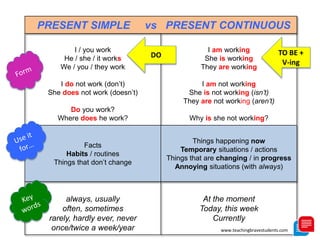
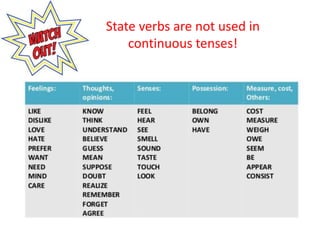
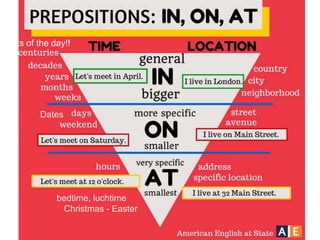
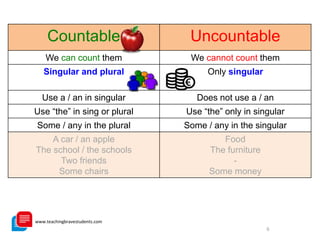
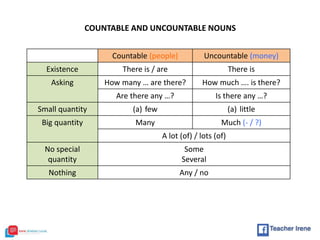
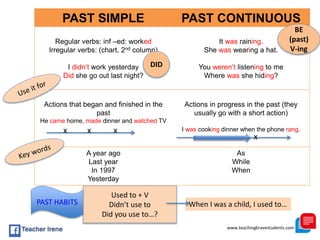
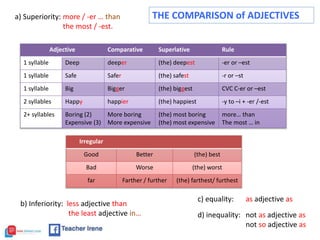
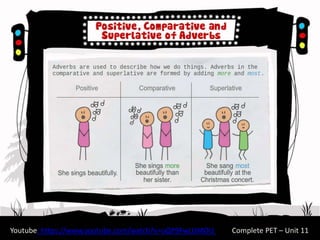
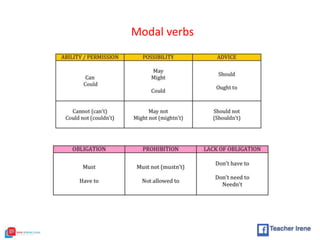
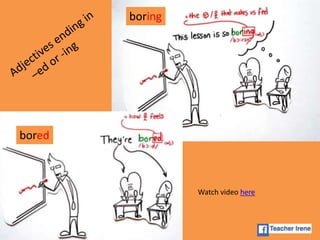
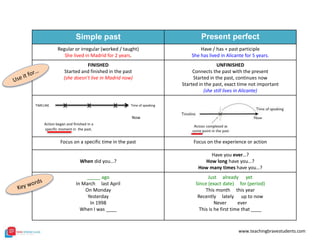
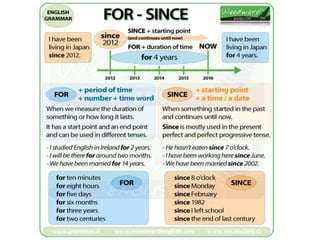
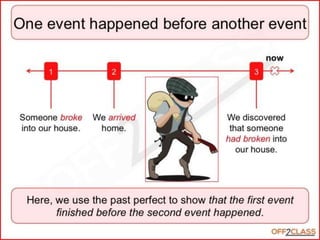
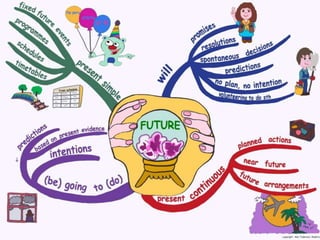
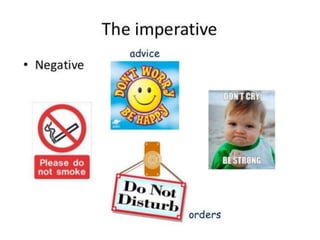
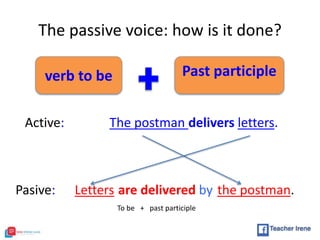
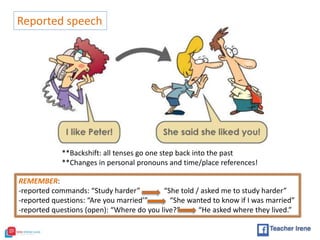
The document provides a comprehensive review of English grammar, focusing on various tenses, including present simple and continuous, past simple, and present perfect. It also covers aspects such as countable and uncountable nouns, comparative and superlative adjectives, modal verbs, and reported speech. Additionally, it includes examples and rules to help learners understand the correct usage of different grammatical structures.