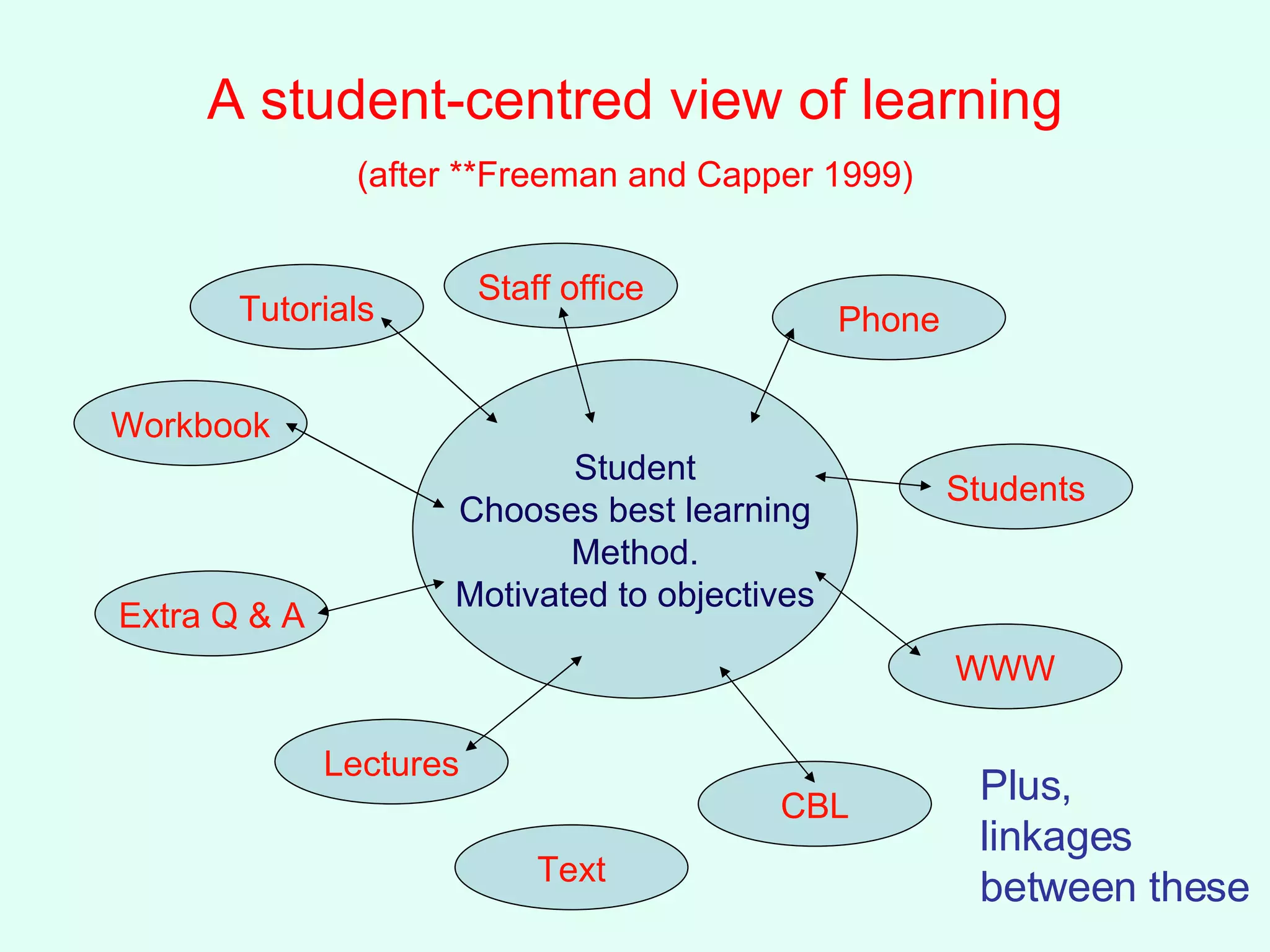
The document discusses various approaches to instructional design and utilizing technology in teaching. It suggests achieving a mix of deficiency, competence, socialization, and counseling models of instruction. It also emphasizes developing a student-centered approach using tools like PowerPoint, email, online discussions, and libraries to enhance learning opportunities while allowing for individual skills and constraints. The goal is to encourage active learning, feedback, and developing understanding through problem-solving and critical thinking.



![The level of technology Many teachers steer clear of engaging with technology - they leave it to the technologists and get on with the business of teaching' (Good, 2001) Is this You? If so, 'Don't Panic' (D. Adams) [I love deadlines. I love the sound of them whooshing past!]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elearning2-1218509735000617-8/75/E-Learning2-4-2048.jpg)






![Clarke and the Medievalists… '[she] argued that we should get back to a medieval concept of the university as a community of scholars unfettered by difficulties of the wider society.' Sage on the stage from this; the lecture? Traveling scholar and student (Name of the Rose - Ecco) Traveling masters and their apprentices (Was this medieval situation as elitist as has been made out? We now have the chance to broaden the scope, access and allow 'elitism for all'.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elearning2-1218509735000617-8/75/E-Learning2-12-2048.jpg)