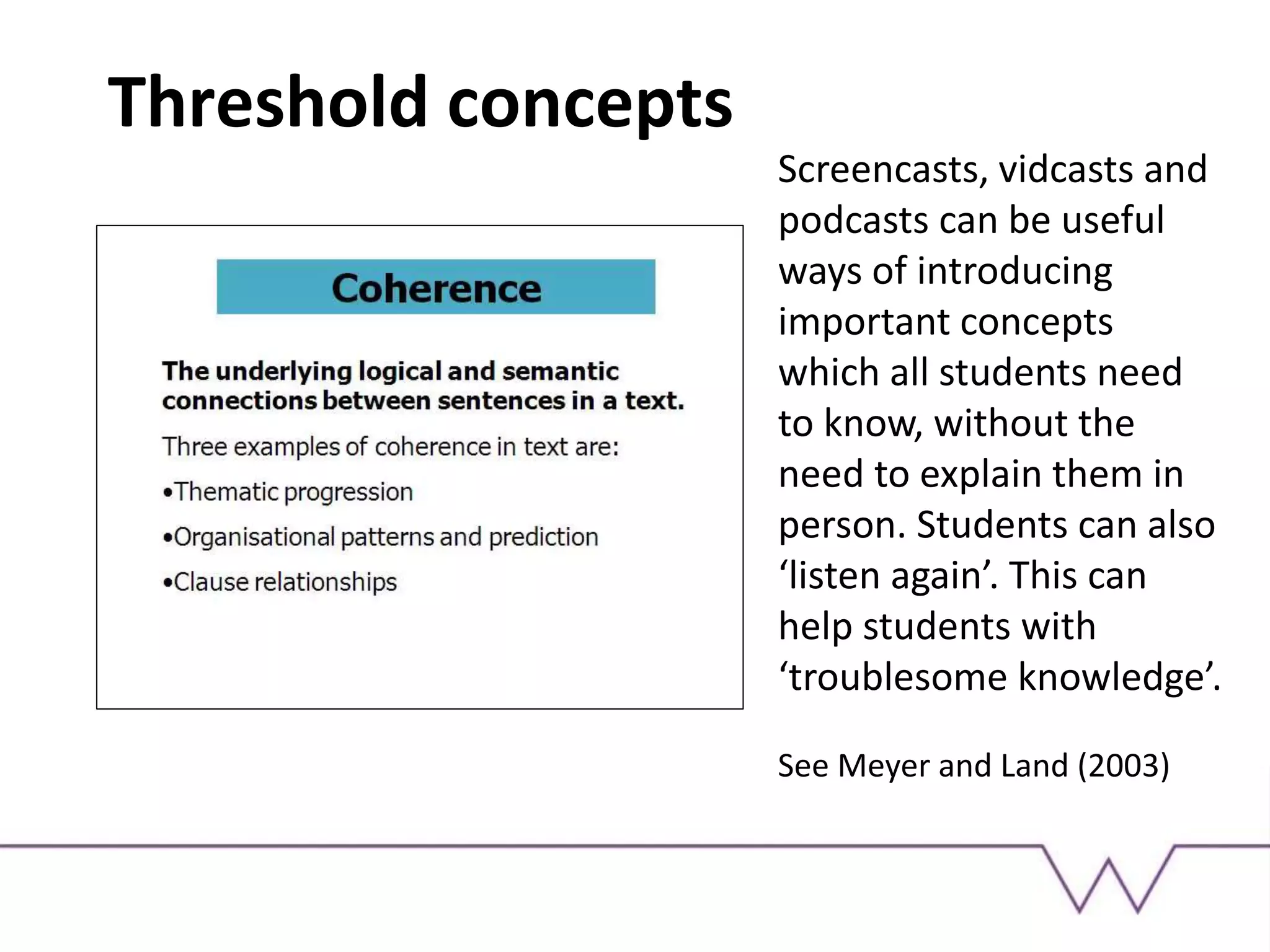
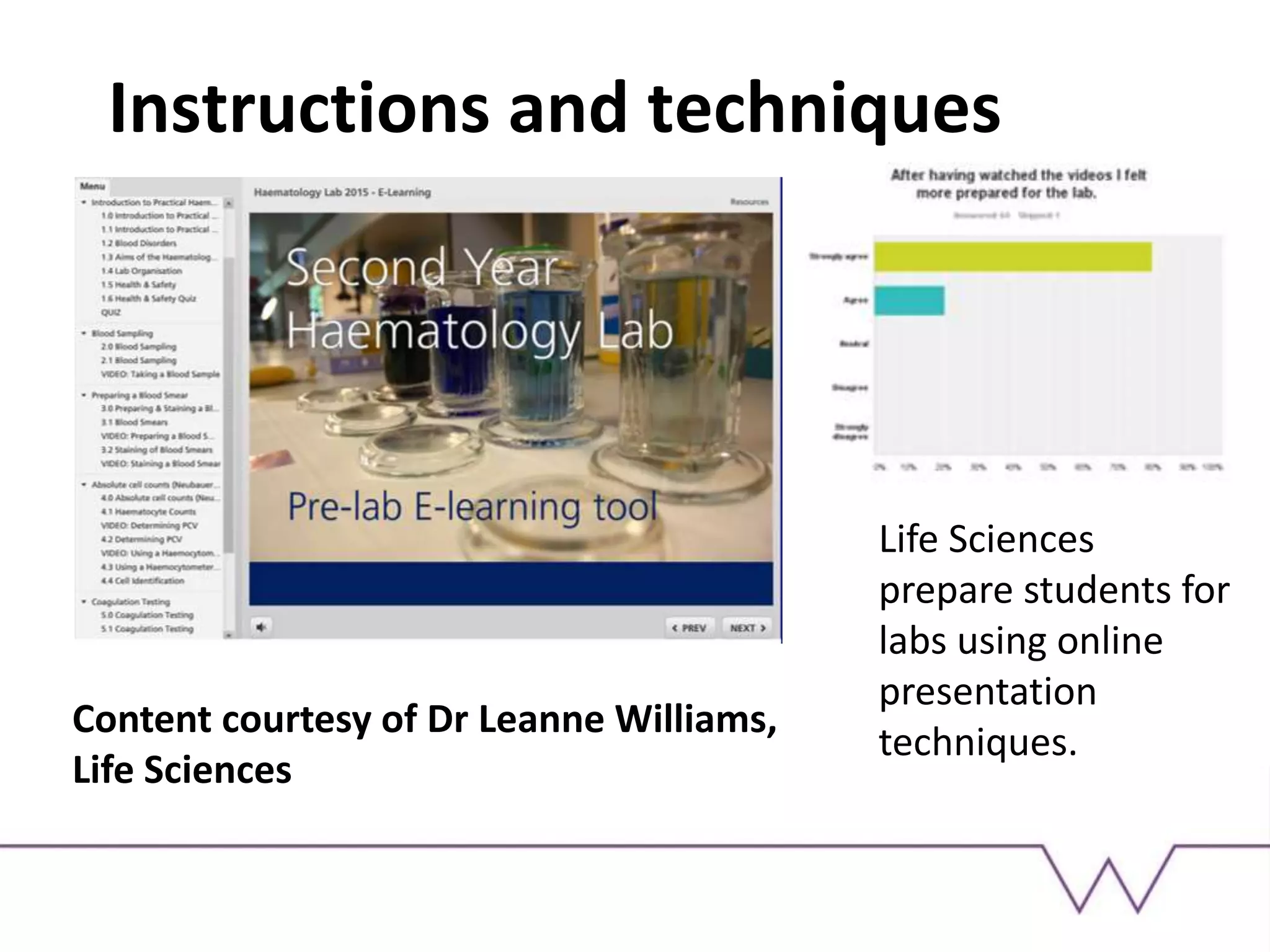
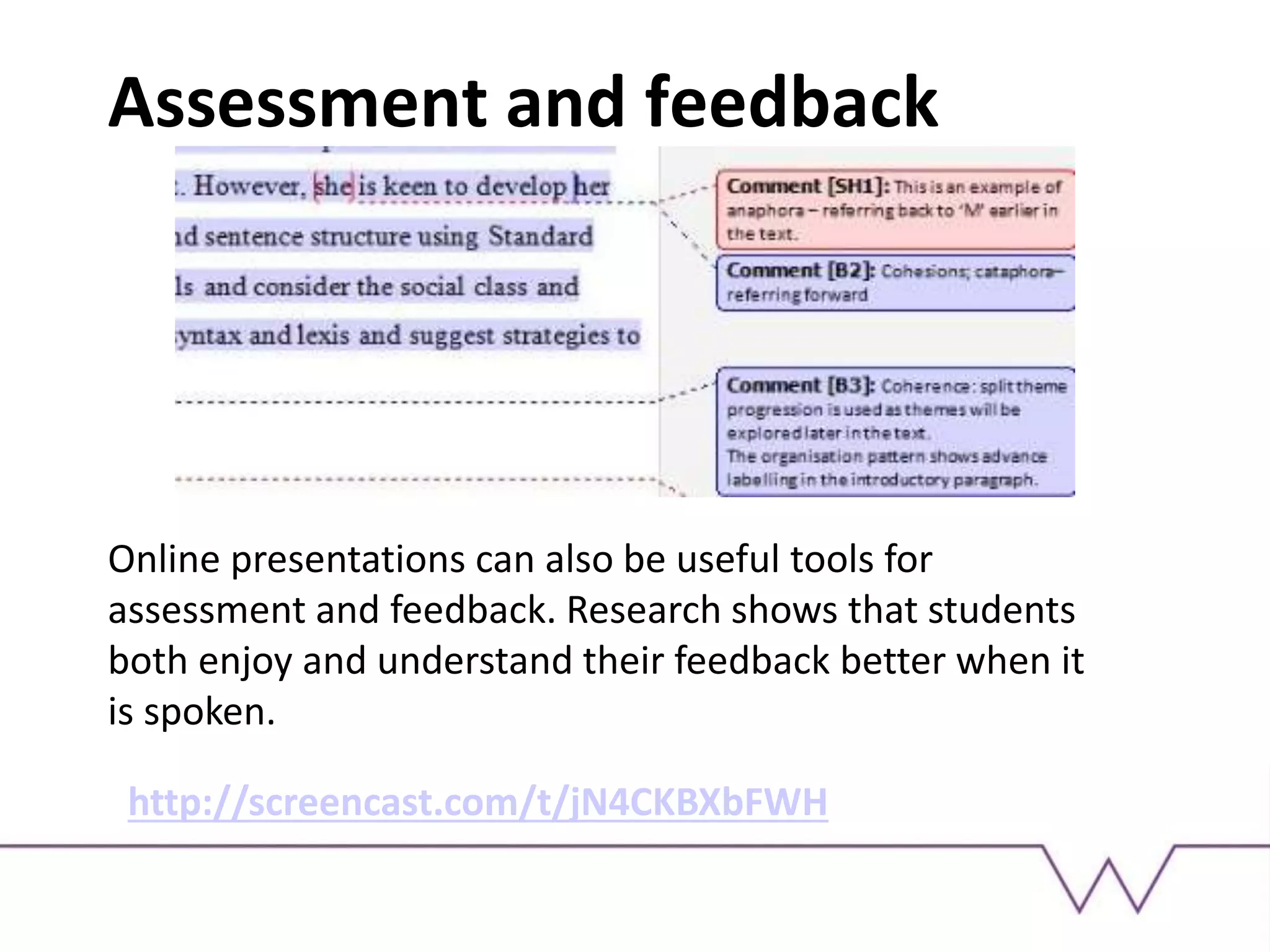
This document discusses using technology-enhanced learning tools like screencasts, podcasts, and digital presentations for teaching. It outlines several learning outcomes related to examining examples of online presentation and considering their benefits and challenges. It then provides examples of how digital presentations can be used, such as for flipped classrooms, explaining concepts, providing feedback, and peer instruction. Finally, it recommends some specific tools for creating digital content and suggests an activity for participants to make a screencast or podcast.