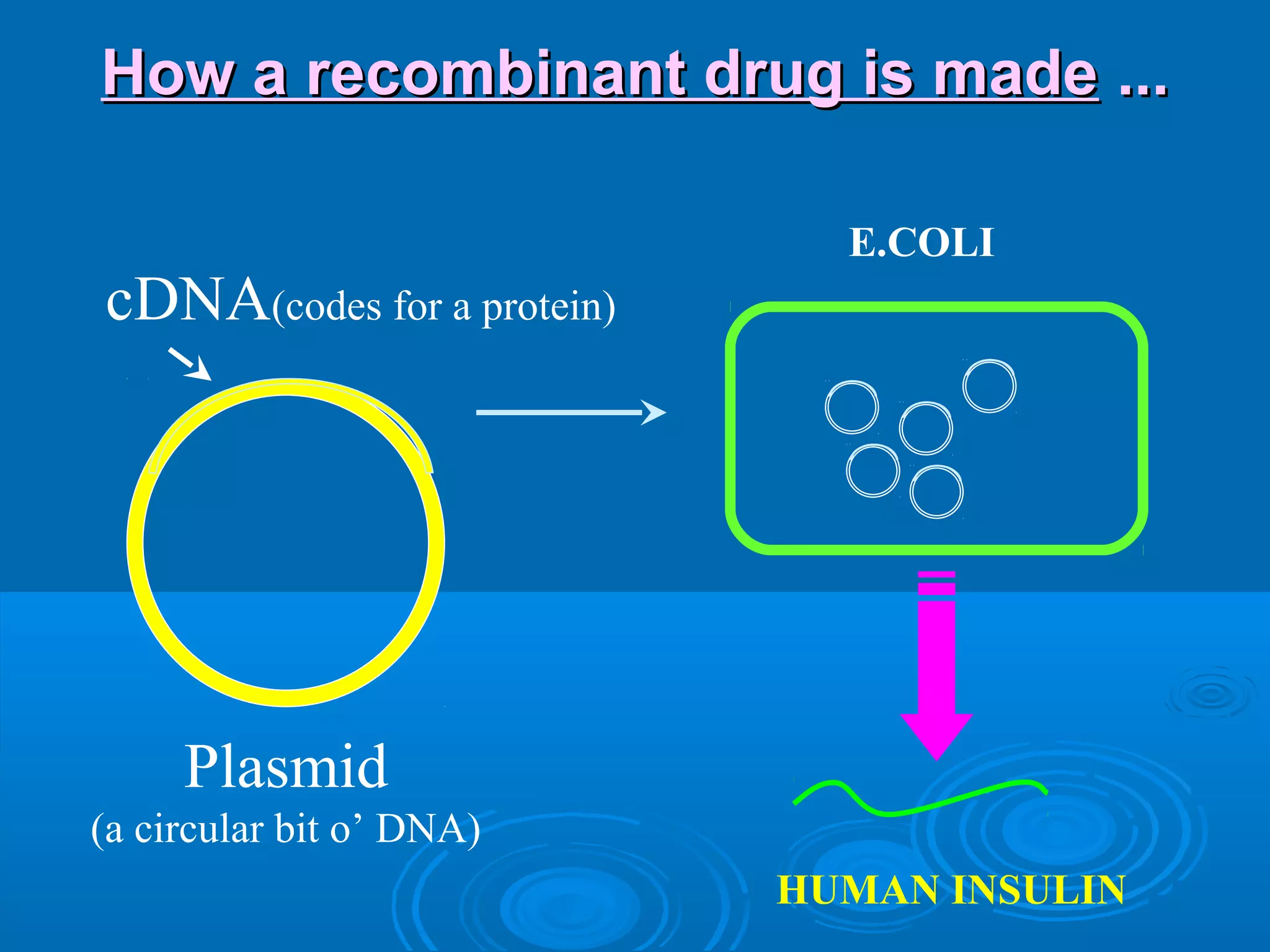
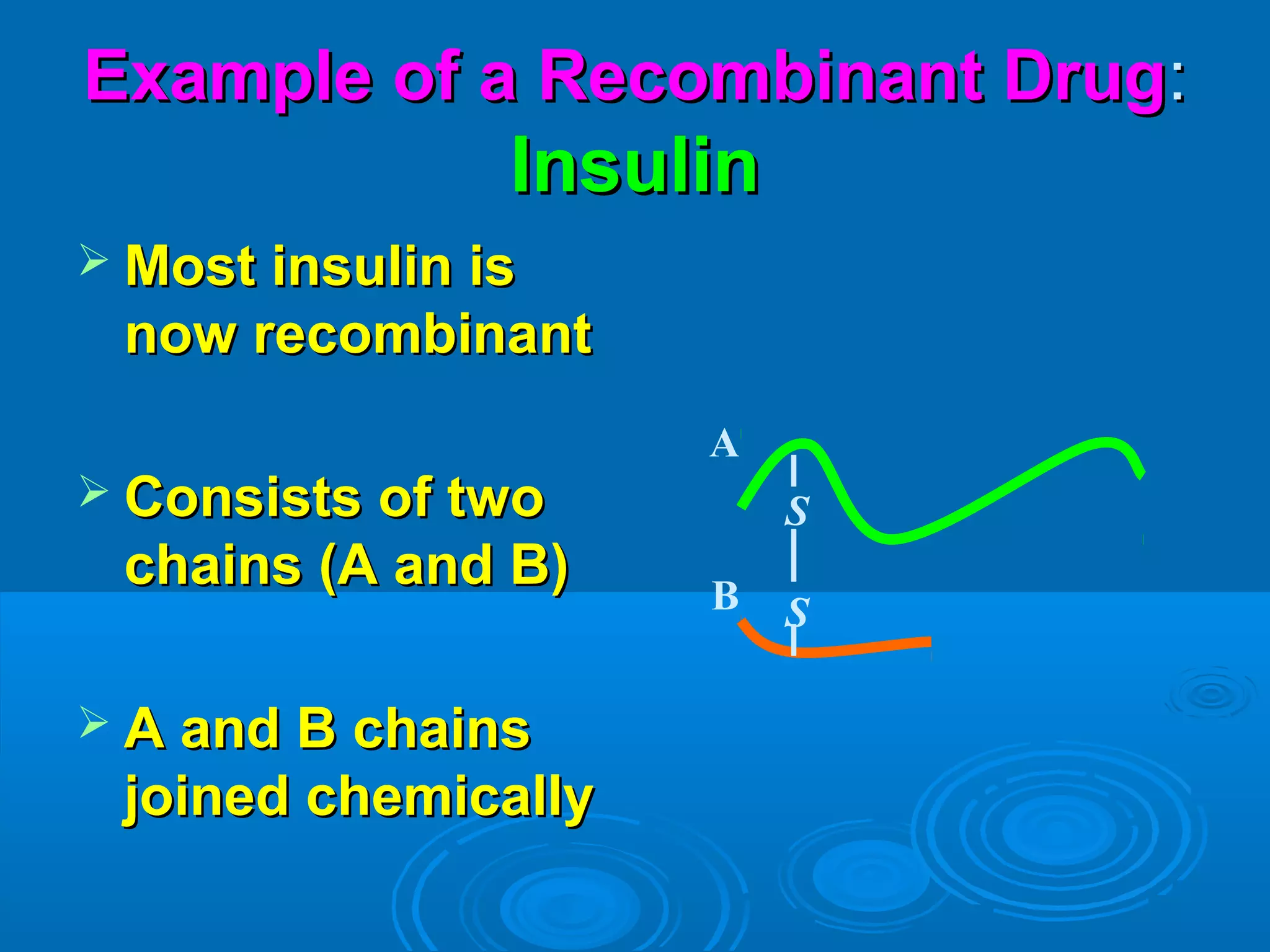
This document discusses sources of drugs and active drug principles. It defines drugs and medicines, and outlines various sources including natural sources from plants, animals, and minerals; microbial sources; human sources; synthetic sources; and those produced through genetic engineering. The key active principles discussed are alkaloids, glycosides, oils, resins, gums, and tannins. Reliable sources of drug information are also listed.