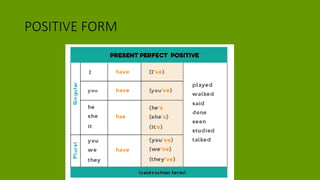
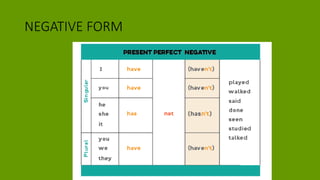
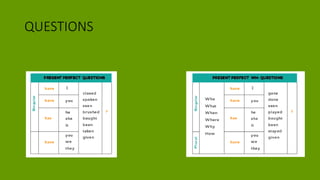
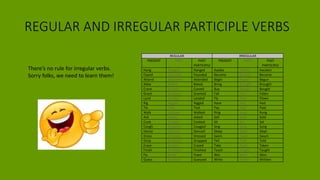
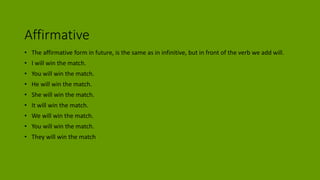
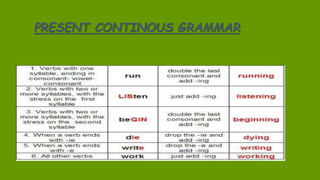
1. The document discusses grammar topics related to time in English, including the present perfect, past simple, future, and present continuous tenses.
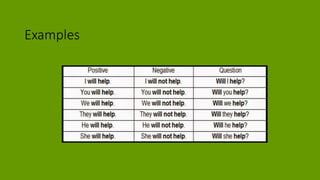
2. Examples are provided to illustrate how to form and use these tenses in positive, negative, and interrogative sentences.
3. Irregular verbs and comparisons between regular and irregular forms are also explained.