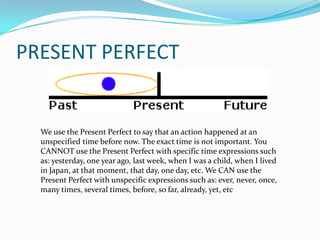
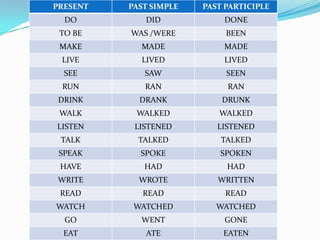
The document discusses adjectives ending in "-ing" and "-ed" in English. It explains that adjectives ending in "-ing" can describe how something makes someone feel or describe a ongoing process or state. Adjectives ending in "-ed" typically describe people's feelings and have a passive meaning, describing someone who has experienced something. It provides examples of common adjectives in these categories and guidance on correctly using "-ing" and "-ed" forms of adjectives.